Establishment of UPLC fingerprint spectrum and determination of indicator components for the medicinal herb of Verbena officinalis
Verbena officinalis L., a plant in the Verbenaceae family, is the dried aboveground part of the plant. It has the effects of promoting blood circulation, dispersing blood stasis, detoxification, diuresis, reducing yellowing, and intercepting malaria. Chemical composition studies have shown that verbena contains volatile oils, iridoids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, and other components, which have various pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, analgesic, cough and asthma relief, anti myocardial ischemia, and cerebral ischemia. The 2020 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, Part One, uses oleanolic acid and ursolic acid as the content indicators for the medicinal herb of verbena, but its specificity is not strong. Moreover, traditional decoctions are used in traditional Chinese medicine, and lipophilic components such as oleanolic acid and ursolic acid are used as content indicators. It is worth discussing whether this helps with the quality control of medicinal herbs. There are literature reports that by measuring the high content of cyclohexene ether terpenoid glycosides, such as verbascoside and verbascoside, as well as the phenylpropanoid glycoside, verbascoside, in verbascoside, it has certain specificity and positive significance for ensuring the clinical efficacy of verbascoside. The above content indicators have been used in the quality control research of verbascoside standard decoction and formula granules. Fingerprint spectra have also been used for quality control of verbascoside, but the identification of chemical components is mainly focused on verbascoside, verbascoside, and verbascoside. There have been no reports on the study of other water-soluble components. In this study, the establishment of a fingerprint spectrum of verbena herb combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry identification, as well as the establishment of content determination methods for four active ingredients, namely verbascoside, verbascoside, verbascoside, and isoverbascoside, were used to provide reference for the overall quality control of verbena herb.

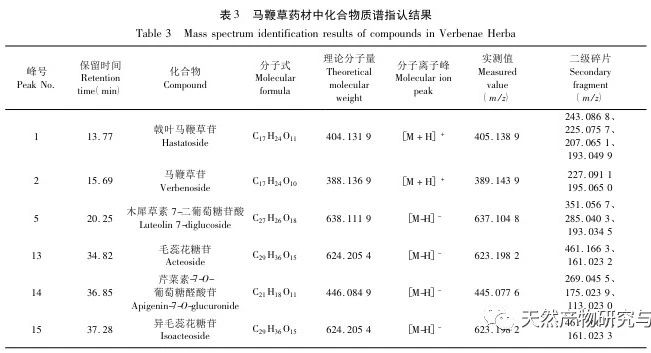
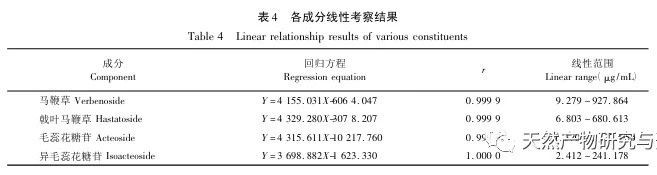
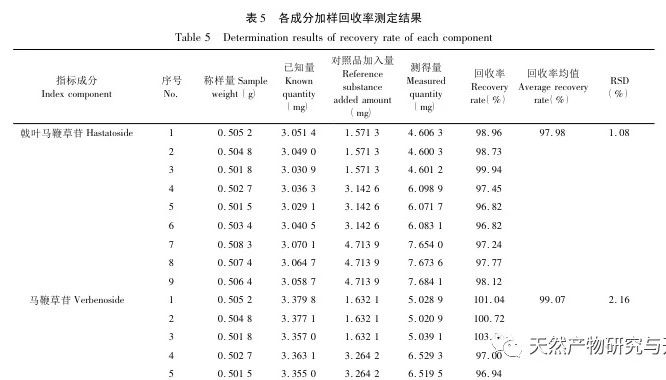
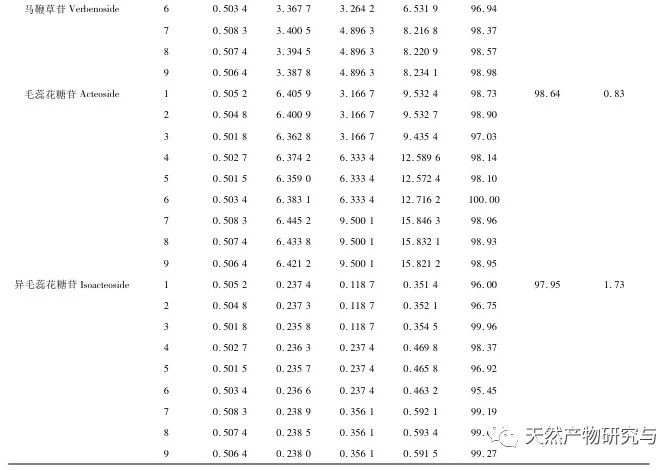
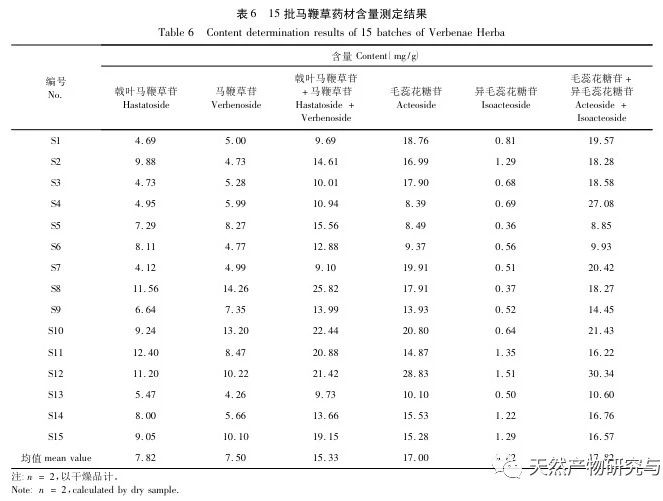
Selection of content indicators. According to literature reports and our previous research, verbascoside can be converted into isoverbascoside under certain conditions. Both verbascoside and isoverbascoside have antioxidant, anti hemolytic, anti angiotensinase activity, blood pressure lowering, and immune function enhancing effects. This indicates that verbascoside and isoverbascoside are of great significance for the quality control and evaluation of verbena. Therefore, based on existing research, our company will increase the determination of isoverbascoside, in order to provide reference for the quality control of Chinese herbal preparations containing verbena. Chemical composition studies have shown that both verbascoside and verbascoside are iridoid glycosides. verbascoside, also known as 5-hydroxyverbascoside, has an additional hydroxyl group at carbon position 5 compared to verbascoside. The chemical structures of the two components are similar, and their absorption curves in UV visible 3D spectra are basically the same. Therefore, it is recommended to combine the two components for detection and calculate the total amount of the two components. In this study, four methods for determining the content of active ingredients were established. The preparation method of the test solution was consistent with the fingerprint spectrum, but the chromatographic conditions were established separately and were not consistent with the fingerprint spectrum. The main considerations were the separation degree, purity, and method reproducibility of the indicator components. The content determination results showed that there were certain differences in the content of verbascoside, verbascoside, verbascoside, and isoverbascoside in different production areas of verbena herb. Even within the same production area, there were also differences in the content of different batches of herbs, which were mainly related to differences in the harvesting time, processing methods, storage methods, and storage time of the herbs. In addition, our company found in our research that there are significant differences in the content of verbascoside, verbascoside, verbascoside, and isoverbascoside in different medicinal parts of the same verbena herb. Among them, the content of verbascoside, verbascoside, verbascoside, and isoverbascoside in the flowers and leaves is significantly higher than that in the stems. Therefore, strictly controlling the harvesting time of medicinal herbs and ensuring the ratio of flowers and leaves in the herbs are of great significance for the quality control of verbena medicinal herbs.
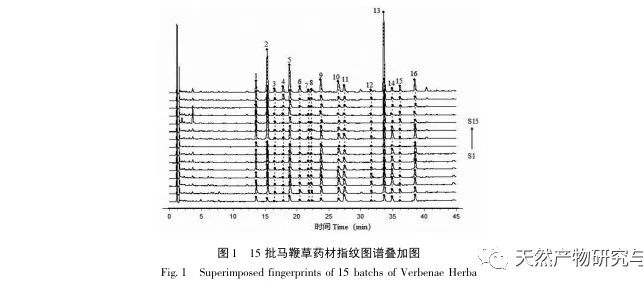
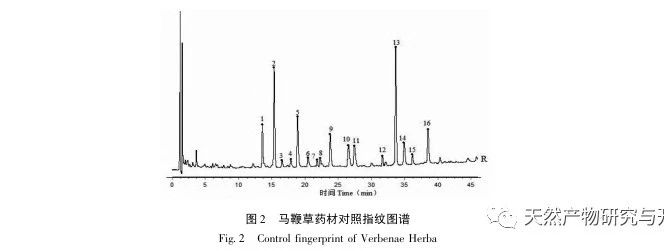
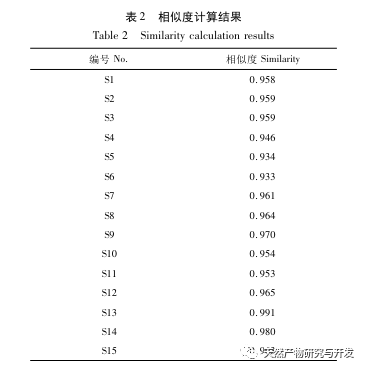
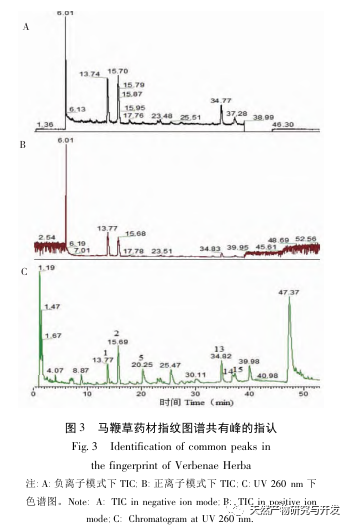
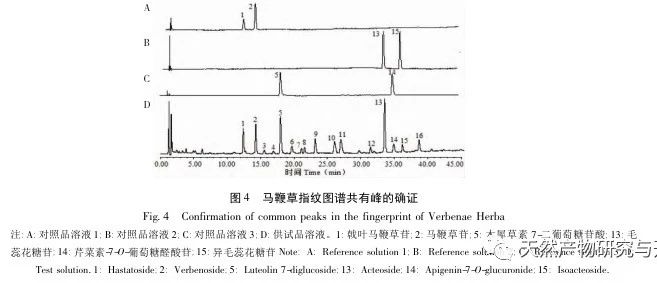
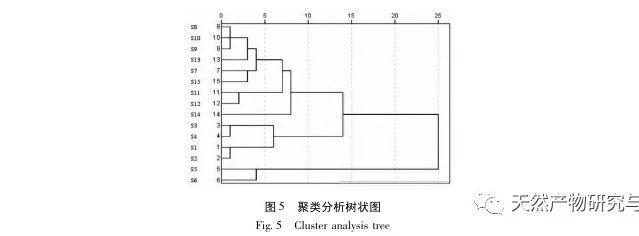
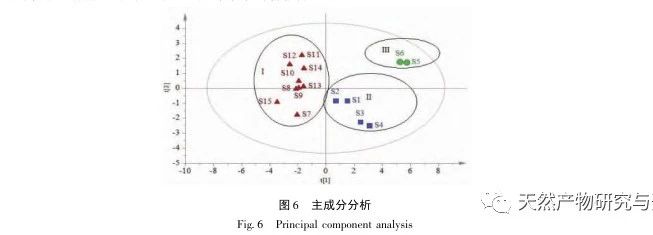
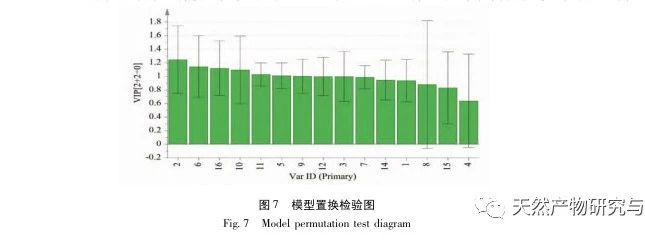
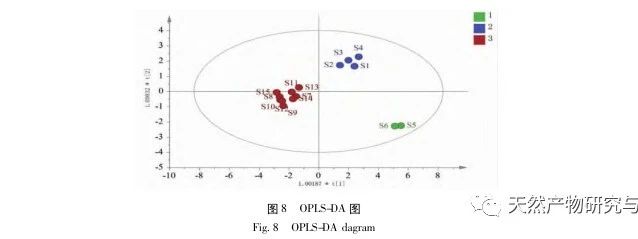
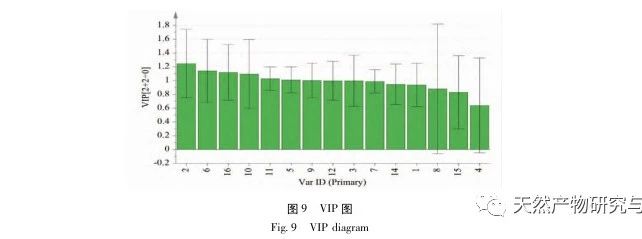
Research on fingerprint spectra. The UPLC method was used to establish the fingerprint spectrum of Herba Verbena. The chromatographic conditions of the fingerprint spectrum and the preparation method of the test solution were systematically investigated. The similarity calculation results showed that the similarity of the fingerprint spectra of 15 batches of medicinal materials was above 0.9, and the overall similarity was high, which can be used for the identification and quality control of Herba Verbena. By using high-resolution mass spectrometry to identify common peaks, three types of active ingredients were identified, namely iridoid glycosides, phenylpropanoid glycosides, and flavonoids. For the first time, fingerprint spectra were used to characterize the three types of active ingredients in verbena, and for the first time, isoverbascoside, luteolin 7-diglucoside, and apigenin 7-O-glucuronide were identified from the fingerprint spectrum of verbena, better reflecting the overall integrity and characteristics of verbena. Using the relative peak area of common peaks as variables, cluster analysis and principal component analysis both classified the 15 batches of medicinal materials into three categories. Among them, the medicinal materials from Henan, Jiangsu, and Guizhou had similar chemical composition ratios. OPLS-DA found seven chromatographic peaks with significant differences in peak ratios, namely peaks 2, 6, 16, 10, 11, 5, and 9. These differences may be related to differences in the harvesting time and processing methods of the medicinal materials.
In summary, this method can effectively analyze the quality differences of Chinese medicinal herbs from different origins, providing a reference for the evaluation of the quality of Chinese medicinal herbs from different origins.
