Effects of aerobic exercise and resveratrol on renal inflammation and apoptosis in diabetes nephropathy rats
Diabetes nephropathy (DKD) is one of the most important complications of diabetes, and its physiological and pathological mechanisms are very complex. The early pathological changes are manifested as glomerular hypertrophy, increased cell exudation, accumulation of extracellular matrix, which triggers inflammatory reaction and interstitial fibrosis of the kidney, produces a large number of inflammatory factors, promotes cell apoptosis, and then aggravates renal tissue damage. Resveratrol (RSV) is a mixture of plant polyphenols. A large number of studies have shown that resveratrol plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of diabetes nephropathy. Resveratrol can significantly reduce the level of serum inflammatory factors in diabetes rats by regulating multiple signal pathways, and reduce the renal vascular permeability in diabetes rats, thereby reducing the changes in renal pathological damage. Resveratrol, as a highly reducing polyphenolic substance, has been shown to regulate the metabolism of oxygen free radicals in the kidneys under DKD conditions. It can reduce the content of malondialdehyde in the kidneys, promote the increase of antioxidant enzyme activity, and exert antioxidant stress resistance. In addition, resveratrol can also inhibit mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix accumulation by regulating the AMPK/NOX4/ROS pathway, delay renal fibrosis, and thus have a protective effect on the kidneys. Research has confirmed that exercise has a good role in the adjuvant treatment of type 2 diabetes, which has antioxidant stress, lipid metabolism regulation and inflammation control, and promotes the recovery of renal function in diabetes. The combination of traditional Chinese medicine and aerobic exercise for the treatment of DKD is currently one of the research directions explored by scholars. Li et al.’s research shows that the combination of Lanzhou Lily polysaccharides and aerobic exercise can promote insulin secretion in rats, effectively reduce blood lipid levels, increase antioxidant enzyme activity, inhibit renal cell apoptosis, and thus improve the structural damage of renal tissue. However, there is limited research on the protective effects of aerobic exercise combined with resveratrol on renal function in diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Therefore, this study aims to explore the effects of resveratrol and aerobic exercise on renal inflammatory reaction and cell apoptosis in diabetes rats through the implementation of resveratrol and aerobic exercise intervention in diabetes rats, so as to provide reference for the comprehensive treatment of diabetes nephropathy.
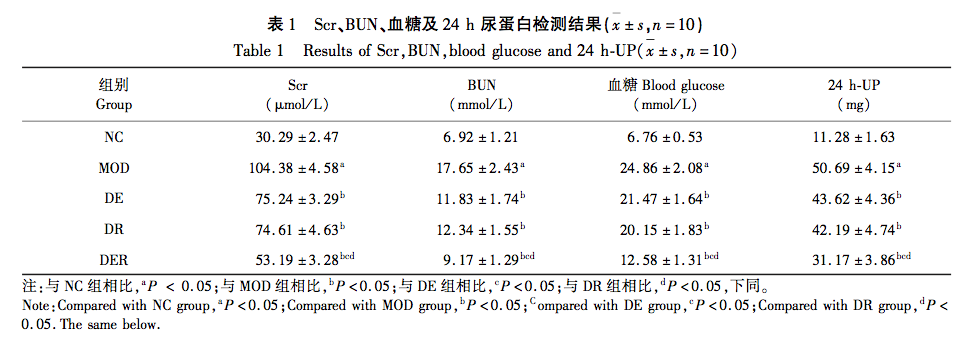



 Early prevention and treatment of diabetes nephropathy is very important. Chinese herbal medicine and exercise therapy combined with traditional methods to treat diabetes nephropathy is one of the research directions of scholars at present. The results of this study showed that the Scr, BUN, blood glucose, and 24-hour urinary protein concentration in the model group were significantly higher than those in the control group, indicating successful modeling. Compared with the model group, the concentration of Scr, BUN, blood sugar and 24h urine protein in the exercise group, drug group and exercise drug group decreased significantly, suggesting that the intervention of aerobic exercise and resveratrol can reduce the renal damage of diabetes and have a certain protective effect on the kidney, especially the joint intervention of aerobic exercise and resveratrol shows a more obvious improvement effect on reducing the renal damage.
Early prevention and treatment of diabetes nephropathy is very important. Chinese herbal medicine and exercise therapy combined with traditional methods to treat diabetes nephropathy is one of the research directions of scholars at present. The results of this study showed that the Scr, BUN, blood glucose, and 24-hour urinary protein concentration in the model group were significantly higher than those in the control group, indicating successful modeling. Compared with the model group, the concentration of Scr, BUN, blood sugar and 24h urine protein in the exercise group, drug group and exercise drug group decreased significantly, suggesting that the intervention of aerobic exercise and resveratrol can reduce the renal damage of diabetes and have a certain protective effect on the kidney, especially the joint intervention of aerobic exercise and resveratrol shows a more obvious improvement effect on reducing the renal damage.
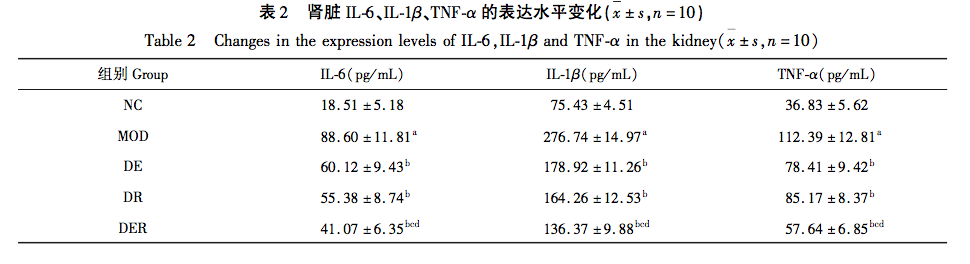
In the pathogenesis of diabetes nephropathy, there are a large number of inflammatory factors in the renal tissue. The structural and functional damage of the kidney is closely related to the abnormal expression of inflammatory factors. Research has confirmed that damaged renal epithelial cells produce various inflammatory mediators such as TNF – α, IL-1 β, IL-6, which induce an exacerbation of inflammatory reactions and thus worsen renal pathological damage. Shi et al studied the protective effect of berbamine on rats with diabetes nephropathy, and confirmed that after berbamine treatment, the expression of serum inflammatory cytokines IL-6, TNF – α and IL-1 β was significantly reduced, thus protecting kidney podocytes from inflammatory damage. The results of this study showed that the levels of TNF – α, IL-6, and IL-1 β in the renal tissue of the model group were significantly upregulated compared to the control group. After intervention with aerobic exercise and resveratrol, the levels of TNF – α, IL-6, and IL-1 β in renal tissue were significantly downregulated in the exercise group, drug group, and exercise drug group, with the downregulation being more pronounced in the exercise drug group. It is suggested that aerobic exercise and resveratrol alone or in combination can act on the inflammatory pathway, promote the reduction of the expression of inflammatory related factors IL-6, TNF – α and IL-1 β, thus reducing the renal pathological damage in diabetes rats, and the combined intervention effect is better than aerobic exercise and resveratrol alone.
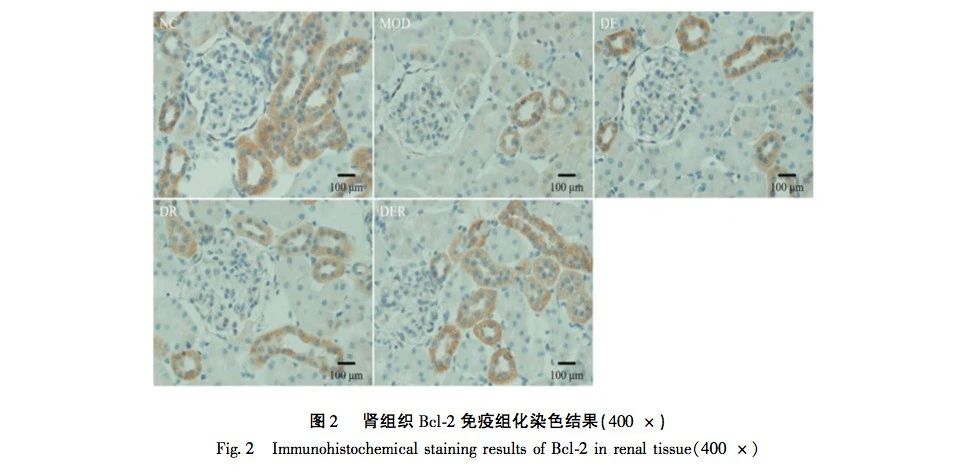
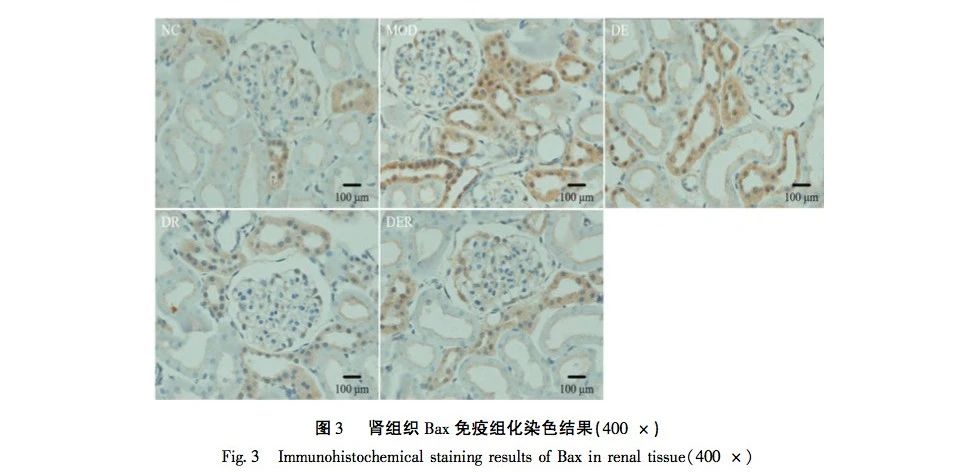
Renal cell apoptosis plays an important role in the development of renal function deterioration in diabetes, and is one of the mechanisms of renal pathological damage in diabetes. The Caspase and Bcl-2 protein families are the main regulatory factors in the process of cell apoptosis. Bax and Bcl-2 play a role in promoting and inhibiting apoptosis, respectively. Caspase-3 is an important terminal shear enzyme in the apoptosis pathway. Zhou et al.’s research has shown that Ganoderma spores activate the PINK1/Parkin pathway, initiate autophagy in kidney cells, significantly downregulate the expression of pro apoptotic proteins, alleviate pathological damage to the kidneys caused by hyperglycemia, and thus inhibit the occurrence of kidney cell apoptosis. Song et al also confirmed that Jiawei Shengjiang Powder can improve renal injury in diabetes nephropathy rats, and its mechanism may be related to down-regulation of RIP1/RIP3/MLKL signaling pathway and prevention of necrotic apoptosis of renal tissue. This experimental study found that the apoptosis rate of renal cells in the model group was significantly increased, Bax and Caspase-3 in renal tissue were significantly upregulated, and Bcl-2 was significantly downregulated, confirming the occurrence of apoptotic damage in renal tissue. After aerobic exercise and intervention with resveratrol, the apoptosis rate of renal cells was significantly reduced in the exercise group, drug group, and exercise drug group, while Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly down regulated and Bcl-2 was significantly up-regulated. The changes were more pronounced in the exercise drug group. It is suggested that aerobic exercise and resveratrol alone or in combination can act on the apoptosis signal pathway, regulate the expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3, and reduce renal cell apoptosis. Among them, aerobic exercise and resveratrol in combination have more obvious effects on inhibiting cell apoptosis, and better improve the prognosis of diabetes kidney injury.
NF – κ B, as a nuclear transcription factor, is widely involved in pathological processes such as inflammation, cell apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Research has found that activated NF – κ B migrates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, activating downstream inflammatory factors, leading to overexpression of genes and exacerbation of inflammatory responses, thereby exacerbating the degree of inflammatory damage. In addition, activated NF – κ B can regulate the transcription of downstream apoptotic genes Bax, Bcl-2, and Caspase-3 after entering the nucleus, promote cell apoptosis, and exacerbate renal structural and functional damage. Sui et al. established an animal model of sepsis induced acute kidney injury in rats and found that hesperidin may inhibit the activation of the NF – κ B pathway, further suppress downstream inflammation and oxidative stress responses, reduce cell apoptosis, and alleviate sepsis induced kidney injury. Diao et al. found that the TIR/BB ring analogue AS-1 has a protective effect on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice, and its mechanism of action may be related to reducing the activation of the NF – κ B signaling pathway, producing anti-inflammatory and anti apoptotic effects. Our experiment confirmed that the expression of NF – κ Bp65 protein in the renal tissue of the model group was significantly increased compared to the control group. After aerobic exercise and resveratrol intervention, the expression of NF – κ Bp65 protein in the kidney decreased, inflammation and cell apoptosis were reduced, and the changes in the exercise drug group were more significant. The mechanism by which aerobic exercise and resveratrol alleviate inflammatory response and apoptosis is closely related to the inhibition of NF – κ Bp65 activation. However, the NF – κ B signaling pathway is influenced by multiple factors, and the regulatory mechanism is very complex. The specific mechanism still needs to be explored in future experiments.
In conclusion, aerobic exercise and resveratrol alone or in combination have a certain protective effect on the kidney of diabetes nephropathy rats, and the combination of aerobic exercise and resveratrol has a more significant effect than the single factor intervention. Its mechanism of action may be by inhibiting the activation of NF – κ Bp65, reducing the expression of inflammatory factors IL-6, TNF – α, and IL-1 β, and downregulating the level of inflammatory response; It may also have an important protective effect on the kidney of diabetes nephropathy rats by regulating apoptosis related factors, down regulating the expression level of Bax and Caspase-3 in renal tissue, up regulating the expression level of Bcl-2, reducing renal cell apoptosis, and alleviating pathological damage of renal tissue. This article discusses the intervention mechanism of aerobic exercise and resveratrol from the perspective of bidirectional regulation of inflammatory response and apoptosis of NF – κ B signaling pathway, aiming to provide experimental basis for exercise and combined Chinese herbal medicine therapy of diabetes nephropathy.
