Study on secondary metabolites of marine fungus Aspergillus terreus
In recent years, marine natural products have attracted the attention of chemists and biologists around the world. More than 16000 marine natural products have been isolated and identified from marine organisms, and marine microorganisms are considered a valuable source for producing new antibiotics, anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory drugs. Marine fungi, especially those related to marine algae, sponges, invertebrates, and sediments, are effective producers of bioactive secondary metabolites. Due to their characteristics in temperature, nutrients, competition, and salinity, they form specific secondary metabolic pathways compared to terrestrial fungi and can produce abundant new active natural products. These novel structural secondary metabolites play an important role in drug discovery.
Aspergillus fungi are one of the most widely distributed fungal groups on Earth, comprising over 300-350 species of fungi. At present, various structural types of secondary metabolites have been discovered in Aspergillus fungi, such as alkaloids, terpenes, lignin, steroids, polyketones, cyclic peptides, etc., and they have various biological activities such as anti-tumor, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, etc. Aspergillus terreus is widely present in nature and is often isolated from the rhizosphere of soil, decaying organic matter, and marine environments. In addition to producing the lipid-lowering drug lovastatin and its intermediates, Aspergillus terreus can also produce various economically significant secondary metabolites. The same bacterium, due to different sources and environments, produces different metabolites. In this study, a strain of Aspergillus terreus isolated from the sea mud of the the Nansha Islands was selected as the research object, and the rice solid medium was used for large-scale fermentation. Its secondary metabolites were isolated, purified and identified, and the in vitro neuroprotective activity of PC12 cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation was evaluated, in order to find metabolites with novel structure and good activity, and further enrich the secondary metabolites of Aspergillus fungi.
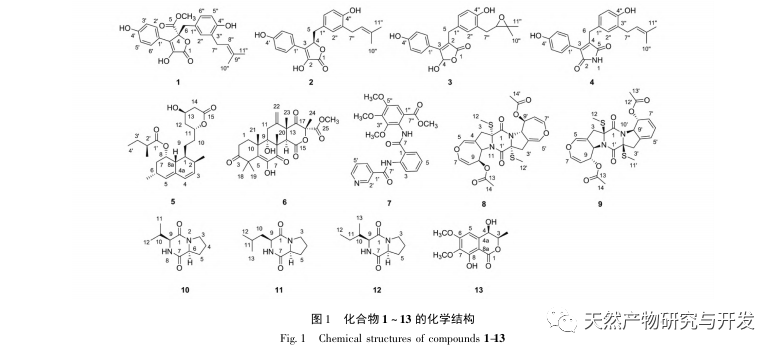
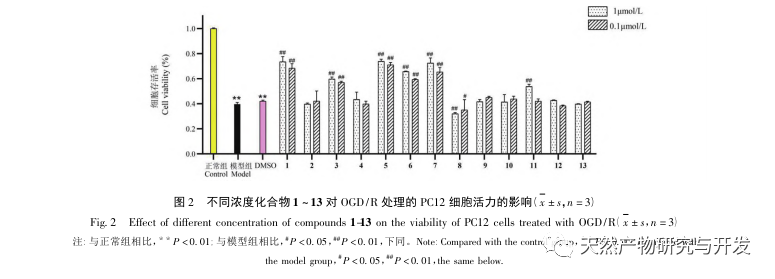
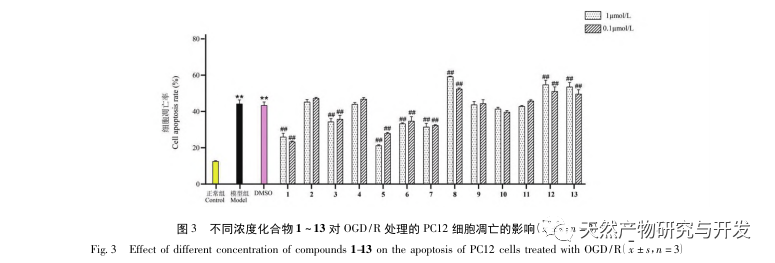 In this study, the secondary metabolites of marine source Aspergillus terreus were separated and purified by macroporous adsorption resin, silica gel, gel column chromatography and semi preparative liquid methods. Thirteen compounds were isolated and identified, among which compounds 1 to 3 were γ – butyrolactone derivatives, compound 4 was a class of marine natural alkaloid maleimide (2,5-pyrrolidone) derivatives, compound 5 was statin drug lovastatin, compound 6 was terpene compound, and compound 7 was methyl benzoate compound. Its NMR data were reported for the first time. Compounds 8 to 12 were five diketopiperazines, among which compounds 8 and 9 were thiodiketopiperazine, and compound 13 It is a benzopyranone compound. Preliminary in vitro neuroprotective activity tests showed that compounds 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 can significantly reduce cell damage caused by oxidative stress. This study investigated the neuroprotective activity of secondary metabolites and individual compounds in Aspergillus oryzae rice fermentation products, providing a scientific reference for further exploration of the chemical diversity of Aspergillus oryzae secondary metabolites in the future.
In this study, the secondary metabolites of marine source Aspergillus terreus were separated and purified by macroporous adsorption resin, silica gel, gel column chromatography and semi preparative liquid methods. Thirteen compounds were isolated and identified, among which compounds 1 to 3 were γ – butyrolactone derivatives, compound 4 was a class of marine natural alkaloid maleimide (2,5-pyrrolidone) derivatives, compound 5 was statin drug lovastatin, compound 6 was terpene compound, and compound 7 was methyl benzoate compound. Its NMR data were reported for the first time. Compounds 8 to 12 were five diketopiperazines, among which compounds 8 and 9 were thiodiketopiperazine, and compound 13 It is a benzopyranone compound. Preliminary in vitro neuroprotective activity tests showed that compounds 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 can significantly reduce cell damage caused by oxidative stress. This study investigated the neuroprotective activity of secondary metabolites and individual compounds in Aspergillus oryzae rice fermentation products, providing a scientific reference for further exploration of the chemical diversity of Aspergillus oryzae secondary metabolites in the future.
