The intensification of economic development and social competition has led to an increasing incidence of epidemic diseases related to sleep disorders, and the 2018 China Sleep Quality Report points out that 83.81% of the respondents in China have sleep disturbances, of which difficulty in falling asleep accounts for 25.83%, and light sleep accounts for 26.49%.
According to the WHO survey, about 27% of the global population has sleep disorders, and the incidence of insomnia among adults in China is as high as 38.2%, making sleep disorders an important health issue of global concern.
2,000 years ago, the Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine had records of sleep disorders such as “the eyes do not close”, “no sleep” and “no lying down”, etc. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that the causes of sleep disorders are mostly based on emotions, diet or deficiency of qi and blood, and so on. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that the etiology of sleep disorders is mostly caused by internal injuries such as emotion, diet or deficiency of qi and blood, and that sleep disorders are prone to cause qi and blood disharmony of the heart, liver, gallbladder, spleen, stomach and kidney, as well as the imbalance of yin and yang. Modern medicine believes that the occurrence of sleep disorders is often related to neurotransmitters, immune regulation, intestinal flora, environmental and psychological factors, etc. Clinical treatment is often based on drug therapy, supplemented by psychological and behavioral interventions.
Continuous sleep disorders will cause chronic fatigue, memory loss, low immunity, cardiovascular damage and metabolic disorders, and other related diseases, and even lead to suicide in serious cases, therefore, improving sleep plays a key role in regulating the subhealth of the human body, lowering the occurrence of related epidemics, and improving the quality of life of the people.
Currently, chemical drugs used in the treatment of sleep disorders include barbiturates, benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepines, etc. These drugs have fast onset of action and clear mechanism of action, but long-term use of these drugs is prone to side effects such as residual effect, amnesia effect and drug withdrawal effect, etc. In comparison, Chinese medicine can improve sleep. In contrast, Chinese medicine to improve sleep disorders follow the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, through the adjustment of internal organs, qi, blood, yin and yang, so that the body to restore the normal state.
In Chinese medicine practice, natural medicinal herbs or (with) daily food are often used to improve sleep after compounding and consuming, and the use of natural food and medicine resources to improve sleep disorders is highly safe, not easy to appear resistance and dependence, and it is a sustainable mode of slow conditioning.
The use of natural food and medicine resources for the proper formulation of food and medicine formulas is not only unnecessary to change the traditional dietary habits, but also meets the needs of safety and health, so it is highly respected by the general public. Chinese dietary culture and traditional Chinese medicine practice have accumulated a wealth of methods for the management of sleep disorders, and the experience of applying many food and drug resources has been recorded in the canonical books, and the functions of related food and drug resources have been confirmed in modern medical research.
This paper summarizes and analyzes the types, functions and health food applications of major food and drug resources, such as common food, food and drug derived Chinese herbs, and traditional Chinese medicine diets, which have the effect of improving sleep, and it is intended to provide certain references for the high-value utilization of food and drug resources to improve sleep function and the research and development of health food to improve sleep function.
01
Food and drug resources for improving sleep
It is recorded in Huangdi Neijing – Taisu that “food is food on an empty stomach, and food is medicine for patients”, which is the idea of food and medicine in Chinese medicine science. Food and drug resources are the carriers of nutritional and functional components, and the improvement of sleep function is often associated with the functional components contained in food and drug resources, i.e. the material basis.
Traditional food culture and Chinese medicine literature have recorded a large number of food and medicine resources with sleep-improving effects, Chinese medicine diets and their applications, and modern medical and nutritional studies have also discovered the sleep-improving functions and mechanisms of many food and medicine resources, which are mainly related to common foods, food and medicine homologous Chinese herbs and Chinese medicine diets.
1.1 Common Food
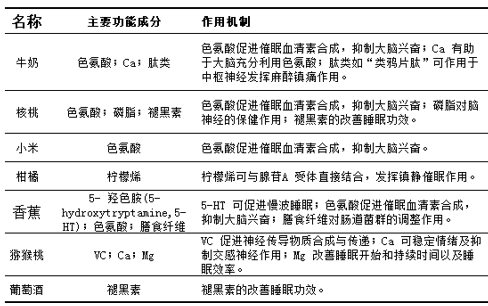
According to Sun Simiao, “food can expel the evils and stabilize the five organs, and please the spirit and refresh the mind in order to capitalize the blood”, indicating that food can not only satisfy the hunger, but also heal the disease and fitness. In recent years, the restorative effect of food and its components on human subhealth has received increasing attention and concern, and the sleep-improving functions and mechanisms of common foods have been gradually studied, and the common foods and their functional mechanisms summarized after literature analysis are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 shows that most of the foods that improve sleep contain tryptophan, melatonin, Ca and other major functional or nutritional components, such as millet is rich in tryptophan, which can promote the synthesis of hypnotic serotonin, thereby inhibiting brain excitation to improve sleep.
Ca helps the brain to make full use of tryptophan to stabilize mood and inhibit sympathetic nerves. The melatonin contained in wine can regulate the cycle of sleep and wakefulness, and can also resist free radicals, which is an important active substance to improve the quality of sleep, improve body functions and enhance the quality of life.
It is analyzed that the material basis of the sleep-improving effect of different foods is not the same, and it is speculated that the mechanism of regulating sleep disorders by different foods may not be the same. Since daily food regulation of sub-health does not need to change consumers’ living habits, thus making continuous nutrition and health intervention possible, the development of functional foods with sleep-improving effects based on common foods has a good market prospect.
Table 1 Main functional components and their mechanisms of action of common foods for improving sleep.
1.2 Chinese herbal medicines of the same origin as food and medicine
Both food and medicine of Chinese herbal medicine is often called food and medicine with resources, from ancient times to the present more attention to improve sleep function of food and medicine with class of Chinese herbal medicines are mainly sour jujube kernel, longan meat (cinnamon), lily, jujube, gardenia, Poria, lotus, etc., most of the efficacy of Chinese medicine to tranquilize the spirit and replenish the deficiency is the main, efficacy components involved in the saponins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides, and other chemical components, the modern pharmacology mechanism to regulate the neurotransmitters. The modern pharmacological mechanism is based on the regulation of neurotransmitters. Table 2 summarizes the types, clinical efficacy, functional components and pharmacological effects of the major food and drug homologues of Chinese herbal medicines for improving sleep function after literature analysis.
Table 2 Clinical efficacy in Chinese medicine, main functional components and pharmacological effects of Chinese herbal medicines of the same origin to improve sleep function.
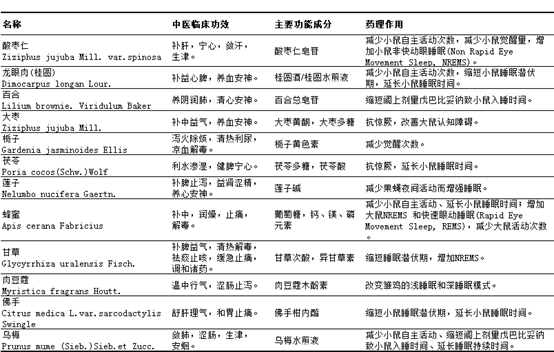
The list of Chinese herbal medicines that are both food and medicine is an official confirmation of the experience and knowledge in the utilization of resources of the same origin as food and medicine, and is an important part of the resources of traditional Chinese medicine. Because of their safety in consumption and higher efficacy in improving sleep than ordinary food, homologous Chinese herbal medicines are widely used in daily health care, health food and health-enhancing medicinal food.
The material basis of homologous herbs also involves saponins, polysaccharides, terpenoids, alkaloids and other chemical compositions, which suggests that there is a diversity in the mechanism of action for improving sleep. At present, most of the studies on the function of food and drug homologous herbs to improve sleep are established at the level of animal experiments, and the evaluation of behavioral indexes of experimental animals is the main focus, so the understanding of their related functional mechanisms is still to be studied in depth.
1.3 Traditional Chinese medicine diet
Traditional Chinese medicine diet is a combination of traditional Chinese medicine knowledge and daily cooking, often with high security Chinese herbs and ordinary food as raw materials, cooked and processed into a diet with therapeutic health effects. Traditional Chinese medicine diet is one of the main strategies of traditional Chinese medicine disease prevention and fitness, through the “medicine with food flavor, food to help medicine” to achieve the effect of comprehensive regulation of various human diseases.
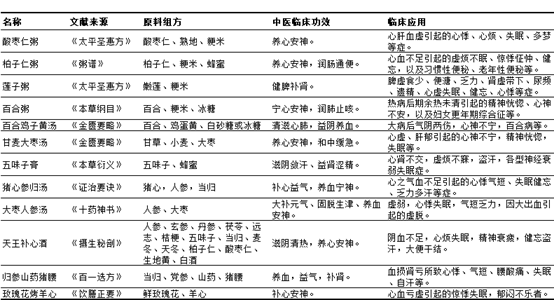
Improve sleep function of Chinese herbal medicine raw materials are mainly to nourish the heart and tranquilize the mind and the town to tranquilize the mind two categories, so tranquilize the mind class of Chinese medicine meal is often divided into nourish the heart and tranquilize the mind and the town to tranquilize the mind two categories. Nourish the heart and tranquilize the mind medicinal diet often to sour jujube nut, cypress kernel, lily, lotus seed, jujube, rose, etc. for the composition of raw materials, its role is moderate, no toxic side effects, easy to serve for a long time; heavy town of tranquilize the mind medicinal diet commonly used as a raw material for the composition of the bones, magnetite, vermilion and other Chinese medicinal herbs, with certain toxic side effects, should not be served for a long time, is not considered as a general development of functional foods as a resource. The literature sources, raw material formulas, main effects and clinical applications of common medicinal diets for nourishing the heart and calming the mind are summarized in Table 3.
In Table 3, 12 medicinal dietary formulas for improving sleep function were collected. Analyzed from the perspective of Chinese medicine, most of the dietary formulas are based on the functional raw materials of food and medicine resources for nourishing the heart and tranquillizing the mind, with ingredients such as nourishing the heart and strengthening the spleen as the carriers, which are calm in nature and suitable for use in qi, blood, yin, and yang deficiencies, etc.; the modern functional analysis is based on the improvement of the gastrointestinal tract function and the enhancement of the immune system as the main governing mechanism, which is mostly suitable for palpitations, insomnia, Modern functional analysis takes improving gastrointestinal function and enhancing immunity as the main regulating mechanism.
Chinese medicine diet will improve the sleep of Chinese herbs and food in the nutrition, efficacy and sensory application of a reasonable combination, not only do not have to change the traditional dietary habits, but also to strengthen the body, prevention and treatment of diseases, can be well integrated into daily life, consumer acceptability.
Based on Chinese medicine dietary development in line with modern requirements of health food or special health food has a good feasibility and high reliability, part of the health care function of the tranquility class dietary has been verified. Shao Yuan found that the addition of Ganmai Dazao Tang to randomly selected postpartum female patients treated with Ganmai Dazao Tang for 2 weeks could effectively improve the sleep disorders of postpartum females and correct the state of depression, and the efficacy of the treatment is worthy of affirmation. Through clinical observation, Liu Yuan and Li Xianxiao found that the application of Erxian Tang combined with Ganmai Dazao Tang and Ganmai Dazao Tang combined with Sour Jujube Ren Tang can effectively improve the sleep quality of patients with menopausal insomnia, and the clinical effect is definite.
Table 3 Literature source, raw material composition, clinical efficacy and clinical application of 12 Chinese medicine dietary prescriptions for nourishing the heart and tranquilizing the mind.
The list of Chinese herbal medicines that are both food and medicine is an official confirmation of the experience and knowledge in the utilization of resources of the same origin as food and medicine, and is an important part of the resources of traditional Chinese medicine. Because of their safety in consumption and higher efficacy in improving sleep than ordinary food, homologous Chinese herbal medicines are widely used in daily health care, health food and health-enhancing medicinal food.
The material basis of homologous herbs also involves saponins, polysaccharides, terpenoids, alkaloids and other chemical compositions, which suggests that there is a diversity in the mechanism of action for improving sleep. At present, most of the studies on the function of food and drug homologous herbs to improve sleep are established at the level of animal experiments, and the evaluation of behavioral indexes of experimental animals is the main focus, so the understanding of their related functional mechanisms is still to be studied in depth.
1.3 Traditional Chinese medicine diet
Traditional Chinese medicine diet is a combination of traditional Chinese medicine knowledge and daily cooking, often with high security Chinese herbs and ordinary food as raw materials, cooked and processed into a diet with therapeutic health effects. Traditional Chinese medicine diet is one of the main strategies of traditional Chinese medicine disease prevention and fitness, through the “medicine with food flavor, food to help medicine” to achieve the effect of comprehensive regulation of various human diseases.
Improve sleep function of Chinese herbal medicine raw materials are mainly to nourish the heart and tranquilize the mind and the town to tranquilize the mind two categories, so tranquilize the mind class of Chinese medicine meal is often divided into nourish the heart and tranquilize the mind and the town to tranquilize the mind two categories. Nourish the heart and tranquilize the mind medicinal diet often to sour jujube nut, cypress kernel, lily, lotus seed, jujube, rose, etc. for the composition of raw materials, its role is moderate, no toxic side effects, easy to serve for a long time; heavy town of tranquilize the mind medicinal diet commonly used as a raw material for the composition of the bones, magnetite, vermilion and other Chinese medicinal herbs, with certain toxic side effects, should not be served for a long time, is not considered as a general development of functional foods as a resource. The literature sources, raw material formulas, main effects and clinical applications of common medicinal diets for nourishing the heart and calming the mind are summarized in Table 3.
In Table 3, 12 medicinal dietary formulas for improving sleep function were collected. Analyzed from the perspective of Chinese medicine, most of the dietary formulas are based on the functional raw materials of food and medicine resources for nourishing the heart and tranquillizing the mind, with ingredients such as nourishing the heart and strengthening the spleen as the carriers, which are calm in nature and suitable for use in qi, blood, yin, and yang deficiencies, etc.; the modern functional analysis is based on the improvement of the gastrointestinal tract function and the enhancement of the immune system as the main governing mechanism, which is mostly suitable for palpitations, insomnia, Modern functional analysis takes improving gastrointestinal function and enhancing immunity as the main regulating mechanism.
Chinese medicine diet will improve the sleep of Chinese herbs and food in the nutrition, efficacy and sensory application of a reasonable combination, not only do not have to change the traditional dietary habits, but also to strengthen the body, prevention and treatment of diseases, can be well integrated into daily life, consumer acceptability.
Based on Chinese medicine dietary development in line with modern requirements of health food or special health food has a good feasibility and high reliability, part of the health care function of the tranquility class dietary has been verified. Shao Yuan found that the addition of Ganmai Dazao Tang to randomly selected postpartum female patients treated with Ganmai Dazao Tang for 2 weeks could effectively improve the sleep disorders of postpartum females and correct the state of depression, and the efficacy of the treatment is worthy of affirmation. Through clinical observation, Liu Yuan and Li Xianxiao found that the application of Erxian Tang combined with Ganmai Dazao Tang and Ganmai Dazao Tang combined with Sour Jujube Ren Tang can effectively improve the sleep quality of patients with menopausal insomnia, and the clinical effect is definite.
Table 3 Literature source, raw material composition, clinical efficacy and clinical application of 12 Chinese medicine dietary prescriptions for nourishing the heart and tranquilizing the mind.
Functional Mechanisms of Food and Drug Resources to Improve Sleep
The experience of traditional Chinese medicine in regulating sleep disorders originates from the results of long-term practice and observation of human beings, and the function and mechanism of action of related food and drug resources have been gradually verified in modern experimental studies. According to the comprehensive analysis of the literature, the improvement of sleep by natural food and drug resources mainly involves the mechanisms of neurotransmitter regulation, immune regulation and intestinal flora adjustment.
2.1 Neurotransmitter regulation
2.1.1 γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
GABA is a widely distributed in vertebrates, plants and microorganisms in the non-protein amino acids, is a strong neuroinhibitory amino acids, with sedative, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, lowering blood pressure physiological effects. Wang Liling et al. found that red dates improve sleep with its rich GABA active ingredient.
GABA receptor is a Cl-channel, its activation will lead to the opening of Cl-channel, increase the permeability of cell membrane to Cl-, so that the Cl- flow into the nerve cells caused by the hyperpolarization of the cell membrane, inhibition of neuron cell agitation, so as to achieve the sedative-hypnotic effect. GABAA receptor is also known as γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor, and its endogenous ligand is GABA.
Shah et al. found that Poria cocos acid could elevate the level of Cl- and increase the level of GABAA receptor α- and β-subunit proteins in primary cultured neuronal cells of rat hypothalamus, thus enhancing the hypnotic effect induced by pentobarbital in rats.
Nam et al. found that methanolic extract of longan enhanced the hypnotic effect of pentobarbital in mice, and the mechanism of action was to increase the sensitivity of GABAA receptor to pentobarbital through direct activation of GABAA receptor or increase the expression of subunit of GABAA receptor to improve the sleep effect. It has also been reported in the literature that GABA can improve sleep through the gut-brain axis, brain tissue permeability and its metabolites in vivo.
As a functional ingredient, GABA was recognized as a new food ingredient by the Ministry of Health in 2009, and is now widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
2.1.2 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)
5-HT is an inhibitory neurotransmitter widely found in mammalian tissues, mainly distributed in the pineal gland and hypothalamus, and is involved in the regulation of physiological functions such as nociception, sleep and body temperature, etc. 5-HT is mainly produced by the cells of the nucleus tractus solitarius, and it plays an important role in slow-wave sleep.
Studies have shown that after electrodestruction of the anterior part of the nucleus accumbens, the animals will be insomniac and the slow-wave sleep will be significantly reduced; however, after the injection of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), the sleep will be restored to normal. Tryptophan and 5-HTP are both precursors of 5-HT, and tryptophan is catalyzed by tryptophan hydroxylase to generate 5-HTP, which is then catalyzed by 5-HTP decarboxylase and pyridoxine cofactor enzyme to generate 5-HT. Therefore, the mechanism of improvement of sleep through dietary intake of tryptophan-rich foods such as milk and millet is related to 5-HT.
The literature suggests that 5-HT can promote both arousal and slow-wave sleep, which is related to the activated 5-HT-receptor subtype. Xiao Weihua found that cypress kernel oil can improve sleep through three pathways: 5-HT, Norepinephrine (NE) and Dopamine (DA). The 5-HT pathway may improve sleep by promoting the release of 5-HT from the suprachiasmatic nucleus to promote slow-wave sleep, or by promoting the accelerated release of 5-HT from the infrachiasmatic nucleus to trigger REMS in the NE system of the lower part of the macula densa.
Huang Jiecong et al. found that the Foshan Ning Shen formula (Foshan, Lily, Jujube nut, Poria, and Lotus seed) could improve sleep by increasing the content of 5-HT and up-regulating the expression level of 5-HT1AR protein and mRNA. It was found that sour jujube kernel soup could reduce the time of voluntary activity in rats, and its mechanism of improving sleep was related to the expression of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT2AR.
2.1.3 Norepinephrine (NE) and Dopamine (DA)
NE is a neurotransmitter that regulates the sleep-wake process, and its release peaks in the wake state, begins to decline in the NREMS state, and falls to a minimum in the REMS state. Many drugs used to treat insomnia work by inhibiting NE to affect signaling.
NE is mainly found in the cells of the blue-spot region and plays an important role in fast-wave sleep. If the head of the blue spot is destroyed, the EEG shows sleep-like synchronized slow wave; if the middle and back of the blue spot are destroyed, fast wave sleep disappears. DA is the precursor for synthesizing NE in vivo, and it is generally believed that when DA neurons are excited, arousal increases, and sleep decreases in the animal; conversely, the duration of sleep increases.
The DA pathway can improve the sleep quality of mice by regulating the DA content in the midbrain and inhibiting the activity of DA neurons in the brain. Xiao Weihua found that the NE pathway of cypress seed oil promotes the release of NE in the middle and lower parts of the blue spot, thus promoting REMS; Kang Lu et al. found that gardenia black bean soup and Tianwang Xinxin Tonic Dan can regulate the content of NE and 5-HT, thus improving the sleep of mice.
2.1.4 Glutamic acid (Glu)
Glu is one of the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain and plays an important role in the central nervous system. When a nerve impulse is transmitted to a nerve ending, Glu is released from the presynaptic membrane and rapidly diffuses into the synapse, where it binds to the receptor and opens the Na+ and K+ channel gates, resulting in an excitatory effect.
Literature suggests that Glu has a high affinity for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptor), which can cause repeated opening of NMDA receptor channels, resulting in Ca2+ inward flow and release of intracellular Ca2+ from the cells caused by activation of the Glu receptor, resulting in a sustained increase in the intracellular concentration of Ca2+, which in turn can lead to sleep disorders. Du Chenhui et al. found that sour jujube kernel could significantly reduce the Glu content in rats, and it can be hypothesized that its functional mechanism is related to the regulation of Glu content.
In addition, Zhang Shunbo et al. found that the total saponin of sour jujube kernel could reduce the excitatory neurotoxicity in the brain by down-regulating the content and ratio of two neurotransmitters, Glu and GABA, so as to achieve the effect of improving sleep, which indicated that sour jujube kernel could play a sedative-hypnotic role through the mechanism of Glu and GABA.
GABA is a strong neuroinhibitory amino acid, while Glu is an excitatory neurotransmitter. Therefore, many sleep-improving resources work by improving the excitatory/inhibitory metabolic imbalance of Glu/GABA and regulating the ratio of Glu/GABA.
2.1.5 Melatonin
Melatonin is an amine hormone produced by the pineal gland in mammals and humans that reduces the time of awakening and the time of falling asleep. Melatonin regulates sleep by activating the MT1 and MT2 receptors, with MT1 mainly inhibiting neuronal activity and regulating sleep, and MT2 mainly involved in circadian rhythms. Rodriguez-Naranjo et al. found that melatonin was formed in wine during the fermentation process, and therefore consumption of wine could help improve sleep.
Walnuts are rich in tryptophan and melatonin, and food-borne tryptophan can eventually be converted into melatonin in the body, so walnuts can improve sleep and melatonin mechanism. At present, the physiological function of melatonin, especially as a dietary supplement, has been widely studied at home and abroad, indicating that it has many physiological functions such as improving sleep, regulating jet lag, anti-aging, immune regulation, anti-tumor and so on.
2.1.6 Other neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters such as nitric oxide (NO), acetylcholine (Ach) and histamine can also participate in the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle, and the regulation of their content can improve sleep. Huang Lili et al. found that Sibisan can significantly increase the NO content and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity in the whole brain of mice; increasing the endogenous NO content in an appropriate amount can prolong the sleep time and shorten the sleep latency period of mice, which indicates that Sibisan can play the function of improving sleep by increasing the NO content and enhancing the activity of NOS in an appropriate amount.
Sun Yina et al. found that ginseng, Acorus calamus and ginseng-acorus calamus pairs could prolong the sleep time and shorten the sleep latency period of mice, and there were significant differences in Ach content and acetylcholine transferase (ChAT) activity between the Chinese medicine intervention group and the sleep deprivation group, which indicated that the tranquilizing effect of ginseng-acorus calamus was related to the regulation of Ach content.
2.2 Immunomodulation
When bacterial and viral infections activate the body’s immune function and also promote sleep, its immunomodulatory substances may act on the central nervous system and thus affect the sleep process, and many immune-enhancing agents may also increase sleep.Imeri et al. have shown that interleukin 1 (IL-1) may interact with the central nervous system and thus promote the regulation of normal sleep.2.2.2.3.1 The effects of ginseng-calamus tranquilizers on sleep are not limited by the presence of tumor necrosis factor (TNF).
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is also one of the important cytokines of the immune system, which can be involved in the regulation of NREMS and promote sleep by enhancing the function of the 5-HT system. Wang Wanli found that ginsenoside Rb1 can regulate the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α in the hippocampus and hypothalamus of rats, thus changing the sleep structure, indicating that ginsenoside Rb1 may be related to the regulation of immune cytokines.
2.3 Regulation of intestinal flora
Intestinal flora is an important part of the human gastrointestinal tract and a major participant in the brain-gut axis.Reynolds et al. believe that sleep has a close relationship with intestinal flora, and that a short period of sleep triggers a physiological stress response, and both physiological and psychological stresses can disrupt the normal function of intestinal flora. Gut flora then communicates with the central nervous system through neural, immune and endocrine pathways, thus affecting brain function and behavior.
Jackson et al. found that improving the distribution of gut microorganisms was effective in improving sleep and mood. Chen Tingqiang found that banana oligosaccharides can adjust the composition of intestinal microflora, and that banana’s ability to improve sleep may be related to its ability to improve intestinal flora.
03
Health food and resource application for improving sleep
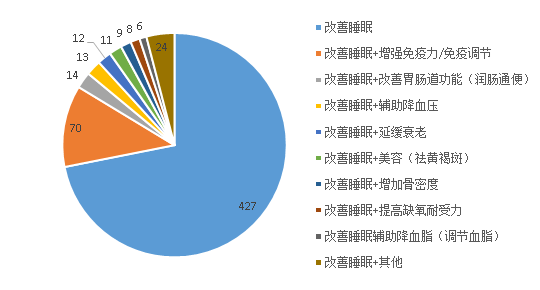
According to the special food information search platform on the website of the State Market Supervision Administration, a total of 594 health food products with sleep-improving function have been approved for registration in China. By analyzing and summarizing the functions and formulas of all the products, it is found that more health food products with sleep-improving function have been approved to enhance immunity, improve the function of the gastrointestinal tract (laxative), and assist in lowering blood pressure, etc. The distribution of the functions is shown in Fig. 1. The distribution of product functions is shown in Figure 1.
The frequency of distribution of functions of health food products with function of improving sleep is preceded by functions of enhancing immunity, improving gastrointestinal function (laxative) and assisting in lowering blood pressure, and it can be hypothesized that improvement of sleep may be more connected with other functions or mechanisms mentioned above. Sleep disorders affect immune function, gastrointestinal function, and inflammatory processes, and alterations in intestinal flora can also affect sleep.
Ali et al. found that sleep quality was highly correlated with intestinal mucosal inflammation, and the prevalence of sleep disorders in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease was as high as 100%; 61% of patients with accompanying sleep disorders in remission had endoscopic histologic inflammation of the mucosa. Nan Wang et al. concluded that nutrients can be metabolized into small molecules, such as GABA and 5-HT, after being absorbed and utilized by intestinal microorganisms, which can be fed back to the central nervous system through the vagus nerve, thus realizing the communication between the intestines and the brain and thus affecting sleep.
Peng Wei et al. also summarized and analyzed that intestinal flora and sleep disorders can interact with each other through the neurological, endocrine, immune and metabolic pathways of the gut-brain axis, for example, intestinal flora can promote sleep by enhancing the ability of IL-1 and TNF-α.
Figure 1: Frequency distribution of sleep-improving health food products can be used to explore the connection between sleep and various subhealth problems from another perspective, as well as the synergistic relationship between sleep-improving and other health functions.
Figure 1 Statistics on the number of health food products for improving sleep
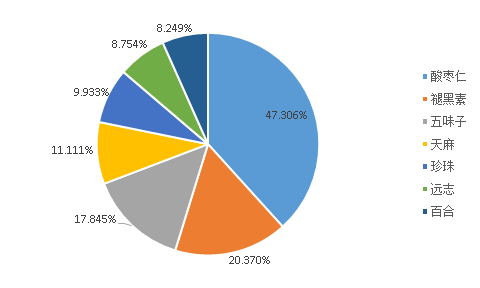
Through the analysis of the raw material formula of the sleep improvement health food, it is found that the most used food and drug resources in the sleep improvement health food are, in order, jujube seed, melatonin, schizandra, asparagus, pearl, farnesol, lily, etc., and most of them are mostly based on the application of compound prescription of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs. Melatonin-based health food products for improving sleep are mainly melatonin single formula and melatonin + vitamins.
Figure 2 shows the results of the frequency analysis of the application of 7 major raw materials in the formula of health food for improving sleep. Figure 2 shows that, except for melatonin, the ones with higher frequency of application in the formula are Chinese herbal medicines, which are, in order, jujube kernel, schizandra chinensis, tianmai, pearl, farzhi, and lily of the valley, and the frequency of use of food and medicine resources reflects, to a certain extent, the value and status of the relevant resources in the application of health food for improving sleep, and the frequency of use indicates that the resources can be used for improving sleep. The frequency of use shows that among the Chinese herbal medicines that can be used in health food, Schisandra chinensis and Tianma are more frequently applied; and sour jujube kernel and lily of the valley have a better application prospect as Chinese herbal medicines of the food and medicine homologous category.
Fig. 2 Distribution of the usage frequency of main raw materials for health food to improve sleep
Conclusion
Sleep disorder is a modern chronic epidemic disease with insidious onset and long duration, which seriously threatens human health. Natural food and medicine resources have better efficacy and higher safety in improving sleep, which is in line with the modern health concept of natural, green and healthy.
Chinese medicine is a great treasure trove, and its results are all derived from real-world practical research with high practical application value. The development of safe and effective health food based on natural food and medicine resources as raw materials, modern food engineering technology, combined with the use of Chinese medicine and modern nutrition theory has a good market prospect.
Modern medical research has found that the functional components of food and medicine resources to improve sleep mainly involve tryptophan, melatonin, Ca, saponins, flavonoids, polysaccharides, etc.; its mechanism of action mainly involves neurotransmitter regulation, immune regulation, intestinal flora adjustment, etc., and there is also a complex interaction between each function and mechanism.
With the in-depth study of the functional components and mechanisms of modern medicine, the diversity of active components and functional mechanisms of food and drug resources for improving sleep will be further analyzed, especially the correlation between improving sleep and enhancing immunity, improving gastrointestinal function, lowering blood pressure and other functions is highly expected.
