The “Terms and Definitions” of the “General Rules for Compounded Food Additives” GB 26687-2011 (hereinafter referred to as GB 26687) describes compounded food additives as follows: In order to improve the quality of food and facilitate the processing of food, two or more single-species food additives are mixed together by physical methods, with or without the addition of excipients, to form a food additive. It is a food additive made by mixing two or more single species of food additives with or without the addition of excipients in order to improve the quality of food. It can be seen that the formulation of compound food additives is composed of two or more single species of food additives with or without the addition of excipients.
GB 26687 requires that each single species of food additives used in the production of compounded food additives should comply with the “National Standard for Food Safety, Standard for the Use of Food Additives” GB 2760-2014 (hereinafter referred to as GB 2760) and the Ministry of Health’s bulletin, and have a common scope of use.GB 26687 also specifies the attributes and functions of excipients, which are used for the processing of compounded food additives, storage, dissolution and other processes, storage and dissolution and other process purposes and added food ingredients.
Not all single species of food additives meeting the above requirements can be used to formulate the same compounded food additive formula, and some non-compliance phenomena often occur in the process of formula development, as illustrated in the following examples.
Formulation Components of Compounded Food Additives and Their Scope of Use
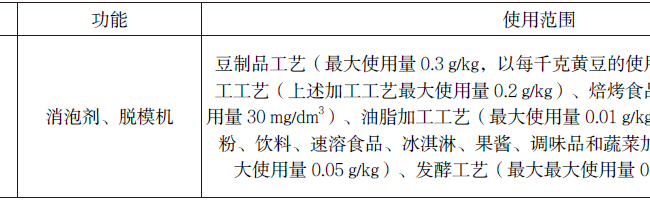
For example, for a compounded food additive, seven substances are used in the formula components, which are four single species of food additives (gelatin, morpholine fatty acid salt (also known as fruit wax), hydrogenated rosin glycerides, ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate) and three processing aids for the food industry (hereinafter referred to as processing aids) (ethanol, polydimethylsiloxane, ammonia).
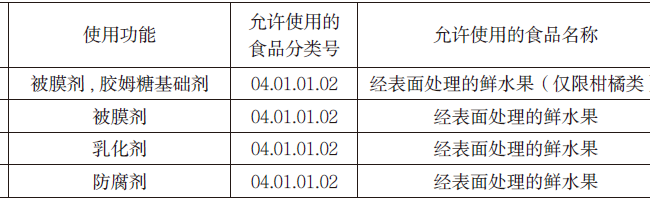
The query of Table A.1 (Allowable Use Species, Scope of Use, and Maximum Use Amount or Residue Amount of Food Additives) of GB 2760 showed that GB 2760 allowed the use of these four single-species food additives and they had a common scope of use, which could be used in surface-treated citrus fresh fruits. See Table 1 for details.
Mechanism of action of each component in the formulation
① granular violet gel (function: film agent), dissolved in food additives ethanol (processing agent, co-solvent) after the emulsion.
② dissolved emulsion-like gelatin and emulsion-like morpholine fatty acid salts ( aka wax ) ( function: film agent ) in the hydrogenated rosin glycerides ( function: emulsifier ) under the action of the emulsification reaction, the formation of a uniformly dispersed emulsion.
③In the process of emulsification of violet gum and morpholine fatty acid salt ( aka fruit wax ), in order to reduce the surface tension, polydimethylsiloxane (processing aids, defoamers) is also used to eliminate foam.
④Ammonia (processing aids, clarifiers) was also added to the emulsification process to help clarify the emulsion, and the emulsion was eventually turned into a solution, which was sprayed onto the surface of citrus fresh fruits by forming a mist through an atomizer.
⑤ In order to prevent this compounded food additive from rotting and deteriorating, ethyl para-hydroxybenzoate (function: preservative) is added to extend the storage period.
Application principles of the components in the formulation
Table 1 Use function, use range and maximum use amount of each single species of food additives in the formulation
Table 2 List of processing aids that require a defined function and scope of use, using polydimethylsiloxane as an example
Table 1 shows that the function of violet gum is as a coating agent, the function of gum gum base and morpholine fatty acid salts (a.k.a. fruit waxes) is as a coating agent, the function of hydrogenated rosin glycerides is as an emulsifying agent, and the function of ethyl para-hydroxybenzoate is as a preservative.
The formula is composed of different functions of a single species of food additives, analyzing the role of the mechanism between the components of the case formulation, the purple gum in the compound food additives to play the function of the periplasmic agent, does not play the function of the gum sugar base agent, and the compound food additives in the terminal food to play the function of the periplasmic agent, sprayed on the exterior of citrus fresh fruits, to play a role in the glazing, to prevent the evaporation of water and preservation of freshness and quality.
According to the naming principle of compound food additives, the compound food additive can be named as a compound coating agent based on the main function it plays in the terminal food.
Among them, ethanol is used to help dissolve gelatin, hydrogenated rosin glycerides are used to help the emulsion disperse evenly, ammonia is used to help clarify the emulsion solution, polydimethylsiloxane is used to help the emulsion defoam, and p-hydroxy products additives (including processing aids), which are not food raw materials, do not satisfy the definition of the attributes of excipients of compounded food additives as defined in GB 26687.
GB 2760 “Terms and Definitions” describes food additives as synthetic or natural substances added to food to improve food quality and color, aroma and taste, as well as for preservation, freshness and processing needs.
The functional descriptions of various food additives in GB 2760 Appendix D “Functional Classes of Food Additives” indicate that food additives (including processing aids) are intended for food products such as confectionery, meat products and flour.
Combined with GB 2760 “Terms and Definitions” and the functional descriptions in Appendix D, it can be seen that the various functions of food additives (including processing aids) only act on food, and the various functions of food additives do not act on food additives (except for flavors for food).
The functions of ethanol, hydrogenated rosin glycerides, ammonia, polydimethylsiloxane, and ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate in the formulation in this case acted on the compounded film coatings and not on the end food product (surface-treated citrus fresh fruit).
The three processing aids [ethanol, dimethicone and ammonia] in the formulation are specified in GB 2760. Checklist C.1 shows that ethanol and ammonia do not need to be limited in terms of their scope of use and residue levels, while Checklist C.2 shows that dimethicone needs to be limited in terms of its function and scope of use. However, GB 2760 Appendix C “Principles for the Use of Processing Auxiliaries” states that processing auxiliaries should be used in the process of food production and processing. The name of Table C.1 is “Can be used in all kinds of food processing, and the residue level need not be limited”.
Ethyl benzoate is used to help preservative of the compound film agent, so it can be seen that the process purpose of ethanol, hydrogenated rosin glyceride, ammonia, polydimethylsiloxane and ethyl para-hydroxybenzoate is to act on the compound film agent.
According to the definition of GB 26687 on the function of excipients added for the purpose of processing, storage and dissolution of compounded food additives, these five food additives (including processing aids) should be categorized as excipients in the formula.
GB 26687 also stipulates that the attributes of excipients in compound food additives can only be food raw materials, not food additives. However, these five substances are the list of food-restricted processing aids”, not ‘the list of processing aids that can be used in the processing of various types of food additives and whose residue levels do not need to be restricted’; the name of Table C.2 is ‘the list of processing aids that need to be specified in terms of function and scope of use’, and the name of this list is ‘the list of processing aids that need to be specified in terms of function and scope of use’, which should be categorized as auxiliaries in this formula. Table C.2 is titled “List of Processing Auxiliaries Requiring Specification of Function and Scope of Use”, and the scope of use of the processing aids in this list is food processing, not the processing of food additives.
Take polydimethylsiloxane as an example, we can see that Table 2 stipulates that the scope of use of polydimethylsiloxane is the food processing process of soybean products, meat products, beer, bakery products, oils and fats, etc., and it is not mentioned that it can be used in the processing process of food additives.
Meanwhile, the function description of processing aids in Appendix D “Food Additives Functional Classes” shows that it is a variety of substances that can help food processing to be carried out smoothly. This shows that processing aids can only be used in food production and processing, and cannot be used in the production and processing of compounded food additives. The processing aids ethanol, ammonia and polydimethylsiloxane used in this formula are all used in the production process of compounded coating agent, which is beyond the scope of use of processing aids.
In summary, although the formulation components of the compound coating agent comply with the provisions of GB 2760 and have a common scope of use, they can act in the surface treatment of citrus fresh fruits. However, it does not meet the requirements of GB 26687 on the “terminology and definitions” of compound food additives; GB 2760 on the “terminology and definitions” of food additives; GB 2760 on the functional categories of food additives; GB 2760 on the functional categories of food additives; and GB 2760 on the functional categories of food additives. It does not meet the requirements of GB 2760 for the functional categories of food additives; it does not meet the requirements of GB 2760 for the scope of use of processing aids.