Studies on Chemical Constituents and Anti inflammatory Activity of Siraitia grosvenorii Fruit Residue
Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle) C. Jeffrey ex Lu et Z. Y. Zhang is the fruit of perennial vine plants of the genus Siraitia in Cucurbitaceae, also known as Rakhanate, Pseudobalsam pear, and Momordica glabra, etc., known as “fairy fruit”, which is the first batch of medicinal and food homologous Chinese herbal medicines published by the National Health Commission and the State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration. Siraitia grosvenorii is widely distributed in Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi and southern Hunan. The name of Momordica grosvenorii was first recorded in the Annals of Xiuren County (AD 1830), and the earliest written record of its use as a medicine was recorded in the Annals of Lingui County (AD 1905), which recorded that “Momordica grosvenorii is as large as a persimmon, hollow, sweet, cool in nature, and can cure fatigue and cough”. Momordica grosvenorii is usually effective in clearing away heat and moistening the lung, facilitating the throat and opening the sound, smoothing the intestines and relieving constipation. It is widely used in the folk for the treatment of whooping cough, phlegm fire cough, oral ulcer, sore throat, aphonia, blood dryness and constipation, and has significant effects on acute and chronic bronchitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other diseases. Modern pharmacological and chemical composition studies show that Momordica grosvenorii has a wide range of pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, antiviral and anti-tumor. Its main chemical components include triterpenoids (mainly cucurbitane type tetracyclic triterpenoids), flavonoids, lignans, fatty acids, amino acids, sugars and other compounds. Among them, Momordica grosvenorii triterpenoid saponins have low toxicity, low calorie, high sweetness and other characteristics, and can be used as sugar substitutes or sweeteners for sugar free health food and drinks. For a long time, Hunan Huacheng Biological Resources Co., Ltd. has been using water extraction and other processes to extract only the main triterpene saponins from Siraitia grosvenorii, and its pomace is used as feed additive for livestock and poultry, but there are still a large number of active ingredients in the pomace, which can not be effectively used, and its chemical composition and pharmacological activity have not been systematically reported. In order to develop and utilize the plant resources more rationally and give full play to its medicinal value, this experiment carried out research on the chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro of its fruit residue, with a view to providing scientific reference for the further development and utilization of Momordica grosvenorii fruit residue.
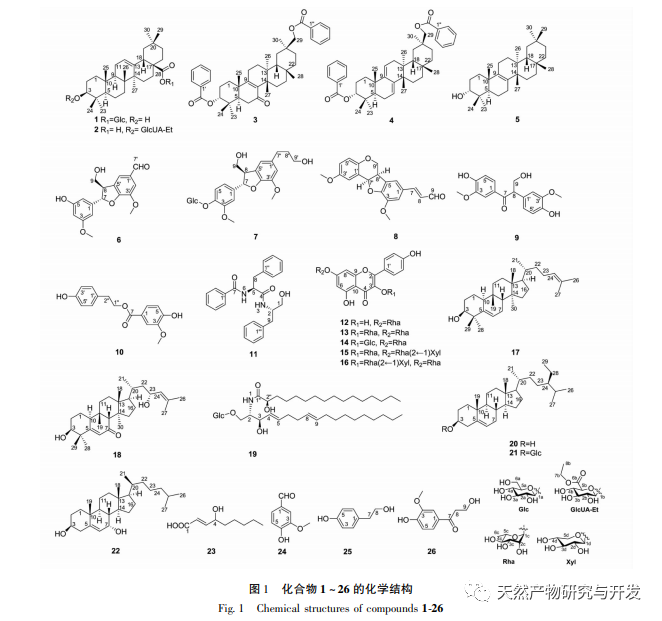
Luohanguo has been used for a long time in southern Hunan, Guangxi, Guizhou and other places since ancient times to treat acute and chronic tracheitis, pharyngitis, bronchial asthma, whooping cough, stomach heat, constipation, acute tonsillitis and other diseases. diabetes patients can also take it. It has a definite effect, can be used as both medicine and food, and has a very good health care effect on the human body. However, the current research is mainly focused on the study of momordica grosvenorii saponins, while the study of other effective ingredients is less. In order to fully and reasonably develop and utilize this plant resource, this paper has carried out research on the chemical components of its fruit residue, and comprehensively used a variety of chromatographic separation methods to separate 26 compounds from the water extracted fruit residue extract of Arhat grosvenorii, of which 12 compounds were isolated from the genus Momordica for the first time, and 7 compounds were separated from the cucurbitaceae for the first time, and their structures were identified, further supplementing and expanding the type and quantity of chemical components in momordica grosvenorii. In order to further study the mechanism of siraitia grosvenorii in the treatment of pharyngolaryngitis, the effects of each compound on the expression of inflammatory factors TNF – α, IL-1 β and IL-6 in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS were evaluated. It was found that seven compounds had a certain intensity of anti-inflammatory activity, which might be related to their inhibition of the release of inflammatory factors. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of Momordica grosvenorii needs to be further studied through systematic in vivo and in vitro experiments. The results of this study can provide some experimental basis for the full development of Momordica grosvenorii resources, improving the utilization rate of Arhat grosvenorii fruit residue and clinical application of Momordica grosvenorii medicinal materials.
