Exploring the medication pattern and mechanism of action of marine traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of breast hyperplasia based on data mining and network pharmacology
Breast hyperplasia is a degenerative disease caused by the proliferation of breast fibers and epithelial tissue. Its clinical manifestations mainly include hard lumps on both or one side of the breast, often accompanied by pain. The condition of this disease is related to menstrual cycle and emotional changes, and is more common in women aged 25-44. Hyperplasia of breast has the characteristics of high incidence rate, difficult to cure, and easy to recur. In recent years, the incidence rate of hyperplasia of breast has increased year by year, and the incidence has a trend of youth. This disease has a certain tendency of malignancy, of which the incidence rate of breast cancer is higher in patients with severe hyperplasia of breast, atypical hyperplasia of breast, and cystic hyperplasia of breast. Traditional Chinese medicine has a long history and rich experience in the treatment of breast hyperplasia. traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations such as Rukang Tablets and Rupixiao Tablets that have been listed have good effects.
Marine traditional Chinese medicine is an important component of traditional Chinese medicine, which refers to natural medicines derived from the ocean and used for disease prevention and treatment under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine theory. Marine traditional Chinese medicine mostly grows in coastal areas affected by seawater infiltration, such as sea areas, beaches, coastal wetlands, and saline soils. The unique growth environment makes marine traditional Chinese medicine have unique medicinal value. At present, there are relatively few types of marine derived drugs on the market, and the success rate of related drug development is high, which makes marine traditional Chinese medicine have great development space.
Patent literature is an important component of intellectual property, encompassing over 90% of the latest global technological information and reflecting the technical features of inventions and creations. Novelty, creativity, and practicality are important factors that affect whether a patent can be granted authorization. After multiple reviews, only patent applications that meet the requirements and have better quality can be granted authorization. This study focuses on the authorized patent formula for the treatment of breast hyperplasia, aiming to explore the medication rules and the mechanism of the core drug group’s therapeutic effect of the patent formula containing marine traditional Chinese medicine, in order to provide reference for the application of relevant patents and the development and utilization of related drugs.













 Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia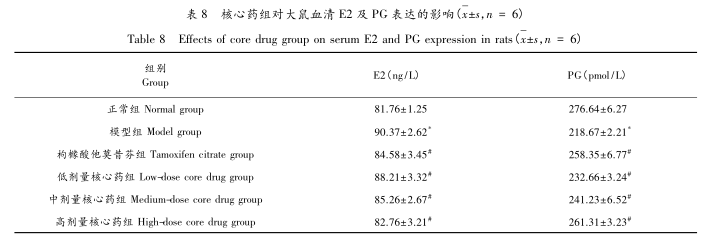

In traditional Chinese medicine, breast hyperplasia is classified as a “breast fetish”. The book “Surgical Authenticity” states: “Depression harms the liver, thoughts harm the spleen, and thoughts accumulate in the heart, causing the meridians to become rough and astringent, forming nuclei.” It is pointed out that the onset of this disease is often caused by emotional disorders and excessive emotions, which damage the liver and spleen, leading to liver dysfunction and spleen dysfunction; Or due to liver and kidney deficiency, imbalance of the Chong and Ren meridians, phlegm coagulation, blood stasis and stagnation of the milk vessels, coagulation and nucleation can lead to this disease.
Data mining was conducted on authorized patent formulations containing marine traditional Chinese medicine, and it was found that the main marine traditional Chinese medicines used to treat breast hyperplasia in the patent formulations were oysters, seaweed, and kelp. Oysters can nourish yang and yin, soften and disperse nodules, and have functions such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor. Oyster hydrolysates can produce strong immune stimulatory effects and have anti-tumor activity; Seaweed is cold in nature, bitter and salty in taste, and can soften, firm, and disperse lumps. It is a commonly used medication for treating breast hyperplasia in clinical practice. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” believes that seaweed is “salty and moist, but soft and firm, and can relieve heat through cold water circulation, and can dispel hardness and aggregation”; Kunbu is cold in nature and salty in taste, with functions similar to seaweed. Pharmacological studies have shown that Kunbu has the ability to regulate immunity and anti-tumor effects. In addition, Kunbu can downregulate the expression of Bcl-2 gene protein, increasing the sensitivity of abnormally proliferating breast cancer cells to chemotherapy drugs. Among non marine drugs, Chaihu is a commonly used medication for treating breast hyperplasia. Chaihu can regulate liver qi, soothe the liver and relieve depression, regulate qi, and is good at treating breast hyperplasia of liver qi stagnation type; Danggui is the “holy medicine for nourishing blood”, which can not only nourish blood, but also promote blood circulation and promote stagnation. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and immune regulating effects; Prunella vulgaris can clear the liver and meridian fire, as well as disperse nodules and reduce swelling. Its therapeutic effect on breast diseases was first recorded in the “Shennong Bencao Jing” and has been widely verified for over a thousand years. Research has confirmed that Prunella vulgaris inhibits breast hyperplasia by regulating hormone metabolism levels; On the other hand, Prunella vulgaris can regulate immune function and eliminate diseased cells in the body.
Cluster analysis was conducted on high-frequency drugs, and in category A, Curcuma zedoaria and Polygonatum sibiricum can promote blood circulation, promote qi circulation, and relieve pain, while seaweed and kelp can soften, firm, and disperse lumps. The efficacy of this group of drugs is mainly focused on promoting blood circulation, dispersing, accumulating, and relieving pain; In category B, Xiangfu and Chaihu can soothe the liver, regulate qi, and relieve stagnation. The two medicines are components of Chaihu Shugan San, which has the effect of regulating qi and relieving depression. Yujin can promote qi circulation and remove blood stasis, Qingpi can break qi and soothe the liver, Wangbuliuxing and Danshen can promote blood circulation, Danggui can nourish blood and promote blood circulation, and oysters can soften and disperse stagnation. The main efficacy of this group of drugs is to soothe the liver, regulate qi, and promote blood circulation; Category C: Prunella vulgaris can clear liver fire, disperse nodules, and reduce swelling. The efficacy of the three types of drug combinations varies and can be flexibly applied according to the specific syndrome type of the patient. The results of association rule analysis showed that the Chaihu Oyster Angelica medicine group had the highest correlation. Chaihu can regulate liver qi and regulate qi, while Angelica can supplement blood and promote blood circulation. The combination of the two drugs can regulate qi and regulate liver qi, as well as supplement blood and nourish liver. When combined with the marine medicine oyster, it can not only soften hardness and disperse lumps, but also prevent excessive dispersion of the liver regulating medicine. This medicine group can regulate qi, promote blood circulation and soothe the liver, help to promote the circulation of the milk meridian, and promote the restoration of normal qi and blood circulation. Literature review found that the Chaihu Oyster Angelica medicine group is mostly used in clinical practice and has good clinical effects. The diameter and height of the nipple can visually reflect the degree of breast hyperplasia from a morphological perspective. The increase of E2 and the decrease of PG lead to excessive proliferation of breast tissue, which plays a dominant role in the pathological process of breast tissue. Experiments have shown that the Chaihu Danggui Oyster Medicine group can reduce nipple diameter, lower nipple height, lower serum E2 expression, increase PG expression levels, improve breast morphology, and inhibit breast hyperplasia.
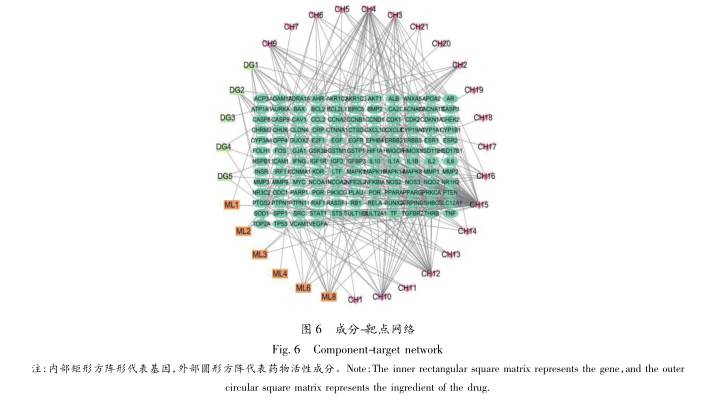
Further analysis of the core drug group using network pharmacology revealed that quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, and β – sitosterol had the highest degree values. Quercetin has a structure similar to estrogen, with estrogenic effects and bidirectional regulatory effects on estrogen. In addition, Quercetin can downregulate Bcl-2 protein expression and upregulate Bax protein expression, thereby inducing cell apoptosis and treating breast hyperplasia; Kaempferol is a flavonoid compound with anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. Kaempferol can activate caspase, promote cell apoptosis, and inhibit cell proliferation; Isorhamnetin has antioxidant activity and can be mediated by the AKT and ERK signaling pathways, inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting cell apoptosis; β – sitosterol has anti-inflammatory effects, can regulate various cellular signaling pathways, and has inhibitory effects on cell proliferation and angiogenesis.
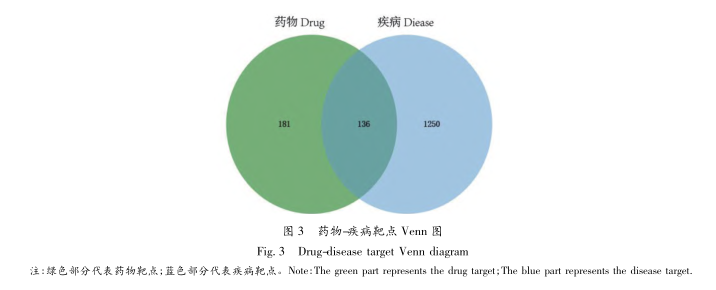
This study identified a total of 317 potential drug targets, and based on topological parameters, it is speculated that TP53, AKT1, ALB, and ESR1 are the core targets of the core formula for treating breast hyperplasia. Research has shown that TP53 regulates Spy1 protein under Nedd4 mediation. When TP53 mutates, Spy1 protein accumulates, leading to breast hyperplasia; In a mouse model, when estrogen receptors are overexpressed, the MMTV promoter activates AKT1, which drives fibroblast transformation and promotes the survival and migration of mammary ductal epithelial cells; ALB is the gene expression of albumin, which comes from the liver and can effectively inhibit the generation of neutrophil trap nets (NETs). NETs are involved in cell killing, aseptic inflammation, tissue damage, and can promote the proliferation of tumor cells to a certain extent. It plays an important role in the disease process of breast cancer. Breast hyperplasia may be cancerous. Combined with relevant literature, it is speculated that ALB may be an important target to prevent breast hyperplasia and canceration; Early genetic defects and environmental conditions in breast tissue may lead to ESR1 mutations, among which mutations at the XbaI locus increase the risk of breast hyperplasia.
Through GO functional enrichment analysis, it was found that the high-frequency drug group may exert therapeutic effects on breast hyperplasia in areas such as membrane rafts. Membrane rafts are cell membrane microstructural domains composed of proteins or globulin, which participate in the regulation of biological functions such as vascular wall cell apoptosis and immune cell activation. The biological processes through which drug groups exert therapeutic effects mainly involve hormone responses, responses to inorganic substances, and cellular responses to lipids, which are closely related to molecular functions such as DNA binding transcription factor binding, protein kinase activity, and kinase binding.
This study found that the P13K ATK signaling pathway may be an important pathway for the treatment of breast hyperplasia in the Chaihu oyster+Angelica medicine group. The P13K ATK signaling pathway is closely related to cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and apoptosis. Activation of the P13K ATK signaling pathway in breast epithelial cells inhibits the growth of estrogen, leading to proliferative changes in breast epithelial cells. Experiments have shown that the core drug group has the ability to inhibit the P13K ATK signaling pathway. Among the top ten core targets in terms of topological values, AKT1, TP53, EGFR, VEGFA, MYC, and IL6 are all located in the P13K ATK signaling pathway, suggesting that they may be important mediators for the core drug group to inhibit the P13K ATK signaling pathway. In addition, the tumor suppressor gene PTEN can inhibit the P13K ATK signaling pathway, thereby suppressing cell proliferation and promoting tumor cell apoptosis. The enrichment analysis results of KEGG pathway showed that drug targets were more likely to act on cancer related pathways, suggesting that Chinese herbal formula could slow down the process of disease development, delay or even prevent the occurrence of breast cancer while treating breast hyperplasia. The core drug group can also act on atherosclerosis, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and other pathways, reflecting the idea of treating different diseases together in TCM theory, and providing reference for relevant applicants to apply for breast hyperplasia compound patent and broaden the scope of patent protection.
In summary, this article uses data mining, network pharmacology, and animal experiments to explore the medication rules of marine traditional Chinese medicine in treating breast hyperplasia and the mechanism of action of core drug groups in treating breast hyperplasia from a theoretical perspective, with authorized patent formulations as the research object. The research results of this article have positive significance for further developing marine traditional Chinese medicine and promoting the application of related patents.
Traditional Chinese medicine oysters often remove meat and use shells as medicine. Currently, the determination of oyster shell components is relatively early, and it is known that the active ingredients are mainly minerals. There are few targets for this type of substance, resulting in small topological parameters of related components and ranking relatively low in the network. However, oysters, as a commonly used clinical drug for treating breast hyperplasia, cannot be ignored for their therapeutic effects. This study reveals the insufficient research on oyster components, targets, and other aspects, providing new ideas for related series of studies. Our research team has designed relevant experiments for in-depth exploration of potential components in oysters, and closely follows the pharmacological research progress of peers. With the continuous disclosure of effective ingredients in oysters, there will be new breakthroughs in the pharmacological mechanism of oyster treatment for breast hyperplasia.
