Exploring the potential mechanism of action of Bufei Huoxue Capsules in treating pulmonary fibrosis based on network pharmacology
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a chronic, irreversible interstitial lung disease characterized by the activation of lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and secretion of extracellular matrix. This disease is the end-stage manifestation of various lung diseases, where normal lung tissue structure is disrupted and replaced by abnormally repaired scar tissue. There are various clinical subtypes of PF, presenting as progressive attacks, among which idiopathic PF is the most common type. The cause of this disease is currently unknown, with a short survival period and no specific treatment drugs available. The incidence rate and mortality of PF are increasing year by year, especially the repeated infection of pulmonary interstitial by various respiratory viruses, which makes the disease more young. At present, there is still a large knowledge gap for the disease in clinic. Although two drugs, pirfenidone and nintedanib, are widely accepted in clinical practice, their clinical efficacy is not satisfactory.
PF belongs to the category of traditional Chinese medicine diseases such as “pulmonary obstruction” or “pulmonary impotence”. At the onset of the disease, prolonged coughing leads to deficiency, mainly manifested as “pulmonary obstruction” due to qi deficiency; The disease continues to develop, and in the late stage, there is a deficiency of both qi and yin, resulting in lung dysfunction. Long term illness leads to coughing and wheezing, which depletes the lung yin and causes lung heat. This can cause the yin fluid to be refluxed, resulting in dryness and dryness of the lungs, loss of nourishment, and ultimately leading to pulmonary impotence. This is what is said in the “Essay on Impotence” of Su Wen: “If the lungs are hot and the leaves are scorched,… then impotence will occur.” This disease is first caused by qi deficiency, leading to diarrhea, sweating, and a lack of body fluids to nourish the organs. Therefore, in clinical practice, nourishing the lungs and yin therapy is used to treat pulmonary impotence while also supplementing qi. The lungs face the hundred meridians and have the function of transporting water, grains, and essence. When heat pathogens damage the lungs and qi depletes the yin, the transportation is lost and the organs are deprived of nourishment, resulting in impotence syndrome.
Bufei Huoxue Capsule (BHC) is made from active ingredients extracted from Astragalus membranaceus, Paeonia lactiflora, and Fructus Psorale, and is widely used in clinical practice for lung diseases. Huangqi has a sweet and slightly warm nature, which can regulate the spleen and lung meridians. It has the functions of nourishing the body, strengthening the exterior, and tonifying the spleen and middle; Red peony has a bitter and slightly cold nature, and belongs to the liver meridian. It has the effects of clearing heat, cooling blood, dispersing blood stasis, and relieving pain; Psoralea has a warm nature, returning to the kidney and spleen meridians. It has the functions of regulating qi, relieving asthma, tonifying the kidneys, and strengthening yang. The three medicines work together to nourish the lungs, strengthen the kidneys, promote blood circulation, and remove blood stasis. This study predicts the potential mechanism of BHC’s anti PF effect through network pharmacology methods, and verifies the results of network pharmacology through animal experiments, enriching the theoretical basis of traditional Chinese medicine’s prevention and treatment of PF and providing research basis for the clinical application of BHC.
As a disease, pulmonary dysfunction must be caused by chronic cough and wheezing, lung qi deficiency, dysfunction of organs, and the lungs controlling the body’s qi. The circulation of blood vessels is unfavorable, coupled with spleen deficiency and excessive dampness, ultimately leading to phlegm coagulation and blood stasis, which in turn exacerbates the syndrome of pulmonary deficiency and forms a vicious cycle. This is the irreversible TCM pathogenesis of clinical progression of PF. Qi deficiency is the initiating factor for the onset of PF, and as the disease progresses, congestion is inevitable in the final stages of the disease. The Inner Canon clearly states: ‘When blood is abundant, it should be determined; when qi is deficient, it should be controlled and induced.’. BHC is precisely based on this method as the main treatment method and theoretical basis for developing latent drug formulations.
The above study found that BHC exerts anti PF function by intervening in the TNF signaling pathway through p38, MMP9, and TNF – α targets. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) was developed in the 1970s by E A. Carswell and his research team discovered that TNF, which is synthesized and secreted by mononuclear macrophages, was not specifically defined until 1958. Subsequently, scientists gradually discovered that other cells, including NK cells and T lymphocytes, can also produce TNF. Research has shown that TNF – α is closely involved in the inflammatory response of local tissues, mainly because it can promote the production of inflammatory substances represented by NLRP3 bodies, induce the activation of lung fibroblasts, and secrete extracellular matrix. At the same time, TNF – α can also exacerbate inflammatory damage, manifested in its ability to act alone or in conjunction with complement C3A and C5A, exerting cytotoxic effects. In summary, TNF – α plays a crucial role in the formation and development of PF. MMPs are zinc dependent proteases whose main function is to degrade ECM. After their first discovery in 1961, multiple proteases of the same family have been discovered. Under normal conditions, the activity of MMP9 is very low. After protein activation, it is mainly responsible for the degradation of ECM. It has been confirmed that the activity of MMP9 is significantly increased in lung tissue of PF patients, and its content is significantly increased in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. The main reason is to adaptively eliminate the adverse effects of ECM secretion. In recent years, various biological processes have been found to be associated with the formation of PF disease, among which p38 protein, which is closely related to cell apoptosis and cell cycle, has received increasing attention. P38, synthesized in type II alveolar epithelial cells, mononuclear pulmonary macrophages, and endothelial cells, participates in multiple stages of PF formation by mediating inflammatory cell infiltration, fibroblast differentiation, and other processes. Through reading relevant literature in recent years, it was found that the process of p38 mediated PF mainly involves the following points: firstly, it is well known that TGF – β is a key molecule in PF formation. p38 promotes the synthesis of TGF – β, induces epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in alveolar epithelial cells, and participates in the formation of PF by activating fibroblasts. Secondly, p38 regulates the activity of NF – κ B protein and participates in the pathogenesis of PF. NF – κ B is a DNA binding protein composed of the p65 and p50 subunits of the Rel protein family. It is an important transcription regulator in eukaryotic cells and can participate in the regulation of immune response in early pulmonary alveolar inflammation (PF) by promoting the transcription of inflammatory genes and TGF – β genes. Thirdly, p38 plays a crucial role in the proliferation and differentiation of fibroblasts, as well as in the deposition of extracellular matrix. In surviving myofibroblasts, p38 participates in the degradation of PF extracellular matrix by promoting mRNA transcription of MMPs.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that the three differentially expressed proteins (TNF – α, MMP-9, p38) in this study are all located at upstream and downstream nodes in the TNF signaling pathway, and their expression is closely related to the occurrence and development of PF. Multiple aspects and signaling pathways involved in the molecular biology changes of PF. From this, it can be seen that the characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine intervention are multi-target and multi pathway effects. At the same time, the various pathways are closely related, influencing and regulating each other. It also reflects the overall concept of the effects of traditional Chinese medicine. In this study, it was found that the changes in three proteins (TNF – α, MMP-9, p38) showed significant high expression in the model group. With changes in dose, protein expression also exhibited gradient changes and concentration dependence. The experimental part not only pointed out the direction for our subsequent research, but also verified the scientific validity of the enrichment analysis results in our previous network pharmacology section.


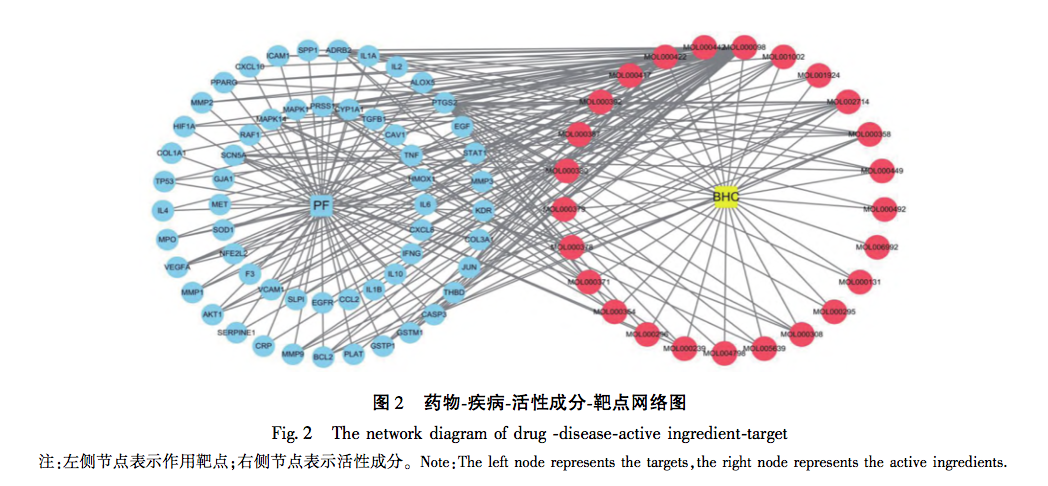
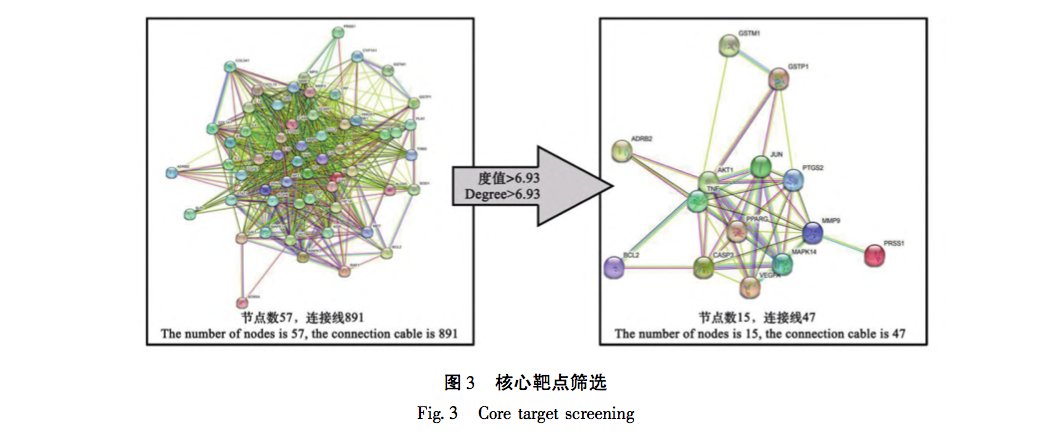
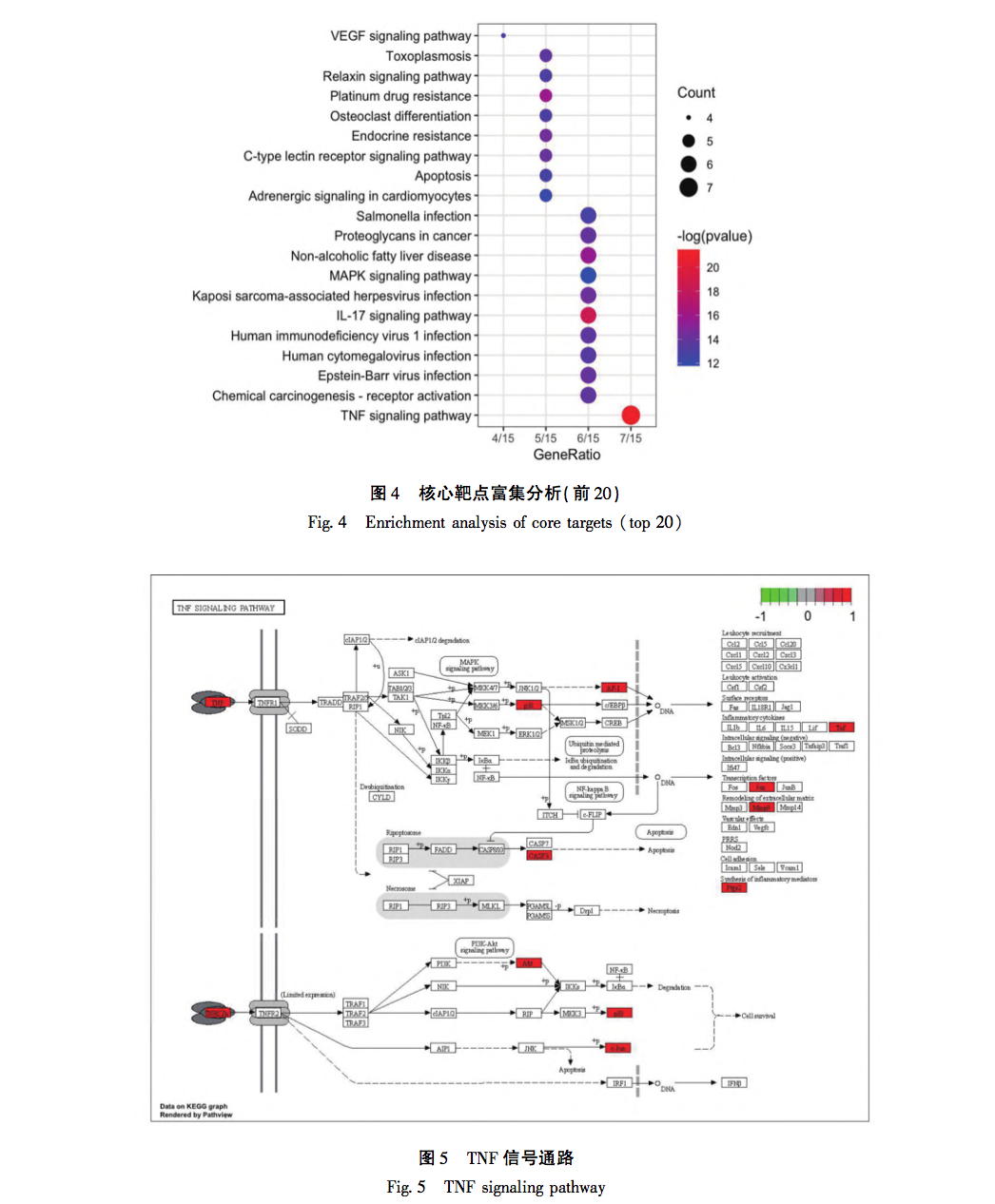
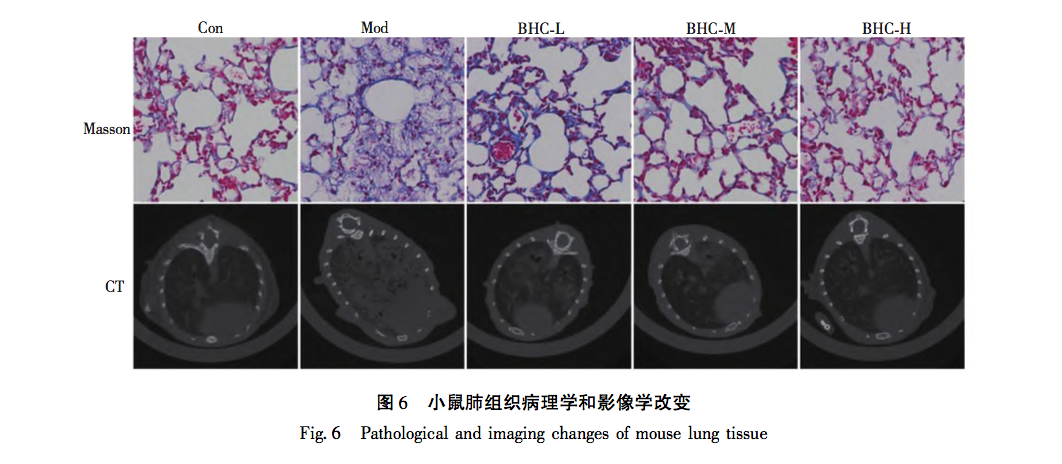
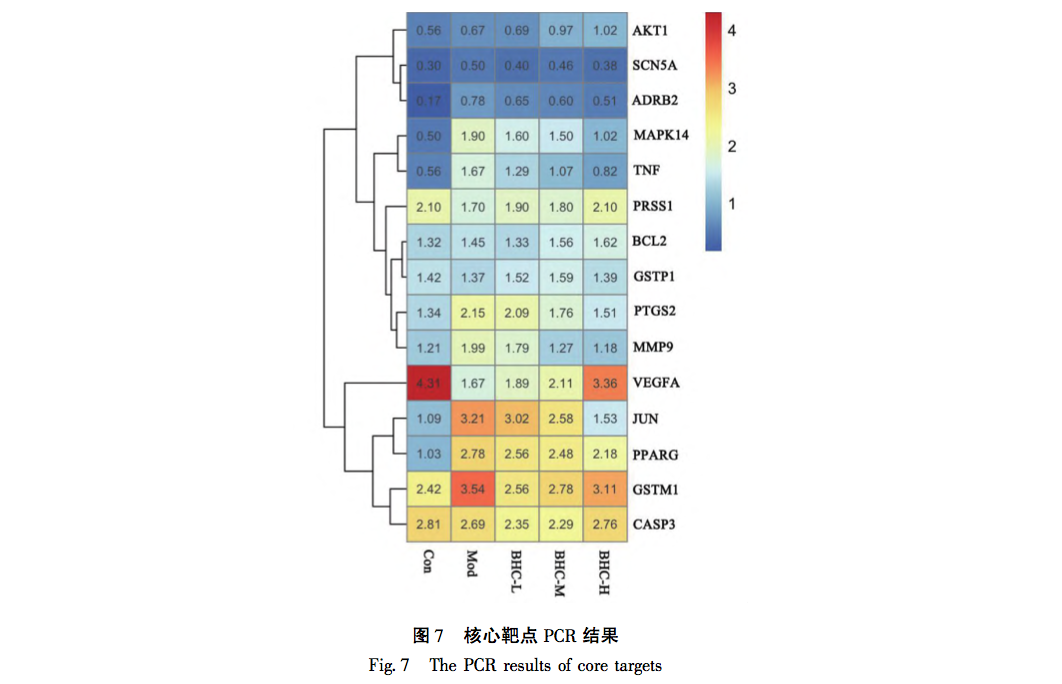
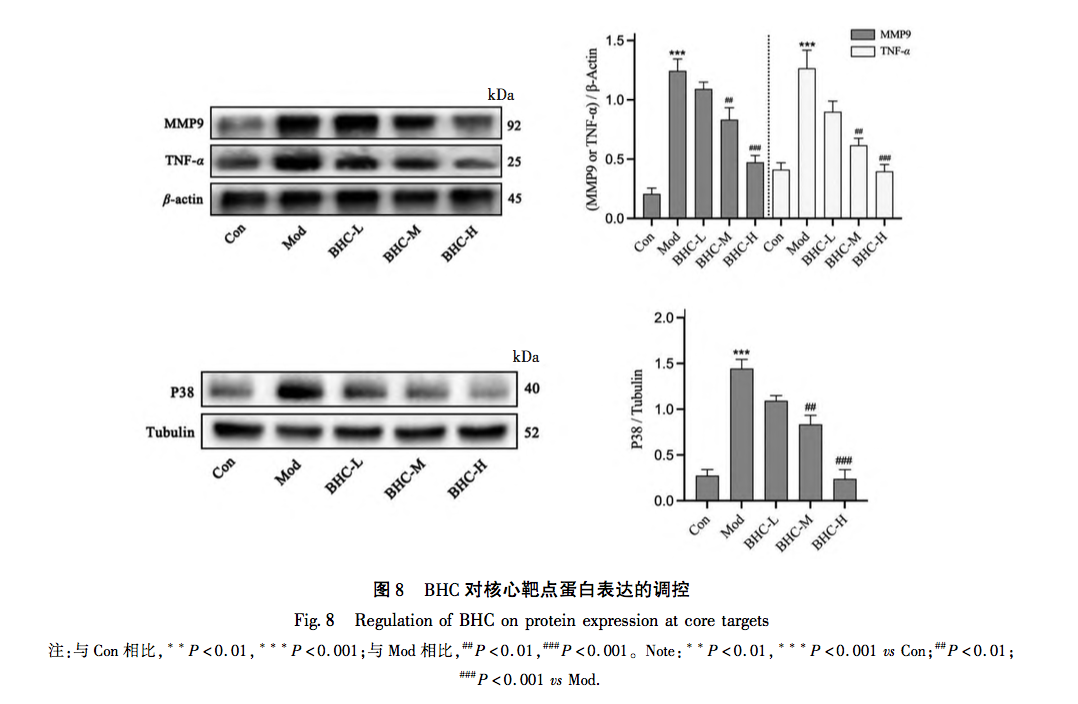 The BHC involved in this study is mainly treated with the method of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis. Due to the rarity of the disease and the complexity of its etiology, there is currently relatively little up-to-date epidemiological data on PF. However, clinically, its incidence rate is rising significantly, which may be due to the long-term existence of novel coronavirus, repeated infection and other factors, which repeatedly stimulate the pulmonary interstitium. Although significant progress has been made in the treatment of COVID-19, there are still many problems to be solved for the long-term sequelae of such patients, especially for the treatment of PF. As is well known, PF is the ultimate result of the slow progression of many lung diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis, and emphysema. In the early stages of PF, it is mainly caused by qi stagnation and blood stasis, poor circulation of qi and blood, and lack of lung nourishment. The characteristics of this stage are rapid onset, short cycle, and easy control. Therefore, early treatment should focus on promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, supplemented by nourishing qi and yin; In end-stage PF patients, qi deficiency and shortness of breath, weak surface defense, and delicate lungs are more susceptible to invasion by external pathogens. The characteristics of this stage are slow disease progression, long cycle, and difficult reversal. In this stage, the treatment strategy should mainly focus on nourishing qi and yin, supplemented by promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis. The animal model involved in this study conforms to the early acute onset stage of PF, and the treatment should mainly focus on promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, which is in line with the efficacy of BHC. This indirectly reveals the effectiveness and scientificity of BHC, and also provides direction for future research of our research group.
The BHC involved in this study is mainly treated with the method of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis. Due to the rarity of the disease and the complexity of its etiology, there is currently relatively little up-to-date epidemiological data on PF. However, clinically, its incidence rate is rising significantly, which may be due to the long-term existence of novel coronavirus, repeated infection and other factors, which repeatedly stimulate the pulmonary interstitium. Although significant progress has been made in the treatment of COVID-19, there are still many problems to be solved for the long-term sequelae of such patients, especially for the treatment of PF. As is well known, PF is the ultimate result of the slow progression of many lung diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis, and emphysema. In the early stages of PF, it is mainly caused by qi stagnation and blood stasis, poor circulation of qi and blood, and lack of lung nourishment. The characteristics of this stage are rapid onset, short cycle, and easy control. Therefore, early treatment should focus on promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, supplemented by nourishing qi and yin; In end-stage PF patients, qi deficiency and shortness of breath, weak surface defense, and delicate lungs are more susceptible to invasion by external pathogens. The characteristics of this stage are slow disease progression, long cycle, and difficult reversal. In this stage, the treatment strategy should mainly focus on nourishing qi and yin, supplemented by promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis. The animal model involved in this study conforms to the early acute onset stage of PF, and the treatment should mainly focus on promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, which is in line with the efficacy of BHC. This indirectly reveals the effectiveness and scientificity of BHC, and also provides direction for future research of our research group.
