Study on the Quality Differences between Zhejiang Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria Based on HPLC-ELSD Fingerprint and Multi component Quantification
Fritillaria thunbergii Miq., a dried bulb of the lily family plant Fritillaria thunbergii Miq., is listed as the top of the “Eight Flavors of Zhejiang” and has been included in various editions of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as the “Chinese Pharmacopoeia”). It is harvested, washed, moistened, cut into thick slices, and dried when the plant withers in early summer; Xi called it “Zhe Bei Pian”. Zhejiang Fritillaria has the functions of clearing heat, resolving phlegm, relieving cough, detoxifying and dispersing nodules, and eliminating carbuncles. It is clinically used to treat wind heat, phlegm fire cough, lung abscess, breast abscess, and sores.
Hubei Fritillaria is a dried bulb of Fritillaria hupehensis Hsiao et K.C. Hsiao, a plant in the lily family. Its main functions are clearing heat and phlegm, relieving cough, and dispersing nodules. It is commonly used in clinical practice to treat symptoms such as lung heat cough and phlegm cough. Both Zhejiang Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria belong to the genus Fritillaria and can be used as traditional Chinese medicine for medicinal purposes; The active ingredients of both are alkaloids, but their types are different. The main active ingredients of Zhejiang Fritillaria include Fritillaria A, Fritillaria B, IsoFritillaria A, etc. The main active ingredients of Hubei Fritillaria include Fritillaria A, Fritillaria B, Hubeijia, Hubeiyi, Hubeixin, etc; Therefore, there are certain differences in the pharmacological effects between Zhejiang Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria. In the 2020 Chinese Pharmacopoeia, under the category of medicinal herbs, Zhejiang Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria were separately listed, indicating that there are certain differences between the two medicinal herbs.
Due to the wide variety and price difference of Fritillaria species in the market, there is a phenomenon of mutual substitution or substitution of fake Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria. Due to limitations in morphological, microscopic, and physicochemical identification, it is not possible to effectively demonstrate the similarities and differences in the quality of the two medicinal materials. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a more specific and accurate method to effectively distinguish and differentiate between the two.
The 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia specifies that the content determination indicators for Fritillaria thunbergii are Fritillaria A and Fritillaria B, while the content determination indicator for Fritillaria thunbergii in Hubei Province selects Fritillaria B, and the content limit of Fritillaria thunbergii B in Hubei Province is significantly higher than the total limit of Fritillaria thunbergii A and Fritillaria thunbergii B in Zhejiang Province, providing objective conditions for the adulteration and use of Fritillaria thunbergii. Faced with the complex chemical composition system of traditional Chinese medicine, using a single quantitative model is no longer sufficient to meet the quality control needs of modern Chinese medicine. At present, there are few reports on the difference in the content of active ingredients between the two types of Fritillaria. Therefore, in this study, HPLC-ELSD method was used to establish fingerprint spectra of Fritillariae Thunbergii Bulbus (FTB) and Fritillariae Hupehensis Bulbus (FHB) in Fritillariae thunbergii and Fritillariae Hupehensis Bulbus in Hubei, respectively. At the same time, five identical alkaloid components were determined, and a comprehensive comparative study was conducted on Fritillariae thunbergii and Hubei from both qualitative and quantitative aspects, providing reference for the identification and quality evaluation of the two medicinal materials.

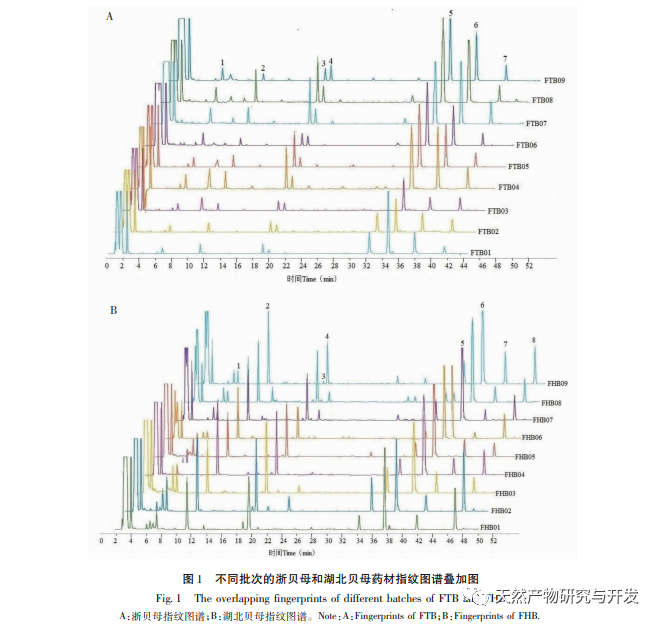


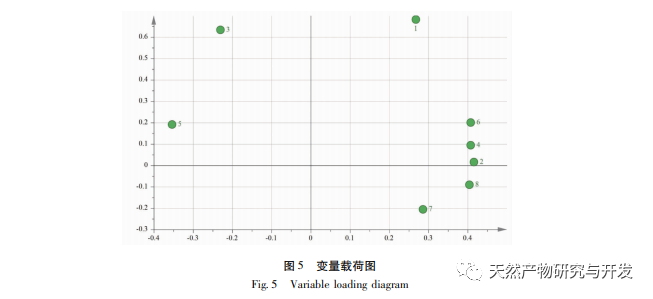
In the establishment and application of fingerprint spectra, HPLC-ELSD fingerprint spectra of Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii were established based on the characteristics of alkaloid components in Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii. The similarity evaluation results showed that the fingerprint spectra of the same Fritillaria thunbergii were highly similar. Therefore, fingerprint spectra can be used as common features for quality control research of Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii. By comparing the differences between the fingerprint spectra of the two types of Fritillaria, it can be seen that the fingerprint spectrum of Fritillaria thunbergii clearly lacks the peak of the Hubeijia pigment spectrum or the Hubeijia pigment content is extremely low, making it difficult to detect in Fritillaria thunbergii. Therefore, Hubeijia can serve as a differential biomarker for distinguishing and differentiating between two types of Fritillaria, Zhejiang Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria.
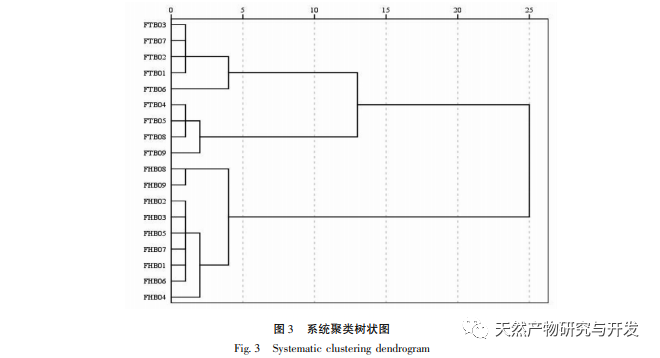
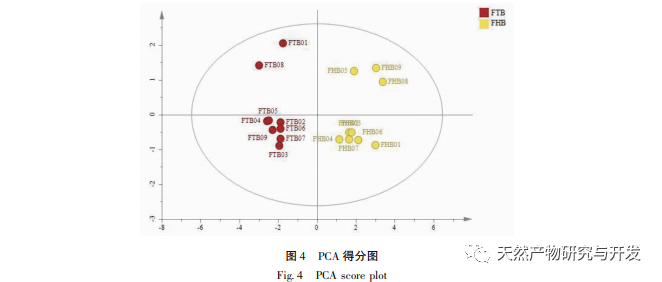
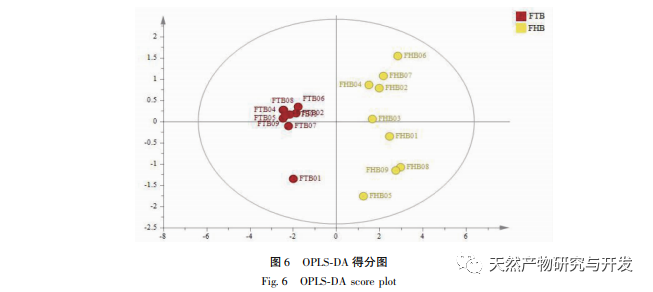
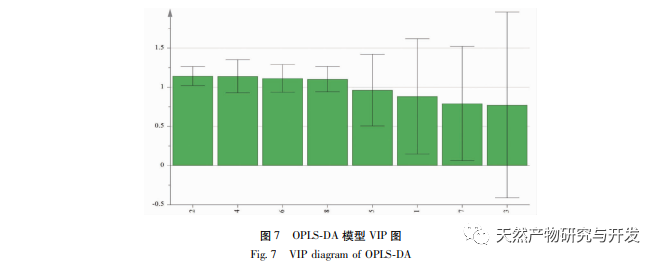
Using the peak area of the common peak as a variable, HCA, PCA, and OPLS-DA analyses were conducted separately. The results of HCA and PCA were able to effectively distinguish and differentiate between Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii, indicating that the combination of fingerprint, HCA, or PCA is an effective method for identifying Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii. To further clarify the differences in chemical composition between the two types of Fritillaria thunbergii, OPLS-DA analysis was used to identify four differential biomarkers. According to the significance of the differences, they were sorted as Fritillaria thunbergii>Peak 4>Berberine A>Berberine B, indicating that there are significant differences in the content of the above components between the two types of Fritillaria thunbergii. This difference is partly due to the differences in the medicinal materials themselves. Different origins may also be closely related to factors such as the planting environment and growth cycle of medicinal herbs.
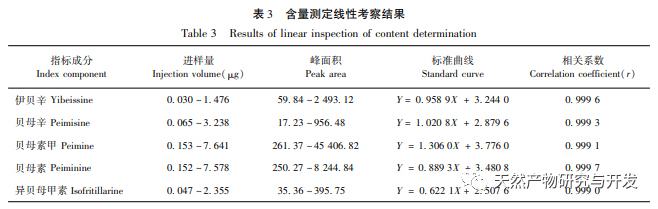
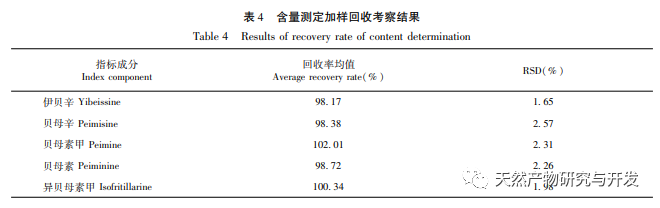
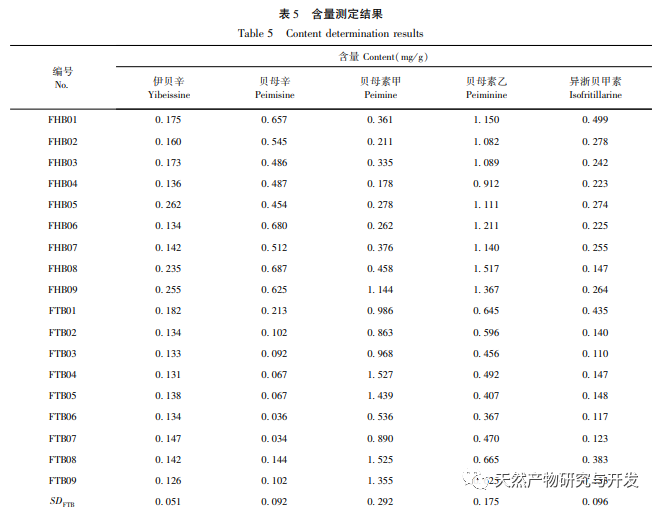
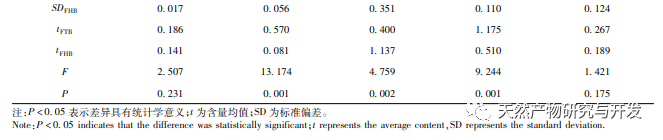
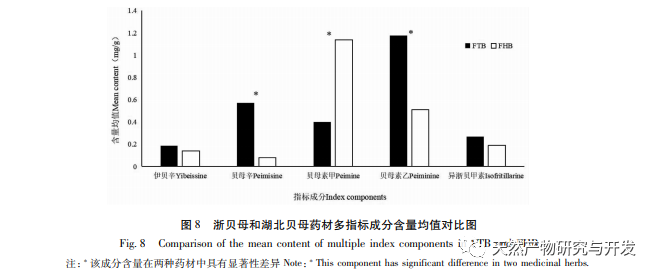
In terms of the selection of content determination indicators, the alkaloids contained in Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii are mainly divided into steroid alkaloids and steroid alkaloids. Research has found that alkaloids have various pharmacological activities such as expectorant, cough suppressant, asthma relieving, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor effects, which are consistent with the functional indications of Zhejiang Fritillaria and Hubei Fritillaria. Five identical alkaloids were identified from the HPLC-ELSD fingerprint spectra of Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii. The content determination results showed that, except for the content difference of ibuprofen, the other four components of Fritillaria thunbergii, Berberine A, Berberine B, and IsoBerberine A had significant differences in content. Among them, the content of Berberine A in Fritillaria thunbergii was significantly higher than that in Fritillaria thunbergii, while the content of Berberine A, Berberine B, and IsoBerberine A was significantly lower than that in Fritillaria thunbergii. Therefore, by measuring the content of Berberine A, Berberine A, Berberine B, and IsoBerberine A, it is possible to distinguish between Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii. The research results obtained are basically consistent with the OPLS-DA analysis results. There are literature reports that the differences in the content and proportion of alkaloids may be an important factor leading to the differences in cough, phlegm, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory effects between the two types of Fritillaria thunbergii. Simultaneous determination of multiple alkaloids is of great significance for the quality control and evaluation of clinically oriented traditional Chinese medicines, Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii. Therefore, it is recommended to increase the determination of berberine and isoberberine in the quality control of Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii medicinal materials.
In summary, this study established HPLC-ELSD fingerprinting methods for Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii, and simultaneously determined the content of five alkaloids, which can provide important references for the identification and quality control of Fritillaria thunbergii and Fritillaria thunbergii medicinal materials.
