Negative regulation of ribosomal protein S12 expression by luteolin inhibits proliferation and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells
Luteolin (Lut) is a natural flavonoid compound, which has been proved to have a good anti-tumor effect in in vitro and in vivo tumor experiments such as liver cancer and breast cancer. In addition, Lut has relatively low cytotoxicity in inhibiting the proliferation of different tumor cells and inducing their apoptosis, making it a potential anti-tumor drug. The previous experiment of this subject confirmed that Lut can affect the activity of PI3K/Akt by up regulating the expression of PETN, and then inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells. However, considering the occurrence and development of breast cancer has a variety of regulatory mechanisms, whether Lut has other mechanisms to inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells remains unclear. Ribosomal protein (RP) is one of the main components of ribosomes, involved in intracellular protein biosynthesis, transcription, translation, and cell proliferation in other regulatory molecular related regions. It shows varying degrees of abnormal expression in colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, and esophageal cancer. Ribosomal protein S12 (RPS12) is highly expressed in cervical cancer patients, while its expression is relatively low in normal tissues. In addition, RPS12 is also overexpressed in gastric cancer tissue and can promote tumor cell metastasis. However, the regulatory role of RPS12 gene in the proliferation of breast cancer cells has not been clearly defined. C-Myc is a regulatory factor for ribosome synthesis. Through cDNA microarray analysis of fibroblasts, it was found that the expression level of RPS12 in cells may be related to c-Myc. This study aims to explore the mechanism of c-Myc and RPS12 in the process of Lut inhibiting the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells, in order to provide new ideas for the development and selection of drugs in the clinical treatment of breast cancer.

Despite the rapid development of medical level in recent years, the effect of clinical treatment for breast cancer is still poor. The main reason is that the development of tumor and the mechanism of early metastasis are not clear. Lut, a natural flavonoid compound, has inhibitory effects on the occurrence and development of various malignant tumors. Although our research group has previously confirmed the inhibitory effect of Lut on breast cancer cell proliferation, its specific mechanism has not yet been clarified. In this study, we found that Lut can down regulate the expression of c-Myc by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, and inhibit the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by negatively regulating the expression of RPS12. This further confirmed the prospect of Lut in the treatment of breast cancer.
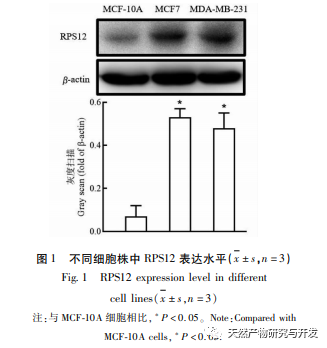
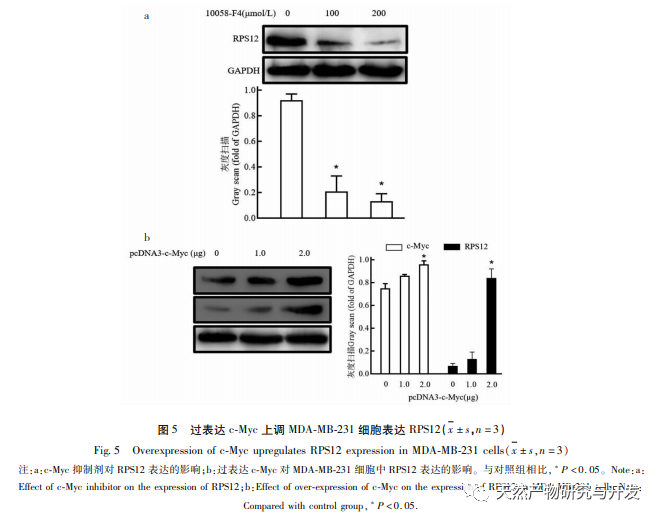
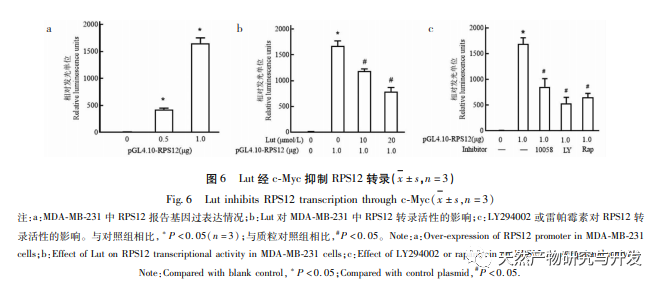
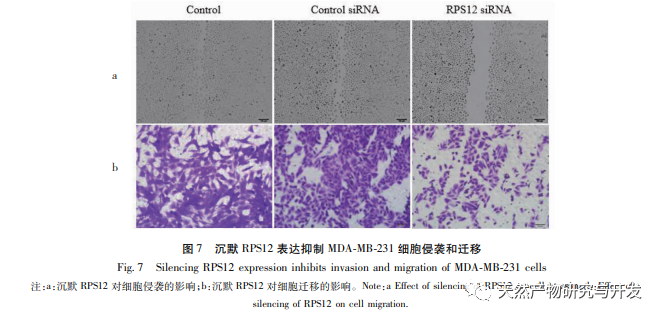
Ribosomes are the main organelles for protein synthesis in cells, and eukaryotic ribosomes contain approximately 80 RPs. RPs are abnormally upregulated in various tumor cells such as cervical cancer and gastric cancer, and are associated with the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells. Research has shown that the expression level of RPS12 in gastric cancer cells is significantly higher than that in normal cells, suggesting that RPS12 may be involved in the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. This study found that RPS12 was also highly expressed in breast cancer cell lines, which was consistent with other tumors. However, when breast cancer cells were treated with Lut, the expression level of RPS12 was significantly reduced. It was confirmed that RPS12 also participated in the regulation of Lut on breast cancer cells. In order to further clarify the role of RPS12 in the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells, we also tested the effect of silencing RPS12 on cell invasion and migration. The results showed that silencing RPS12 could significantly inhibit the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. This also indicates that the high expression of RPS12 in breast cancer may contribute to tumor development and metastasis. The c-Myc gene is currently known as a proto oncogene that can effectively promote cell division and proliferation, and is closely related to the formation and development of various malignant tumors. Research has shown that in colon cancer, MicroRNA-184 can inhibit the proliferation of colon cancer cells and promote cell apoptosis by downregulating the expression level of c-Myc. In addition, c-Myc also has a similar promoting effect on cell proliferation in gastric cancer cells. This study found that c-Myc is also highly expressed in breast cancer cell lines, and down-regulation of c-Myc expression can further inhibit the expression and transcription of RPS12 in cells, which can further inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells. Considering the role of c-Myc in other tumor cells, it has once again been demonstrated that Lut may exert its effect by affecting the expression of c-Myc/RPS12.
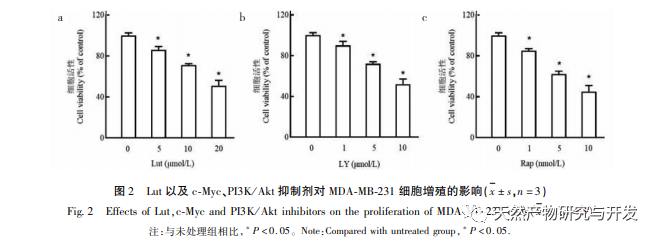
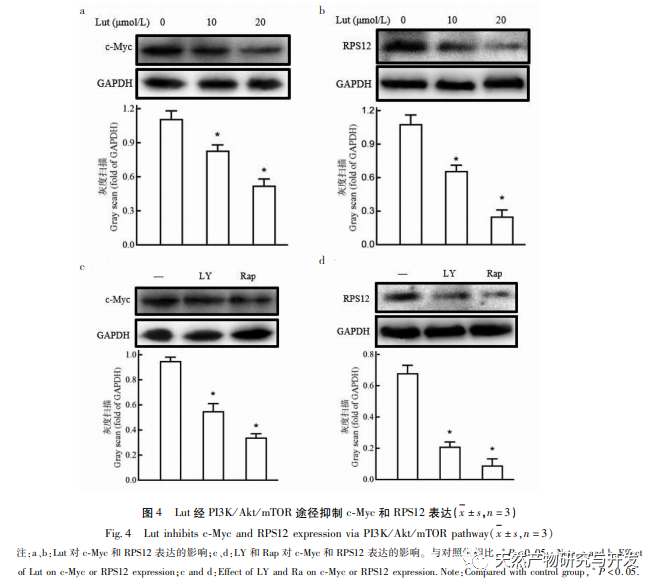
PI3K/Akt is an enzyme active intracellular signaling pathway that can participate in processes such as tumor growth and differentiation. Studies have shown that PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is often abnormally activated during the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells. In this study, both Akt inhibitor LY294002 and mTOR inhibitor rapamycin were used to significantly inhibit the phosphorylation levels of mTOR and S6K. However, rapamycin had no significant effect on Akt phosphorylation levels, as mTOR is a downstream molecule of PI3K/Akt and therefore has no effect on Akt phosphorylation. In addition, PI3K/Ak and mTOR inhibitors can significantly reduce the expression of RPS12 and c-Myc in cells, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation. These results suggest that RPS12 and c-Myc may also be downstream molecules of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, and participate in the regulation of Lut on the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells.
To sum up, Lut can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby downregulating the expression of c-Myc, and then negatively regulating RPS12. These results suggest that RPS12 and c-Myc may be potential targets for the treatment of breast cancer, and Lut can play an anti-tumor role by regulating the expression of RPS12 and c-Myc. This will provide new ideas for the clinical treatment of breast cancer.
