Study on Chemical Components and Antioxidant Activity of Salt skinned Wood Leaves
Rhus chinensis Mill., also known as Galla chinensis, wutong amurensis and Rhus chinensis, belongs to the family Rhus chinensis, which is distributed in China except Northeast, Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang. According to the “Compendium of Materia Medica”, the roots, stems, leaves, and whole body of Yanfu wood can be used as medicine to treat and prevent diseases such as diarrhea, dysentery, colic, hepatitis, etc. Currently, the decoction of Yanfu wood roots is mostly used in clinical practice to treat coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, pulmonary abscess, and chronic diarrhea in children. Research has found that the chemical composition of Rhus chinensis mainly includes lignin, flavonoids, phenols, triterpenes, etc. Currently, research mainly focuses on Rhus chinensis roots, with little research on Rhus chinensis leaves. According to existing research reports, only 13 compounds, including 6 flavonoids, 4 phenolic acids, and 3 triterpenoids, were isolated from the leaves of Saltwood. The ethyl acetate extract of Saltwood leaves showed good antioxidant activity, and polyphenols were found to be the main active ingredients. In order to further clarify and explore the active ingredients of Schisandra chinensis, this study systematically studied the chemical composition of Schisandra chinensis leaves and conducted in vitro antioxidant activity experiments on the isolated and identified compounds, providing a theoretical basis for better development and utilization of the value of Schisandra chinensis.
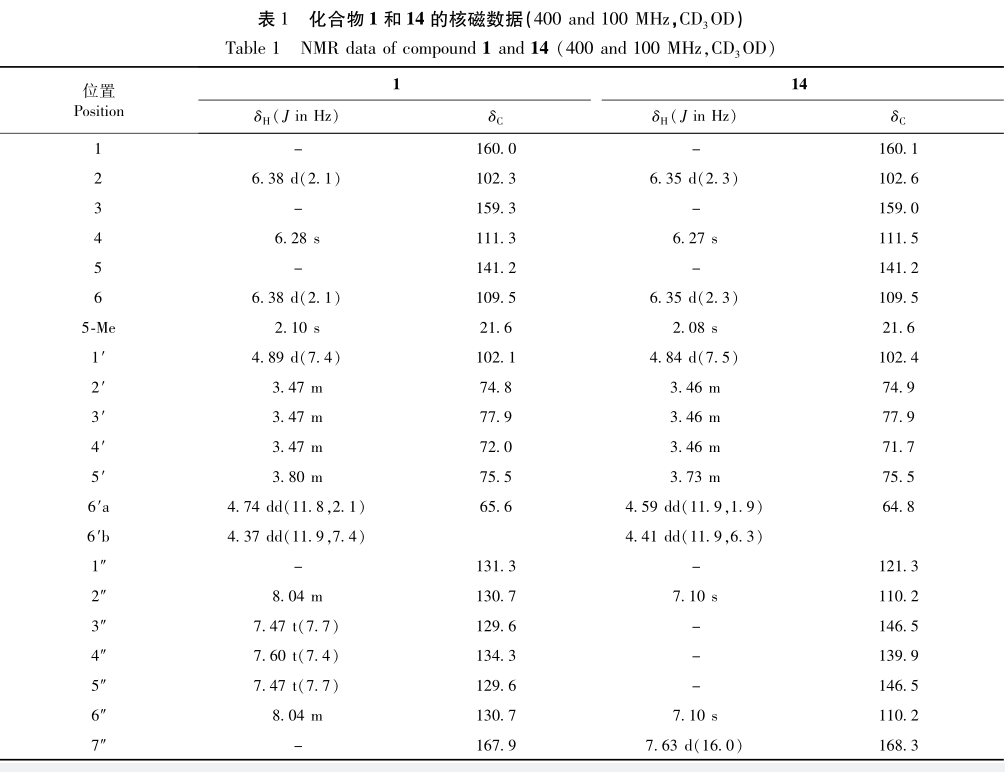
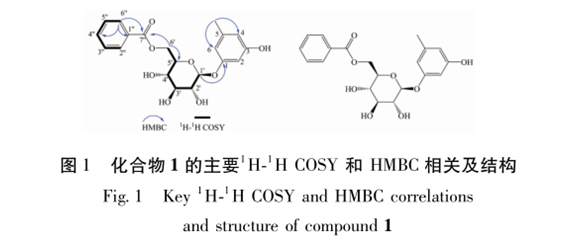
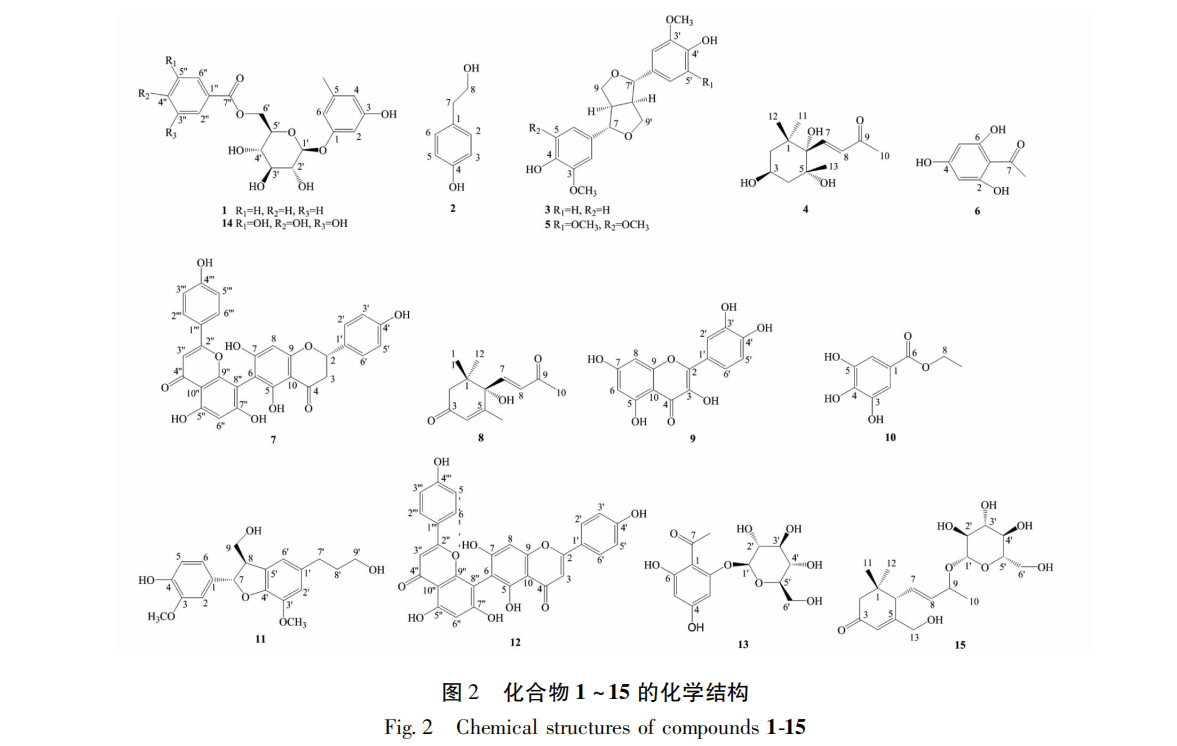
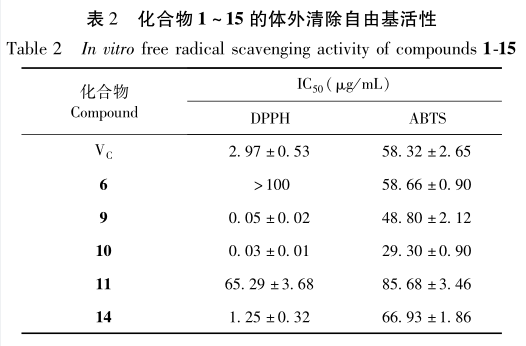 In this study, 15 compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate extraction phase of salt bark wood leaves, including 1 new compound and 14 known compounds. Compounds 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 13, and 15 were isolated from salt bark wood plants for the first time. The results of in vitro antioxidant activity experiments showed that compounds 9, 10, 11, and 14 exhibited good scavenging activity against DPPH and ABTS free radicals, while compound 6 showed good scavenging activity against ABTS free radicals. Among them, compounds 9 and 10 had the strongest free radical scavenging activity, stronger than the positive control VC. Further analysis of the structures of compounds with antioxidant activity revealed that compound 11 is lignin, while the remaining compounds 6, 9, 10, and 14 belong to polyphenolic compounds. Therefore, it is speculated that polyphenolic compounds are the main active ingredients in the in vitro antioxidant activity of salt bark leaves. The results of this experimental study elucidated the main functional components of antioxidant activity in salted wood leaves, enriched the chemical composition and antioxidant activity research of salted wood leaves, and provided a theoretical basis for the material basis research of salted wood leaves.
In this study, 15 compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate extraction phase of salt bark wood leaves, including 1 new compound and 14 known compounds. Compounds 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 13, and 15 were isolated from salt bark wood plants for the first time. The results of in vitro antioxidant activity experiments showed that compounds 9, 10, 11, and 14 exhibited good scavenging activity against DPPH and ABTS free radicals, while compound 6 showed good scavenging activity against ABTS free radicals. Among them, compounds 9 and 10 had the strongest free radical scavenging activity, stronger than the positive control VC. Further analysis of the structures of compounds with antioxidant activity revealed that compound 11 is lignin, while the remaining compounds 6, 9, 10, and 14 belong to polyphenolic compounds. Therefore, it is speculated that polyphenolic compounds are the main active ingredients in the in vitro antioxidant activity of salt bark leaves. The results of this experimental study elucidated the main functional components of antioxidant activity in salted wood leaves, enriched the chemical composition and antioxidant activity research of salted wood leaves, and provided a theoretical basis for the material basis research of salted wood leaves.
