Analysis of differences in volatile metabolites in different parts of palm trees based on extensive targeted metabolomics
Ormosia henryi is an evergreen tree of the legume family, mainly distributed in subtropical regions of China, mainly in provinces such as Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Anhui, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Sichuan, Guizhou, and Yunnan. Due to its low seed setting rate, poor natural regeneration ability, and human destruction, it has depleted wild resources and is in an endangered state. It has been listed as a national second-class key protected plant. The palm tree has a tall tree shape, beautiful wood texture, and red seeds can be used as handicrafts; The entire palm tree can be used as medicine, with the effects of promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis, dispelling wind and reducing swelling. The “National Compilation of Chinese Herbal Medicines” records that the palm tree is used externally for treating fractures on the root bark and burns on the leaves. In folk culture, palm wood is often used to make bed boards, which have a calming effect. Therefore, the palm tree is a unique and precious tree species that combines timber, landscape, and medicinal use.
The volatile substances of plants can act on the human body through the skin and respiratory system, stabilizing the central nervous system, regulating emotions, enhancing immunity, and effectively reducing the harm of microorganisms and viruses to the human body. Modern research has shown that palm trees mainly contain 89 volatile components such as aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, esters, olefins, amines, cyclic hydrocarbons, carboxylic acids, and amides. Among them, beneficial components include β – caryophyllene, limonene, β – ionone, etc., which have high utilization value in forest health, pharmaceutical and daily chemical products, and other fields. In addition, research has found that palm extract can act on the central nervous system, and Lu et al. first proposed that palm leaf extract has preliminary antidepressant effects; Zhu studied the antidepressant effect of palm leaf extract using a chronic unpredictable mild stress mouse model and found that it has significant antidepressant effects.
The composition of volatile components in plants is closely related to tissue parts. Tao et al. analyzed the volatile components in different parts of the wood butterfly and found that they all contain a high amount of alcohol substances, and each part has characteristic substances higher than others; Guo et al. found that the volatile components in the golden flower part of honeysuckle are diverse, with acetic acid, 2-methylbutanal, or 3-methylbutanal being common abundant components in each part. At present, there is no report on the comprehensive analysis of metabolite components in the roots, branches, and leaves of palm trees, as well as the differences in composition among the three parts. Numerous studies have shown that the health benefits of plant volatiles are closely related to the concentration of terpenes released, which are also the main components of volatile compounds in palm trees. Therefore, excavating the highly enriched volatile components in palm trees and identifying the concentrated sites of active components (mainly terpenoids) is of great significance for the development and utilization of palm tree resources.
Widely targeted metabolomics technology can detect metabolites and their contents in biological samples with high precision, high throughput, and wide coverage. Through high-throughput detection and data processing, it reveals the changes in metabolites in biological samples and their responses to different environments, periods, and external stimuli. It has been widely applied in plant abiotic stress, disease resistance, processing, and other aspects. This study aims to use extensive targeted metabolomics techniques to identify and analyze volatile components in the roots, branches, and leaves of palm trees, investigate their diversity and enrichment characteristics, and analyze significant differences in metabolites among the three parts. This will lay the foundation for in-depth analysis of metabolic pathways and gene levels in the future, and provide data support for the selection of palm tree resource utilization parts and the development and utilization of non woody resources.




Plants release volatile compounds during their growth process, which can purify the atmosphere, reduce bacterial content in the air, effectively remove harmful substances from the lungs after entering the human body, eliminate fatigue, improve sleep, enhance human immunity, and assist in the treatment of chronic diseases such as cancer and hypertension. Different parts of plants can release volatile components, and the study of volatile metabolites in different parts of plants is helpful for the development and utilization of different parts of plants.
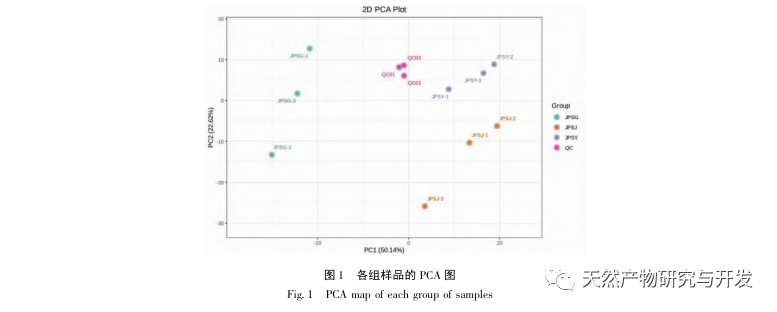
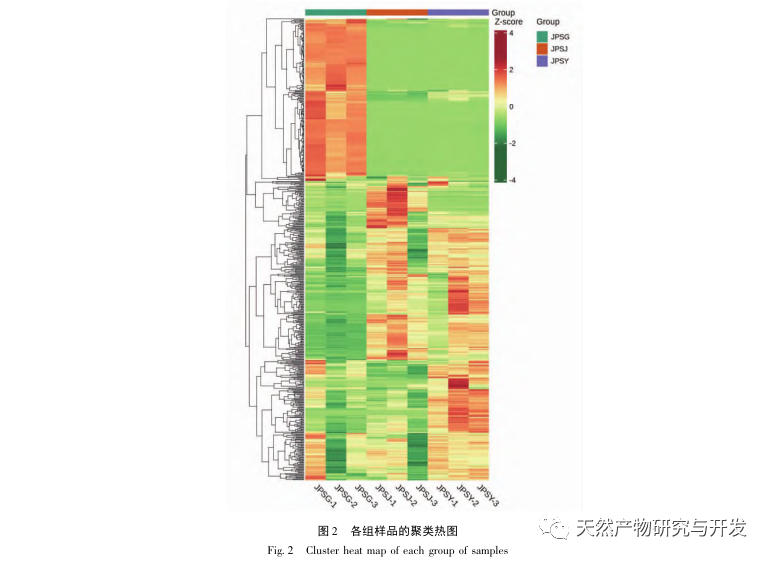
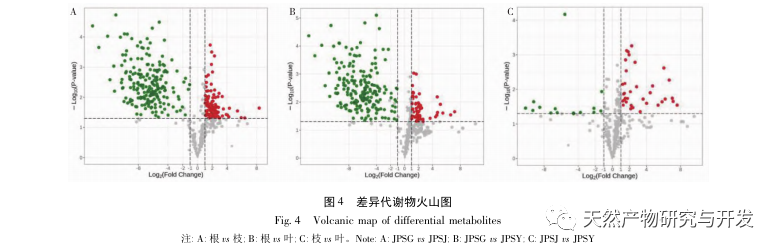
This study conducted metabolomics analysis on volatile metabolites in the roots, branches, and leaves of palm trees, and identified 589 volatile metabolites, divided into 16 categories including terpenes, esters, heterocyclic compounds, and hydrocarbons. From the results of PCA, it can be seen that there are differences between different parts; The clustering results show that most metabolites have relatively high levels in branches and leaves.
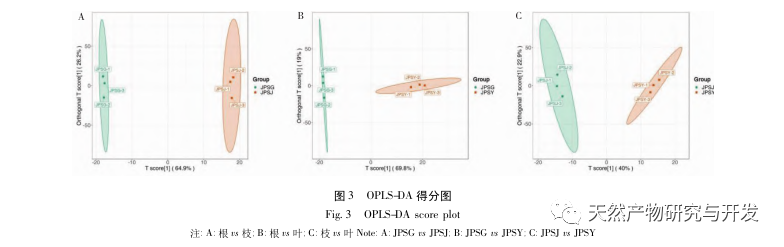
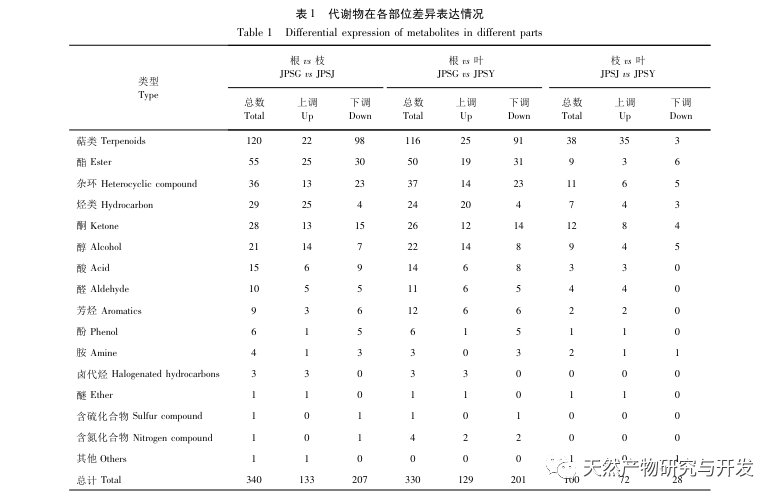
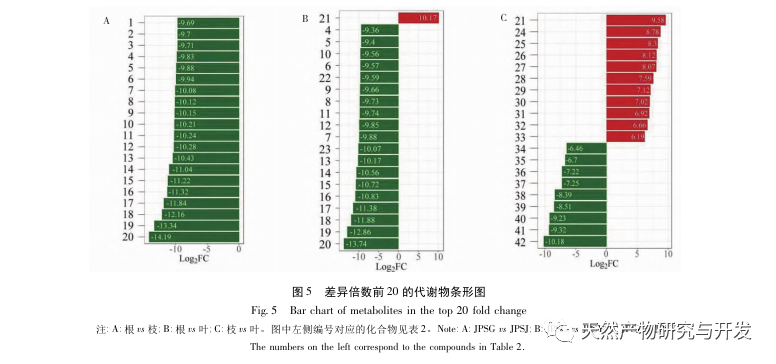
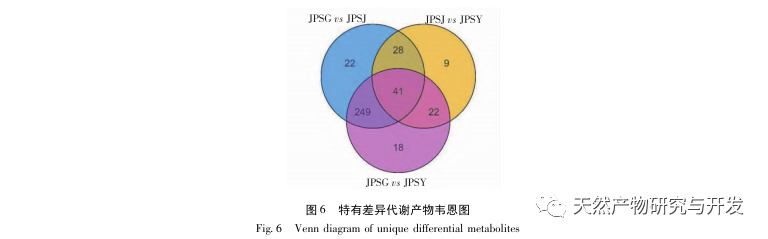
The differential metabolites between roots and branches, roots and leaves are terpenes, esters, heterocyclic compounds, hydrocarbons, and alcohols, among which terpenes, esters, heterocyclic compounds, and downregulated modes are the main ones, with significantly reduced abundance in roots; The upregulation of differential metabolites between hydrocarbons and alcohols is dominant, and these two types of substances accumulate significantly upwards in roots. The differential metabolites between branches and leaves are dominated by upregulated modes, with terpenes being the main upregulated components.
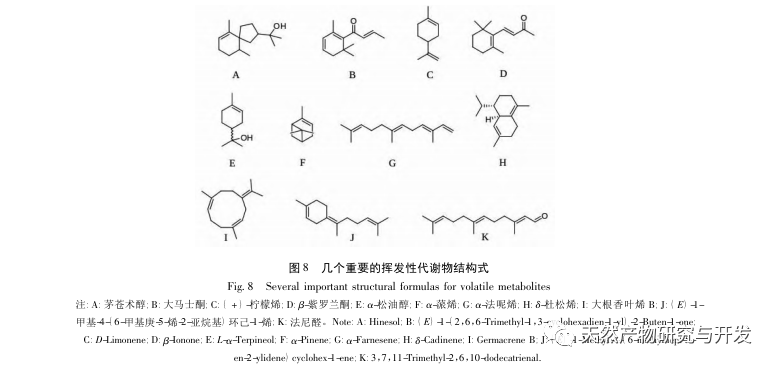
Terpenoids are widely distributed in nature and important volatile compounds of plants. They have anti-tumor, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, sedative and tranquilizing effects, and are widely used in many fields such as essence, spices, daily chemical products, etc. This study identified 162 terpenoid metabolites in palm trees. The accumulation of most terpenoids decreases in roots and accumulates in branches and leaves, with higher levels in leaves. However, the accumulation of terpenoids such as limonene, β – ionone, α – pinene, α – terpineol, magnolol, and cedarol increases. Many of these compounds have been proven to have important pharmacological activities and functional effects, such as limonene, which is one of the important representative components of monotherapy compounds and widely exists in plants such as lemons, oranges, and tangerine peels. It has strong broad-spectrum antibacterial effects and has good inhibitory effects on foodborne pathogens, plant pathogenic fungi, etc; β – ionone is an important spice and a precursor compound for synthesis of retinoic acid, retinol, β – carotene and vitamin A. It has a strong inhibitory effect on breast cancer cells, gastric cancer cells, liver cancer cells, prostate cancer cells, etc; α – Pinene and α – terpineol are the main components of turpentine and intermediates for synthesizing various important organic compounds. They have various activities such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer.
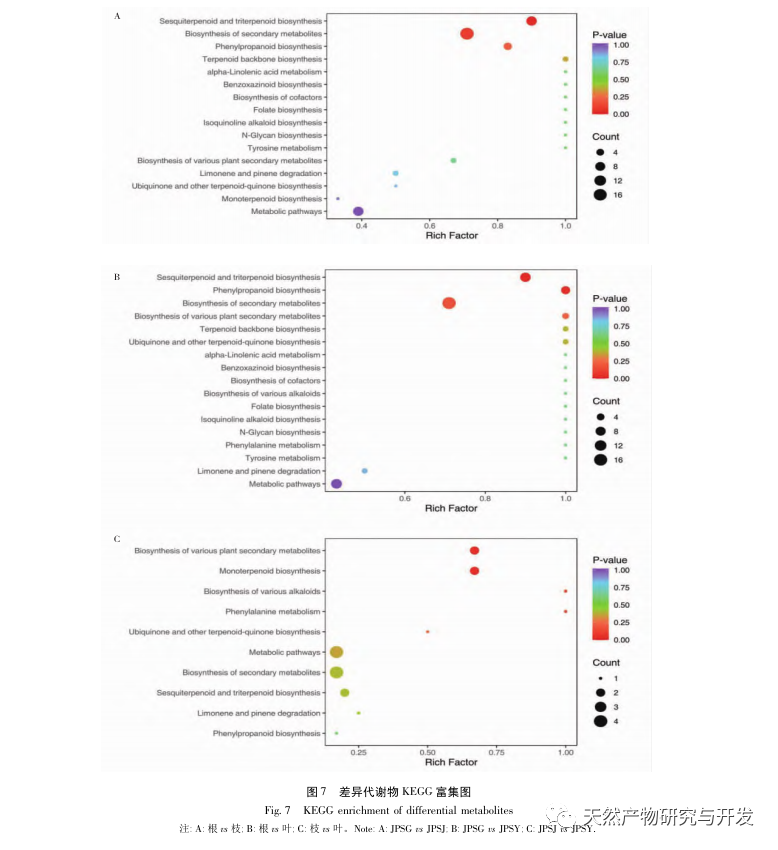
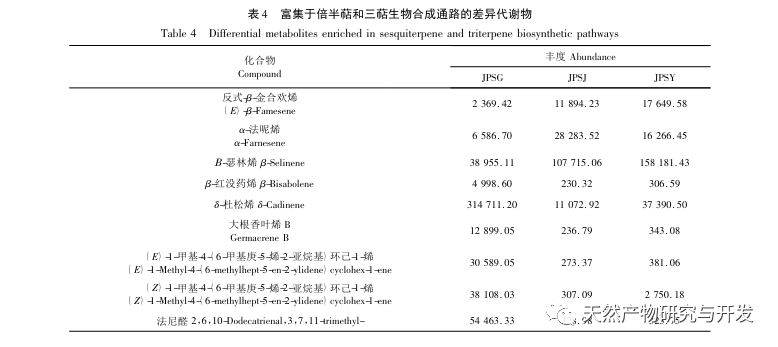
According to the analysis of differential metabolite metabolic pathways, differential metabolites are significantly enriched in the biosynthesis pathways of sesquiterpenes and triterpenes. Nine differential metabolites, including trans – β – farnesene, α – farnesene, β – selenene, and β – myrrh, are involved in this synthetic pathway. The biosynthetic pathways of sesquiterpenes and triterpenes are one of the important pathways for terpenoid synthesis. The differences in terpenoid content in different parts are closely related to the regulation of terpenoid related genes and the catalysis of corresponding enzymes. Further in-depth research is needed on the relevant regulatory genes.
To sum up, the branches and leaves of Anthurium palmatum are rich in volatile metabolites, and the terpenoids with many important activities are up-regulated. The branches and leaves are important parts for the development and utilization of Anthurium palmatum. Based on the volatile metabolites, they can be developed into a series of non wood products such as fragrant powder, incense, essential oil, etc; In addition, in the field of forest health, palm tree can be planted as a tree species to enhance health. It can play a role in the health benefits of volatile metabolites in forest bathing areas, health trails, outdoor leisure places, and other environments.
