Research on Quality Control of Ge Hua Based on HPLC Fingerprint and Multi evaluation Method
Pueraria Flos is a dried flower bud of Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi or Pueraria thomsonii Benth., a plant in the legume family. It is also known as Pueraria lobata, Pueraria lobata, Pueraria lobata, or Epinephelus patchouli. It is recorded in the “Record of Famous Doctors”, “Dian Nan Ben Cao”, and “Ben Cao Gang Mu”, and has the effects of sobering up, clearing dampness and heat, relieving annoyance and nausea. Modern research has shown that Pueraria lobata has effects such as detoxification, blood sugar lowering, blood lipid lowering, antioxidant, myocardial protection, and estrogen like properties. It is widely used as a raw material for the development of health products such as detoxification, liver protection, blood sugar and blood lipid lowering, anti osteoporosis, and immune regulation. Chemical composition studies have shown that Pueraria lobata mainly contains flavonoids, terpenes, steroids, and coumarins, among which Puerarin (Pu), Daidzin (Da), Daidzein (Dae), Genistin (Ge), Genistein (Gee), Kakkalide (Ka), Glycitin (Gl), Tectoridin (Td), Tectorigenin (Tg), and Tectorigenin-7-O-xylosylglucoside are the main components of Pueraria lobata. Tx) is the main chemical component. Ge Hua is mainly distributed in Southeast Asia, with the widest distribution in China. Shaanxi, Sichuan, Guangxi, and Yunnan are the main production areas of Ge Hua. The standards issued by the Ministry and the standards for traditional Chinese medicine in various provinces have clearly stipulated that the flower buds of wild kudzu and pink kudzu are the two medicinal authentic sources of kudzu flowers in China. In order to distinguish them, the former is called kudzu flower, and the latter is called pink kudzu flower. Our research group found that there are significant differences in the chemical composition between the two. At present, there are only departmental and local standards for Ge Hua, and there is confusion in variety identification. The quality control indicators only include traits, identification, and inspection, which are too simple. There have been no reports on the improvement of quality control standards.
Fingerprint spectrum is a comprehensive, macroscopic, and quantifiable chromatographic identification method widely used in the quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine. It can comprehensively reflect the differences in chemical composition characteristics in traditional Chinese medicine, thereby achieving the goal of distinguishing between authenticity and quality. Therefore, this study used HPLC to establish fingerprint spectra of Pueraria lobata from different origins; At the same time, a one test multiple evaluation analysis method (QAMS) was established on this basis for the determination of Pu, Da, Dae, Ge, Gee, Ka, Gl, Td, Tg, and Tx content in Pueraria lobata, systematically evaluating the quality differences of Pueraria lobata medicinal materials from different production areas, providing empirical basis for comprehensive and systematic control of Pueraria lobata quality, and providing reference for the selection and breeding of high-quality germplasm resources of Pueraria lobata.









 The experiment used a diode array detector to perform full wavelength scanning of 10 flavonoids at 200-400nm. The results showed that the UV spectra of Pu, Da, Dae, Ge, Gee, Ka, Gl, Td, Tg, and Tx were similar, with maximum absorption at 256-274nm wavelength. Under the wavelength condition of 265nm, it was found that the 10 tested components had good baseline separation and a stable baseline, which can meet the requirements of quantitative analysis. The experiment investigated 75% ethanol; 95% ethanol; 75% methanol and 25mL each of methanol were used as extraction solvents. When methanol was chosen as the extraction solvent, the number of chromatographic peaks was appropriate and easy to separate. The experiment also examined ultrasound and thermal reflux treatment methods, and ultimately chose ultrasound for 30 minutes, which is a simple and efficient method. The experiment also examined mobile phase systems such as methanol water, acetonitrile water, acetonitrile-0.2% phosphoric acid aqueous solution, and acetonitrile-0.2% formic acid aqueous solution. The final selection of acetonitrile 0.2 phosphate aqueous solution gradient elution system resulted in good separation effect and significant improvement in tailing.
The experiment used a diode array detector to perform full wavelength scanning of 10 flavonoids at 200-400nm. The results showed that the UV spectra of Pu, Da, Dae, Ge, Gee, Ka, Gl, Td, Tg, and Tx were similar, with maximum absorption at 256-274nm wavelength. Under the wavelength condition of 265nm, it was found that the 10 tested components had good baseline separation and a stable baseline, which can meet the requirements of quantitative analysis. The experiment investigated 75% ethanol; 95% ethanol; 75% methanol and 25mL each of methanol were used as extraction solvents. When methanol was chosen as the extraction solvent, the number of chromatographic peaks was appropriate and easy to separate. The experiment also examined ultrasound and thermal reflux treatment methods, and ultimately chose ultrasound for 30 minutes, which is a simple and efficient method. The experiment also examined mobile phase systems such as methanol water, acetonitrile water, acetonitrile-0.2% phosphoric acid aqueous solution, and acetonitrile-0.2% formic acid aqueous solution. The final selection of acetonitrile 0.2 phosphate aqueous solution gradient elution system resulted in good separation effect and significant improvement in tailing.
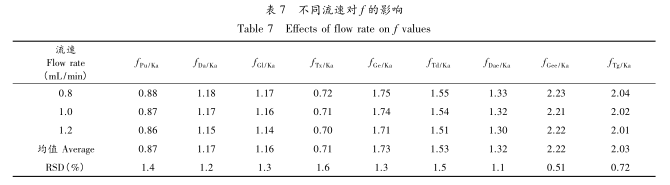
To facilitate the comprehensive quality control of Pueraria lobata, various representative components with clear activity and high content were selected as the indicator components for QAMS content determination in the experiment, mainly including Pu, Da, Dae, Ge, Gee, Ka, Gl, Td, Tg, and Tx as the main chemical components. From the results of measuring the content of each component, the chromatographic separation of each component, and the price and availability of reference standards, it can be seen that Ka has a high content, good separation effect, easy identification in the spectrum, and is in the middle position of the spectrum, which is conducive to the calculation of the relative retention time of other component chromatographic peaks and the identification of chromatographic peaks. Ka has stable properties, is inexpensive and easy to obtain, and has the activity of lowering blood lipids and blood sugar, improving microcirculation, and activating ethanol dehydrogenase. Therefore, Ka was chosen as the reference material for QAMS content determination in this study.
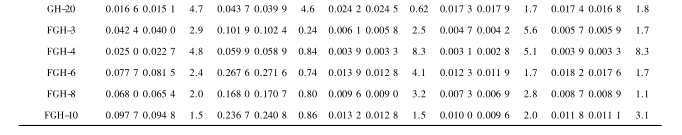
The fingerprint spectrum established in this experiment can effectively characterize the chemical composition information of Pueraria lobata. The QAMS method established based on the fingerprint spectrum can effectively determine the content of the main active ingredients Pu, Da, Gl, Tx, Ge, Td, Dae, Ka, Gee and Tg in Pueraria lobata and Pueraria lobata, which can comprehensively reflect the overall quality information of Pueraria lobata medicinal materials. According to the content determination results and clustering heatmap, it can be intuitively seen that Pueraria lobata and Pueraria lobata can be divided into two categories. There are significant differences in the types and contents of the main active ingredients in 20 batches of Pueraria lobata and 10 batches of Pueraria lobata from different production areas. The differential components are Ka, Da, Gl, Tx, Td, and Ge. The reason is related to the different sources of kudzu flowers and pink kudzu flowers.
Currently, dried flower buds of Pueraria lobata and Pueraria lobata are included as sources of medicinal herbs. Given the significant differences in the main active ingredients between Pueraria lobata and Pueraria lobata, their clinical efficacy should also differ. Therefore, they should be distinguished and used differently in product development and clinical applications. At the same time, Ge Hua has great potential for the development of health products, and it is urgent to establish a standardized Ge Hua quality evaluation system. The fingerprint spectrum established by our research institute combined with the one test multiple evaluation method can achieve multi-component and multi index quality control of Pueraria lobata medicinal materials while reducing the use of reference materials; At the same time, it can distinguish between Pueraria lobata and Pueraria lobata, and effectively evaluate the quality of Pueraria lobata from different origins; The experimental results can provide reference for the modification and improvement of the quality standards of Pueraria lobata, and can provide reference for the selection and breeding of high-quality germplasm resources of Pueraria lobata. It has good application prospects in the overall quality evaluation mode of traditional Chinese medicine.
