Diterpenes with cytotoxic activity in the fermentation products of pink trichoderma
The pink trichothecium roseum, belonging to the Hyphomyceales order of the Deuteromycotina subphylum, was discovered and named in 2008. This fungus is easily isolated from decaying plant bodies, soil, and air, and is a widely distributed plant and vegetable pathogenic fungus worldwide. There have been many studies on the metabolites of pink trichoderma under laboratory culture conditions, with representative structures including sesquiterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, and cyclic peptides. Among them, the most widely studied is trichothecene. Tang et al. reported that monotrichothecene compounds can cause decay in apple cores, while monotrichothecene toxins inhibit and interfere with protein and nucleic acid synthesis in both humans and animals, leading to immune suppression of human and animal health. Consuming food and products contaminated with these toxins can cause widespread toxic effects in humans and animals.



In addition to toxin compounds, compounds with cytotoxic activity have also been found in this fermentation broth, such as the sesquiterpene compound cuspidatol found in this genus, which showed strong immunosuppressive activity in MLR assays with an IC50 value of 11 μ g/mL; Monotrichothecin A has a strong inhibitory effect on the growth of HL-60, SMMC-7721, A549, MCF-7, and SW480 cells, with IC50 values of 0.022, 0.020, 0.015, 0.006, and 0.011 μ mol/L, respectively, which are comparable to the positive control paclitaxel; The diterpene compound rosonolactone has strong anti proliferative and pro apoptotic effects on human cervical cancer HeLa cells; Roseocardin, a cyclic ester peptide compound, has a positive inotropic effect on rat myocardium; The cyclic peptide compound tricomide D exhibited significant cytotoxicity against three human cancer cell lines (MCF-7, SW480, HL-6), with IC50 values of 0.079, 0.107, and 0.149 μ mol/L, respectively. This is the first report of the cytotoxic activity of cyclic peptides. In order to continue searching for novel compounds with cytotoxic activity, our research group isolated and identified a strain of pink trichothecus from the soil where wild Ganoderma lucidum grows in Baise (the hometown of Ganoderma lucidum). We used rice culture medium to expand the fermentation process, in order to discover compounds with novel structures and good biological activity, and provide drug lead structures.
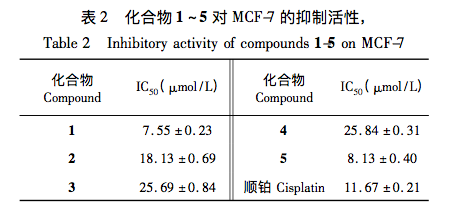
In this study, five compounds were isolated and identified from the fermentation products of T. roseum, all of which are diterpenes. Among them, compound 1 is a new diterpenoid compound. This result enriches the diversity of metabolites produced by pink trichoderma. Five compounds showed varying degrees of inhibitory effects on MCF-7 cells, with compounds 1 and 5 exhibiting the best activity. It is speculated that this may be due to the similar A and B ring structures of compounds 1 and 5, while compound 5, although chain like, has a dominant conformation with spatial extension similar to compound 1. Compounds with this structural feature showed better activity in the activity research model selected in this article. This study enriches the diversity of secondary metabolite structures in Trichothecaum fungi and provides a reference for the screening of anti-tumor active compounds.
