Analysis of Nutritional Components and Evaluation of Edible Safety of Yunshen
Yunshen, also known as stinky ginseng or stinky medicine, is a member of the Campanulaceae family and Codonopsis genus. It is commonly referred to as stinky ginseng due to its unique and strong odor. Yunshen is a unique plant species in the high-altitude mountainous areas of Yunnan, growing in the forest edges and shrubs at an altitude of 700-2800 meters. It is mainly distributed in central, western, and southern Yunnan. It is a medicinal and edible plant that has been widely used and recorded in writing in Yunnan for a long time. It is often stewed with pork ribs, chicken, and other inexpensive supplements to nourish qi, blood, spleen, stomach, and strengthen the body. According to literature data, the main source plants known as cloud ginseng in Yunnan region include Codonopsis bulleyana Forrest ex Diels (also known as Orchid Stinky Ginseng, Hu Mao Ocean Ginseng), Codonopsis micrantha Chipp, Codonopsis subglobosa W. W. Sm. (also known as Tianning Codonopsis, Wushan Codonopsis, and Single Branch Codonopsis), Codonopsis cordifolioidea (also known as Heart Leaf Codonopsis, Edge Codonopsis, and Ancient Lamp Tea Root), and Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf var. volubilis (Nannf.) L. T. Shen and others. Xundian and Yiliang in Kunming, Yunnan are the main cultivation areas of cloud ginseng, with a long history of planting and consumption. The cloud ginseng planted in this area has been identified as wrapped ginseng.
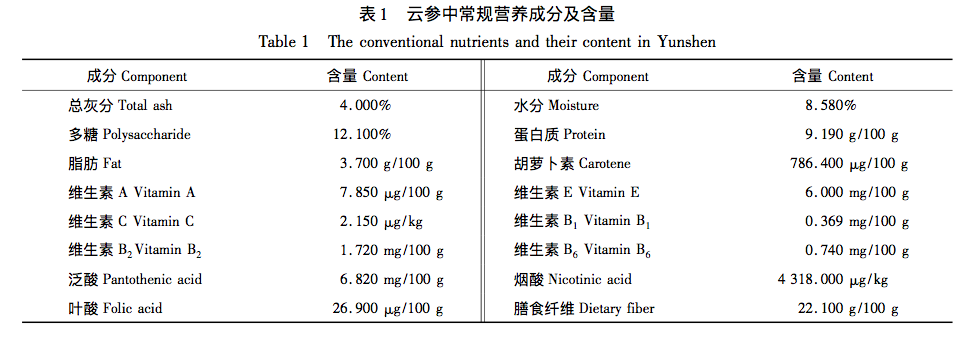
Yunshen is rich in nutrients such as protein, amino acids, carotenoids, vitamins, sugar, and fat, making it a medicinal and edible plant with balanced nutritional content. Li et al. found that Yunshen contains phytochemicals such as flavonoids, coumarins, volatile oils, alkaloids, tannins, phenols, resins, saponins, etc. Among them, flavonoid coumarins are one of the main components. According to books such as “Dictionary of Chinese Ethnic Medicine”, “Flora of Yunnan”, and “National Dictionary of Chinese Herbal Medicine”, the roots of Yunshen have the effects of nourishing the middle and qi, strengthening the spleen and generating fluids. Modern pharmacological research has shown that it has similar effects to Codonopsis pilosula, with the functions of replenishing qi and generating blood, promoting gastrointestinal peristalsis, resisting fatigue, improving the body’s immune system, and enhancing hypoxia tolerance. At present, there have been preliminary studies on the cultivation and nutritional components of cloud ginseng, but there are few systematic research reports on safety evaluation. This article aims to determine the nutritional composition and harmful residues of cloud ginseng, and conduct toxicological safety evaluation experiments, in order to provide reference for the nutritional composition and edible safety of cloud ginseng, and lay a theoretical foundation for the in-depth research and development of cloud ginseng.
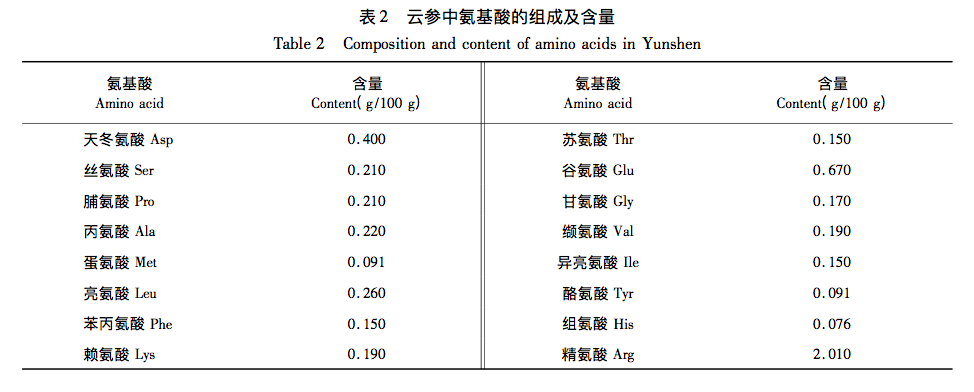
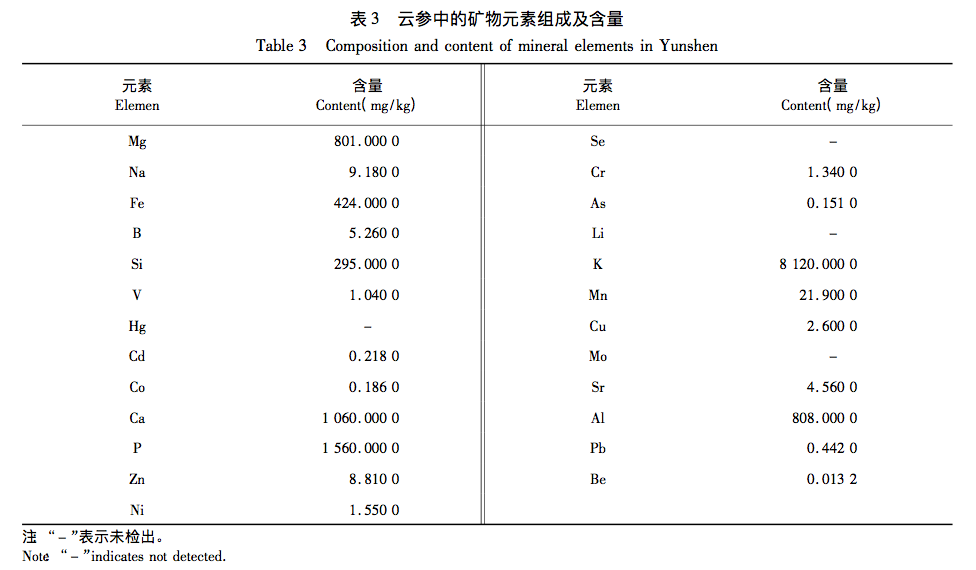
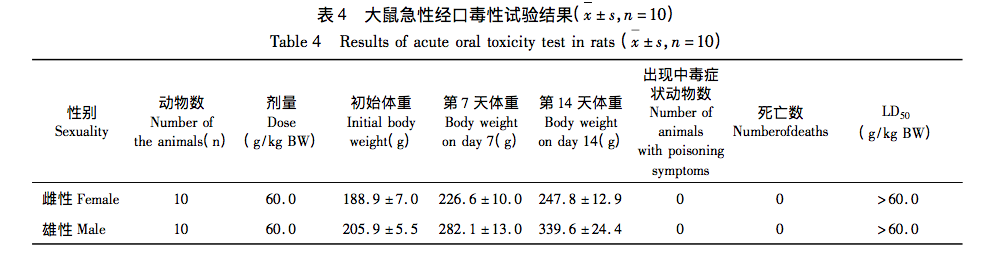
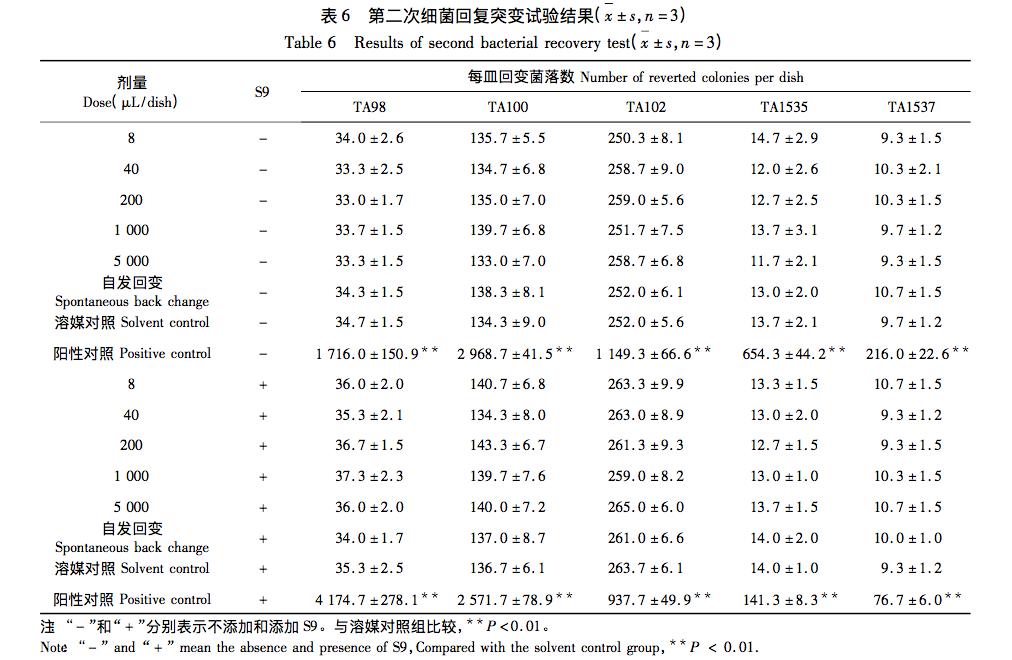
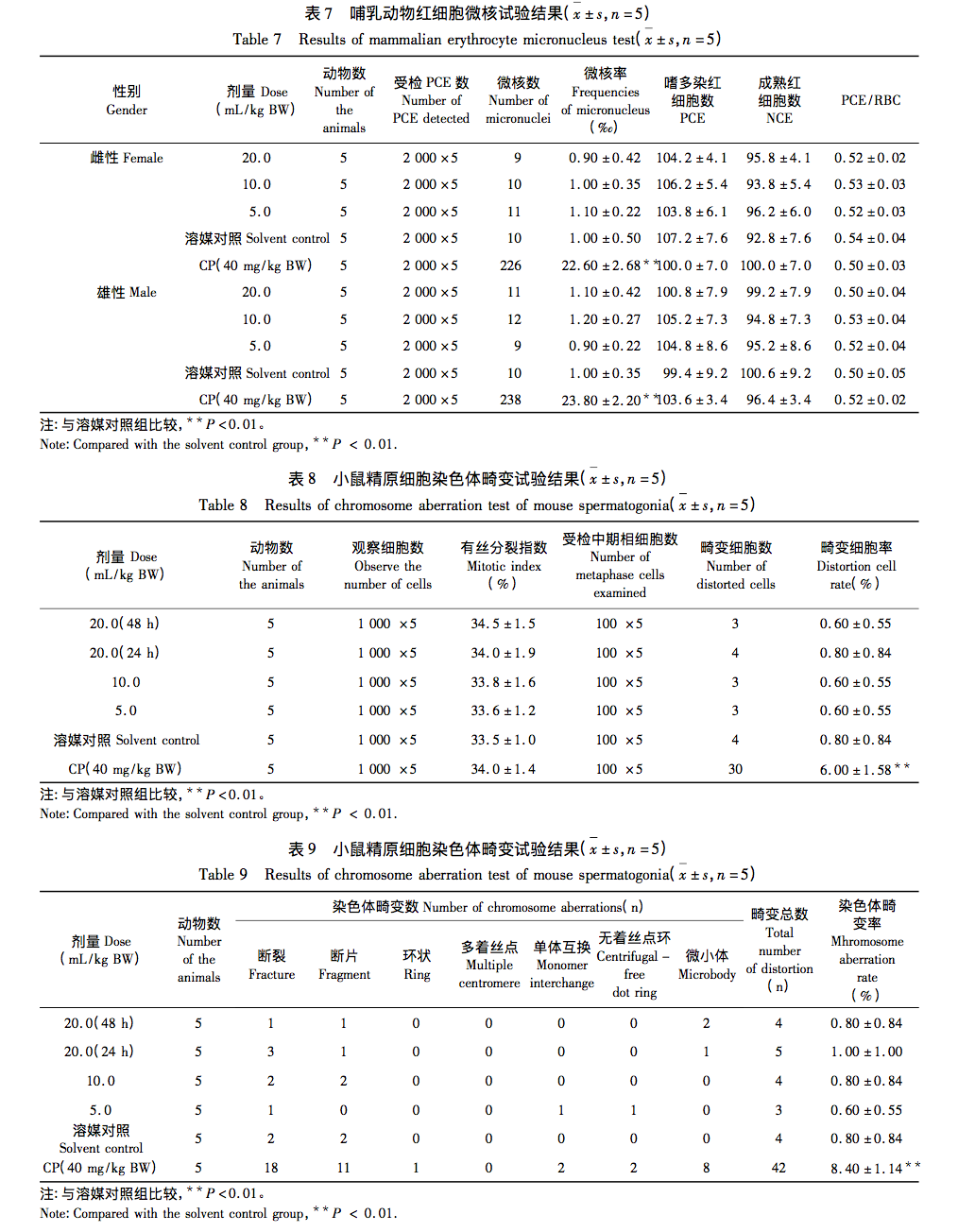
The research results indicate that Yunshen (wrapped Codonopsis pilosula) has rich nutritional components, as well as amino acids, vitamins (especially B vitamins), and various mineral elements. The total content of amino acids in Yunshen reaches 5.238g/100g, among which the top three essential amino acids are leucine, lysine, and valine, while the top three non essential amino acids are arginine, glutamic acid, and aspartic acid. The proportion of medicinal amino acids in all amino acids is relatively high, and the medicinal prospects are broad; B vitamins (especially vitamin B5) and vitamin E account for a large proportion in Yunshen; The mineral elements contained include 21 types such as K and Ca, with K having the highest content, followed by P and Ca. There are no residues of seven pesticides, including enoxymorpholine, jinggangmycin, imidazole, imidacloprid, benzothiadiazole, acetaldehyde, and thiamethoxam, and no foodborne pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella. The acute oral toxicity test results showed that its LD50>60.0g/kgBW, indicating that Yunshen is actually non-toxic; The results of three genetic toxicity tests (bacterial reverse mutation test, mammalian red blood cell micronucleus test, and mouse spermatogonial chromosome aberration test) were all negative, further proving the safety of Yunshen. This indicates that Yunshen has no toxic side effects and has good edible value. It can be widely used in fields such as medicine and food, and has broad prospects for application and development.