Study on the Animal Model of diabetes Kidney Disease with Qi Yin Deficiency Syndrome Based on Intestinal Microflora
At present, most scholars believe that the deficiency of both qi and yin in diabetes kidney disease (DKD) is the basic etiology and pathogenesis of DKD, and its pathological changes are evolved from the deficiency of yin and dryness and heat of thirst, of which the deficiency of both qi and yin is the most fundamental condition, which runs through the course of DKD. This paper takes the deficiency of both qi and yin syndrome as the basic pathogenesis of DKD. On the basis of establishing the model group of diabetes kidney disease rats with high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin (STZ) injection, we use the method of intragastric administration of Qingpi, Zhishi, and Fuzi (Qingpi and Zhishi have the function of soothing the liver and breaking qi, and can dissipate the positive qi when used; Fuzi enters the kidney channel, and can consume the kidney yin when used with high fever) to explore the establishment of animal model of the combination of both qi and yin syndrome of DN and investigate the indicators.
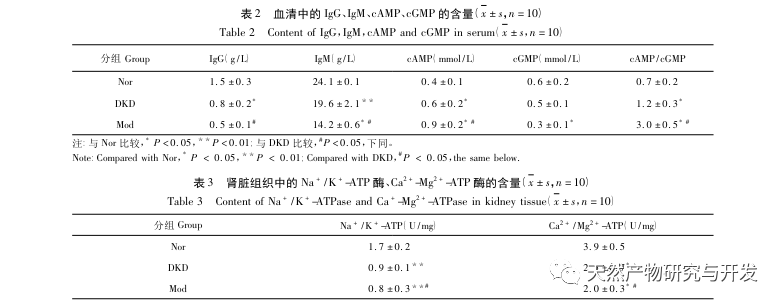
Clinical studies have shown that Qi Yin deficiency can lead to immune decline in DN patients. Changes in the concentrations of human immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin M (IgM) can reflect the immune status of rats. CAMP and cGMP are related to the function of the body’s neuroendocrine system. Some scholars have studied that when patients experience yin-yang imbalance and loss of yin fluid in a state of yin deficiency and internal heat, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), and cAMP/cGMP ratio will be abnormal. Qi deficiency is also related to the energy metabolism of patients. Sodium potassium pump enzyme (Na+/K+- ATP) and calcium magnesium pump enzyme (Ca2+/Mg2+- ATP) are enzymes related to energy metabolism, which can break down adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and release energy. Urine protein is an important test index to judge the health status of patients in the test of diabetes nephropathy. With the help of urine protein, we can distinguish the differences of diabetes nephropathy and provide scientific reference for its diagnosis and treatment.
Research has shown that gut microbiota disruption is associated with the occurrence of DKD, and gut microbiota can regulate kidney function in DKD mouse models. The glomerular filtration rate of DKD patients decreases, and a large amount of metabolic waste such as uric acid and oxalate accumulates in the colon. Changes in the intestinal environment lead to dysbiosis of the gut microbiota. Studies have shown that beneficial bacteria in the gut of DKD patients decrease while pathogenic bacteria increase, resulting in a significant increase in inflammatory factors in the body’s circulation and exacerbating renal inflammatory damage. At present, western medicine DKD model is mostly used in traditional Chinese medicine research on DKD, and the lack of research on diabetes and kidney disease in this field has been limited to a certain extent. Therefore, how to establish animal models that combine disease and syndrome has become a hot topic in the research of animal models in traditional Chinese medicine.


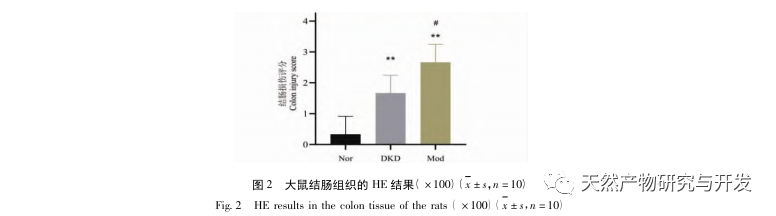
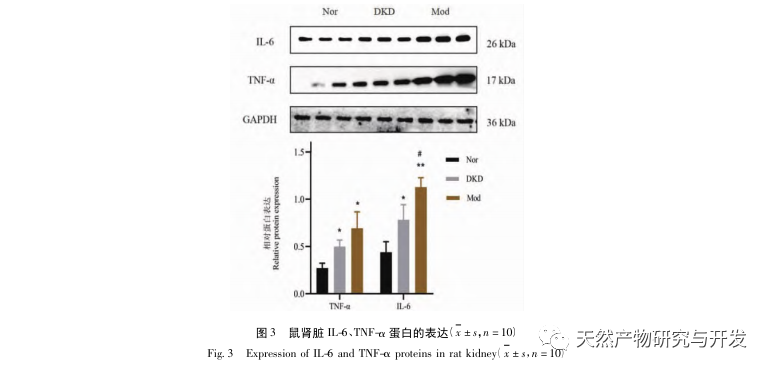
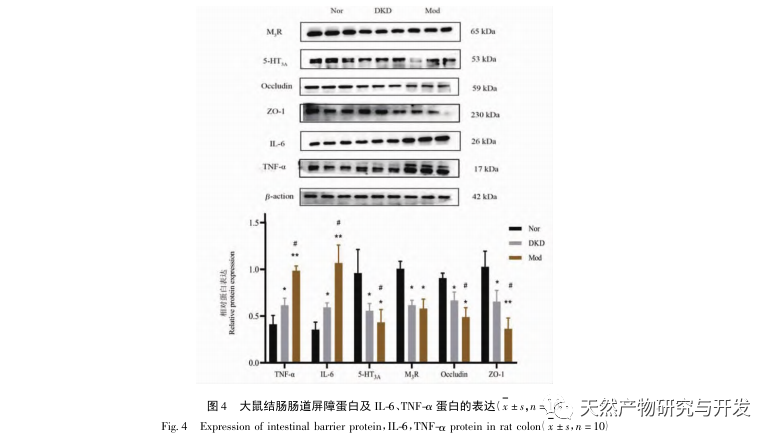
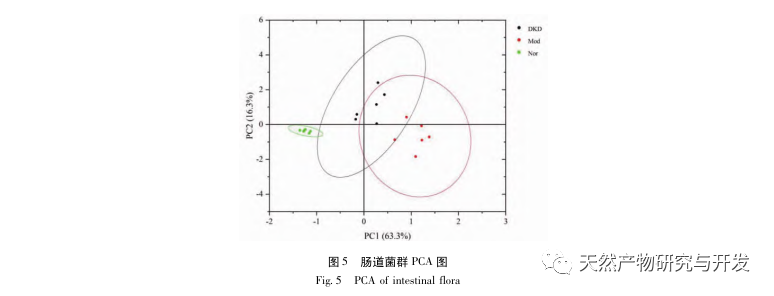
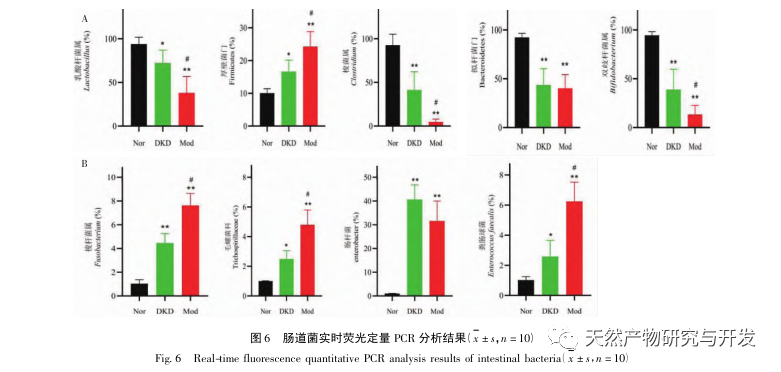
In the continuous development process of diabetes, there will be various complications, the most common of which is the development of DKD. The experimental results showed that the urinary protein levels in DKD rats were significantly higher than those in Nor rats, and the pathological damage to the kidneys and colon in DKD rats was significantly different from that in Nor rats. Therefore, the DKD model was basically successfully established.
The relationship between gut microbiota and DKD Qi Yin deficiency has become one of the hot topics in recent years, and it is believed that the gut and kidneys play a crucial role in immune and inflammatory responses, as well as the intestinal mucosal barrier. If the composition and function of the gut microbiota change, it can lead to damage to the intestinal mucosa, transfer toxins from the body to the bloodstream, induce or exacerbate immune inflammatory reactions, and accelerate the progression of DKD. 160 cases of diabetes nephropathy with deficiency of both qi and yin were studied. The clinical trial showed that Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in DKD patients were significantly lower than those in the control group, while Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus, Yeast and Fusobacterium were higher than those in the control group. The experimental results showed that the content of beneficial bacteria such as Bacteroidetes, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Clostridium in DKD and Mod decreased, while the content of pathogenic bacteria such as Clostridium, Molluscaceae, Escherichia coli, and Enterococcus increased. The results were consistent with previous studies. At the same time, it was found that unlike DKD, the abundance of Firmicutes, Clostridium, Molluscum, and Enterococcus increased significantly in Mod, while the abundance of Lactobacillus, Clostridium, and Bifidobacterium decreased significantly, suggesting that these bacterial genera may be closely related to Qi Yin deficiency syndrome.
Disruption of gut microbiota can lead to increased synthesis of endotoxins in the intestine, exacerbation of inflammatory reactions, disruption of the intestinal barrier, and transfer of harmful substances, thereby exacerbating renal inflammation and accelerating the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). The experimental results showed that the expression of IL-6 and TNF – α proteins in the kidneys and colon was significantly increased, which also confirmed this conclusion. Occludin and ZO-1 proteins are associated with the tight junction status of intestinal tissue. M3R can also protect intestinal mucosal homeostasis by inducing intestinal cytokines, while 5-HT3A can protect the intestinal immune system through the expression of immune system cells. Compared with Nor, the expression of M3R, 5-HT3A, Occludin, and ZO-1 proteins in Mod colon tissue was significantly reduced, indicating that the homeostasis of the intestinal barrier may have been disrupted. This may be caused by changes in the content of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria, ultimately leading to the development of DKD Qi Yin deficiency syndrome.
Qi deficiency is caused by the deficiency of the body’s vital energy. Qi has the functions of promoting, consolidating, transporting and warming. Qi deficiency may lead to the decline of the function of the viscera. Clinical studies show that the contents of urinary microalbumin and immunoglobulin G in patients with diabetes nephropathy are significantly lower than those in healthy patients. The experimental results show that the concentration of IgG and IgM protein in Mod is significantly reduced, indicating that the body immunity of Mod rats is reduced; In the study of 172 patients with DN, it was found that the level of cAMP was positively correlated with the degree of renal injury in patients with diabetes nephropathy. In the experiment, compared with Nor, Mod showed a significant increase in cAMP content and cAMP/cGMP ratio. The cAMP/cGMP ratio appeared abnormally high or low. When cAMP content increased, a large amount of tyrosine hydroxylase was activated, producing a large amount of dopamine to act on the nervous system, affecting human emotions and leading to an increase in excitement. Therefore, virtual heat syndrome often leads to excitement; The study also found that the activities of Na+/K+- ATPase and Ca2+- Mg2+- ATPase in diabetes nephropathy patients were significantly damaged, which led to the damage of cell structure and function, microcirculation block, aggravated renal hypoxia ischemia, increased vascular permeability, and increased urinary protein leakage, leading to further development of kidney disease. The experimental results also showed that the activities of Na+/K+- ATPase and Ca2+- Mg2+- ATPase in Mod kidney were significantly lower than those in Nor and DKD. Chronic kidney disease, due to the long course of disease, led to the depletion of vital energy, and yin fluid damage formed the syndrome of deficiency of both qi and yin, so diabetes kidney disease with deficiency of both qi and yin would lead to energy metabolism of the body. Disorder occurs.
To sum up, by feeding rats with high glucose and high fat for 4 weeks and intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin, aconite, green peel, and fructus aurantii for 8 weeks, the basic syndrome characteristics of diabetes kidney disease with deficiency of both qi and yin can be partially formed. The difference of the symbolic intestinal flora in rats and the measured indicators can reflect the basic characteristics of the disease syndrome combination model to a certain extent, and be used to evaluate the characteristics of diabetes kidney disease model with deficiency of both qi and yin.
