Study on the Mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in Preventing and Treating Atherosclerosis through Nrf2/ARE Signal Pathway
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease. Early onset of AS patients is insidious and there are no obvious clinical manifestations, but as the disease progresses, target organs such as the heart and brain may be affected in the later stages. According to a survey by the World Health Organization (WHO), middle-aged and elderly people are still the main group for cardiovascular adverse events, with approximately 81% of cardiovascular disease patients dying at the age of 65 or older. However, in recent years, the population of AS patients has also tended to be younger. In China, there are nearly 300 million people suffering from cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Although modern medical treatment of AS has certain efficacy, it still cannot reduce the high incidence rate of AS, and there are many adverse reactions after long-term application. Therefore, reducing the incidence of AS is the top priority and mainstream research direction. Oxidative stress is one of the important factors leading to the development of atherosclerosis. Advanced oxidative protein products (AOPP) can serve as early biomarkers and independent strong predictors of atherosclerosis, while reactive oxygen species (ROS) can promote the oxidation of white proteins into AOPP, leading to the outbreak of oxidative stress; Malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH Px) are important biomarkers of oxidative stress response, which can basically reflect the oxidative stress state of the body. The three often interact with each other, leading to oxidative damage to vascular endothelium and tissue cells, resulting in the occurrence of atherosclerosis. Research has found that the nuclear factor E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2)/antioxidant response element (ARE) signaling pathway is a key nuclear transcription factor that regulates oxidative stress. It can activate multiple antioxidant proteins and participate in various biological processes such as cell aging, apoptosis, and proliferation.
Traditional Chinese Medicine generally believes that the main pathogenesis of AS lies in the deficiency of positive qi, which is the root cause of the disease; Phlegm, blood stasis and other pathogenic factors are important pathogenic factors and indicators of disease onset. Therefore, in response to the pathogenesis of AS, this study adopts the basic method of “nourishing the heart, removing blood stasis, and resolving phlegm”, and uses modified Buyang Huanwu Tang to prevent and treat AS. Buyang Huanwu Tang is a classic formula for promoting blood circulation and tonifying qi from Wang Qingren’s “Yi Lin Gai Cuo” in the Qing Dynasty. It is combined with Gualou Xiebai Banxia Tang, which is in line with the pathogenesis of AS. Moreover, the two have significant therapeutic effects on AS related diseases in clinical practice without obvious adverse reactions. Therefore, this study chose to modify Buyang Huanwu Tang accordingly. The preliminary experimental results showed that the modified Buyang Huanwu Tang has a certain effect on the prevention and treatment of AS, by regulating immune inflammatory response, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and affecting signaling pathways such as HMGB1 and Wnt1, reducing plaque area, and alleviating AS lesions. However, the specific mechanism of action has not been elucidated yet. Therefore, this study takes oxidative stress as the starting point to explore the effect of modified Buyang Huanwu Tang on the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, and to elucidate the specific mechanism by which modified Buyang Huanwu Tang regulates atherosclerotic plaques through the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway.









As a disease name of modern medicine, there is no record of “atherosclerosis” in the ancient books of traditional Chinese medicine, which is mainly manifested in the obstruction of blood circulation such as narrowing of the lumen, decreased elasticity of the vascular wall, etc., so it is classified as “chest pain, dizziness, pulse blockage” and other categories. Traditional Chinese Medicine believes that its pathogenesis lies in the deficiency of the body’s righteous qi, which leads to poor circulation of qi and blood. As stated in the book “Yi Lin Gai Cuo”: “If the qi is weak, it cannot reach the blood vessels. If there is no qi in the blood vessels, it will stay and become stagnant; The “Compendium of Medicine” records that “stroke is caused by unfavorable pulse channels and blood gas obstruction”, providing a theoretical basis for the induction of atherosclerosis by blood stasis. Heart deficiency is particularly important in the deficiency of positive qi; Pathological factors such as blood stasis and phlegm turbidity are indicative of the onset of the disease. This study is based on the basic principle of “nourishing the heart, dispelling blood stasis, and resolving phlegm” for the pathogenesis of AS. The formula consists of Huangqi, Danggui Wei, Chishao, Chuanxiong, Taoren, Honghua, Dilong, Gualou, Xiebai, Banxia, Codonopsis pilosula, Ophiopogon japonicus, Schisandra chinensis, and other drugs. Huangqi is the king’s medicine, combined with Codonopsis pilosula, Ophiopogon japonicus, and Schisandra chinensis to nourish qi. It is intended to promote blood circulation when qi is strong, remove blood stasis when blood circulation is strong, and promote blood circulation when blood stasis is removed; Danggui is a medicinal herb that nourishes qi and blood. It is accompanied by earthworms, red peony, peach kernels, red flowers, and Chuanxiong to promote blood circulation and unblock collaterals; Gualou, Xiebai, and Banxia are used to widen the chest, disperse nodules, and clear phlegm and unblock collaterals. The combined use of various medicines has the effects of nourishing qi, nourishing the heart, and clearing turbidity and unblocking collaterals. Modern research has shown that Buyang Huanwu Tang can exert anti AS effects through antioxidant stress, anti-inflammatory, anti endothelial cell damage, apoptosis, and other aspects. Gualou, Xiebai, and Banxia are derived from Gualou Xiebai Banxia Tang. Modern research has shown that Gualou Xiebai Banxia Tang can prevent and treat AS by inhibiting oxidative stress, regulating lipid metabolism, and reducing inflammatory reactions.
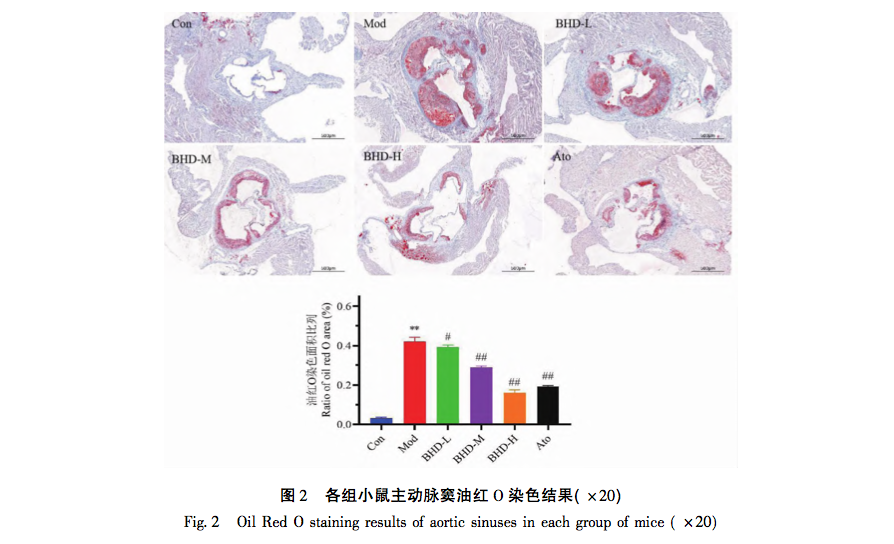
ApoE gene knockout (ApoE -/-) mice were successfully cultivated in 1992 by the Pathology Genetics Laboratory at the University of North Carolina and the Biochemistry Genetics and Metabolism Laboratory at Rockefeller University in the United States. ApoE is an important component of chylomicrons, extremely low-density lipoprotein, and high-density lipoprotein, playing a crucial role in regulating oxidative stress, lipid metabolism, signal transduction, and other aspects. The pathological changes in ApoE -/- mice are very similar to those in humans. They can spontaneously form fibrous plaques and composite plaques under natural diet, and can develop severe hyperlipidemia. Males are more likely to develop AS lesions, and compared with SD rats, ApoE -/- mice model rapidly. When fed with high-fat diet (0.15% cholesterol, 18% hydrogenated cocoa butter) for 8 weeks, lipid plaques and inflammatory infiltration were found in the aorta of randomly dissected mice, confirming successful modeling. Therefore, male ApoE -/- mice are generally selected as the research subjects for the experiment. The level of blood lipid is positively correlated with the occurrence of AS. Under pathological conditions, lipid deposits in the arterial wall, monocyte macrophages are oxidized and phagocytosed into foam cells, thereby reducing the stability of fibrous plaque and accelerating the process of AS. The results of this study showed that the levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C in AS plaques in the Buyang Huanwu Tang group were lower than those in the model group, and no significant lipid deposition or plaque formation was observed in the aortic root, further confirming the anti AS and plaque stabilizing effects of Buyang Huanwu Tang.
Oxidative stress injury refers to the imbalance between the generation of ROS in the body and the clearance of ROS by the antioxidant enzyme system, leading to an increase in ROS accumulation and causing oxidative damage in the body. When too much ROS accumulates in the artery, it will cause oxidative damage to the vascular wall, promote the production of foam cells, eventually induce or aggravate AS, and even promote the rupture of AS plaque, which will seriously affect people’s quality of life. AOPP can participate in the formation and development of AS through various mechanisms. On the one hand, its oxidative metabolism may cause the production of superoxide (H2O2, O-2, OH -), leading to endothelial dysfunction; On the other hand, AOPP can promote the synthesis and release of inflammatory factors, induce and exacerbate the progression of AS. Therefore, antioxidant reactions are particularly important in the prevention and treatment of AS. The Nrf2 signaling pathway is closely related to antioxidant stress. ROS overload in the body can activate the Nrf2/HO signaling pathway, causing Nrf2 to dissociate from the complex formed with Keap1 and accumulate in the cytoplasm in a free state. At the same time, it is phosphorylated and transferred to the nucleus, promoting HO-1 gene expression and enhancing cellular antioxidant stress resistance, thereby exerting a protective effect on cells. The Nrf2 gene is an alkaline leucine zipper transcription factor that is widely present in oxygen consuming organs. It can mediate antioxidant response pathways, maintain cellular redox homeostasis, regulate various antioxidant protein genes, and play a key role in cellular oxidative stress. The Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway is currently known to be the most important endogenous antioxidant pathway, involved in regulating cellular homeostasis, lipid formation, and inflammatory cytokine release. Research has shown that Nrf2 can reduce oxidative stress damage, alleviate inflammatory reactions, protect cells, and regulate various antioxidant enzyme activities through its mediated antioxidant pathway. NQO-1 can reduce NADPH oxidase, decrease ROS levels, and reduce the occurrence of oxidative stress damage. HO-1 is a highly important antioxidant enzyme that has been discovered to promote the breakdown of hemoglobin into substances such as CO, bilirubin, and biliverdin, and has a good preventive effect on the occurrence of atherosclerosis. This study found that Buyang Huanwu Tang can increase the expression of Nrf2, ARE, NQO-1, and HO-1 in the aorta of AS model mice. It is speculated that Buyang Huanwu Tang can activate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway to protect the aorta of AS model mice from oxidative stress damage. Our research group conducted further studies and found that Buyang Huanwu Tang can increase the expression of Nrf2 and ARE proteins, as well as the expression of NQO-1, HO-1 proteins and their mRNA in the aorta of mice. Indicating that Buyang Huanwu Tang can activate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway and exert anti AS effects. SOD is an antioxidant enzyme that can exert antioxidant effects by scavenging oxygen free radicals and has a direct impact on oxidative stress levels. MDA is one of the most important products in the process of membrane lipid peroxidation, which is positively correlated with oxidative stress levels and can reflect the oxidative stress state of the body. GSH Px is an important antioxidant in the body, which is negatively correlated with the degree of oxidative stress and can clear ROS to exert antioxidant effects. The results of this study showed that the Buyang Huanwu Tang group could increase the expression levels of GSH Px and SOD in mouse plasma, and reduce the expression level of MDA; Reduce the expression levels of AOPP and ROS. The above further confirms that Buyang Huanwu Tang has antioxidant and stress relieving effects.
To sum up, Buyang Huanwu Decoction, which is based on the “Heart Benefiting, Blood Stasis Removing and Phlegm Resolving Method”, has the effect of anti oxidative stress, can significantly improve the pathomorphological changes of the aorta, reduce the lipid deposition in the aorta, and its mechanism of anti atherosclerosis may be related to the activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway.
