Chemical composition analysis and preliminary exploration of the mechanism of promoting melanin production in the alcohol extract of Fructus Psorale by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
Vitiligo is a common clinical localized depigmentation skin disease, with a prevalence rate of about 0.5%~2% worldwide. It is easy to diagnose and difficult to treat, with a high incidence rate and a long course of disease, which has a negative impact on the physical and mental health of patients. Psoralea is a dried and mature fruit of the legume plant Psoralea corylifolia L. It is mainly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat erectile dysfunction, nocturnal emissions, lower back and knee pain, and wheezing caused by kidney yang deficiency. It can also be used topically to treat vitiligo and alopecia areata. Not only does our country have a history of using psoriasis to treat vitiligo, but there are also records in Southeast Asian countries such as Japan, South Korea, India, etc. (known as “Babchi seeds”, “Bakuchi powder”, “Bakuchiol”, etc.). There are also various dosage forms for treating vitiligo with psoralen, including decoctions, tinctures, and injections (National Medical Standard Z41022361). Although there are many literature records on the treatment of vitiligo with psoralen, its mechanism of action and material basis for treating vitiligo are not fully understood. Therefore, this article uses ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) technology to study the chemical composition of Psoraleae Fructus alcohol extract (PFE); By conducting experiments on zebrafish to promote melanin production, the effect of PFE on melanin production was investigated. Real time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT PCR) was used to detect the mRNA expression levels of tyrosinase (Tyr), tyrosinase related protein 1 (Tyrp1), and tyrosinase related protein 2 (Tyrp2) in B16-F10 mouse melanoma cells treated with PFE, psoralen (PSO), and isosoralen (IPSO). This study aims to further explore the potential therapeutic effects of PFE on white melanoma cells. The active compounds and targets of vitiligo lay the foundation.
Vitiligo is a locally white spot on the skin caused by damage to melanocytes, which is widely recognized as a difficult and stubborn disease. So far, its etiology and pathogenesis have not been fully understood. Research has shown that skin pigmentation is closely related to the three major metabolic processes of melanocytes in the epidermis, including melanocyte proliferation, synthesis and activation of TYR, and melanin synthesis, as well as the pathway of melanin transfer from melanosomes to keratinocytes. Melanin synthesis is a complex reaction that occurs within melanocytes and is regulated by multiple factors. TYR is the rate limiting enzyme in melanin synthesis, and its activity is regulated by TYRP1 and TYRP2, making it a key regulatory factor in melanin synthesis.
Based on the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of vitiligo, researchers have developed a series of animal models in recent years, such as chemical depigmentation agent induction, melanocyte stress induction, immune induction, exogenous T cell induction, transgenic, melanocyte detachment induction, etc. Mice are the main choice for animals. According to research, 71.4% of human protein coding genes and 82% of pathogenic genes are directly homologous to zebrafish, including many genes related to human skin diseases. Zebrafish larvae are transparent, and the overall and cellular structure of their skin is similar to that of mammalian skin. They have similar melanocytes and melanosomes to humans, and melanocytes are easily observed during individual development. This makes zebrafish a widely used animal model for pigmentation research, including diseases such as vitiligo and melanoma. However, as vitiligo is a complex multifactorial disease, there is currently no animal model that can fully simulate the occurrence and development process of human vitiligo. Therefore, animal models of vitiligo still need to be further explored.
PTU is an inhibitor of TYR, widely used to block pigmentation and improve optical transparency in zebrafish embryos. Studies have shown that using PTU solution instead of fish water after zebrafish gut embryogenesis (5.5 hpf) can effectively inhibit melanin production and maintain zebrafish transparency. The results of this experiment indicate that after treating zebrafish with PFE for 18 hours after PTU modeling, compared with the group treated with embryo culture medium, PFE can accelerate the regeneration of melanin in the eyes, abdomen, spine, and tail of zebrafish fry, which is consistent with the clinical application of psoralen in the treatment of vitiligo.

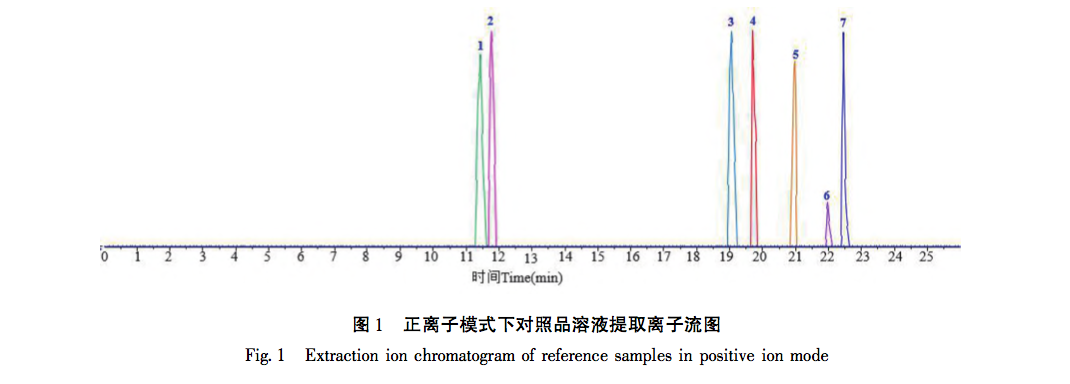
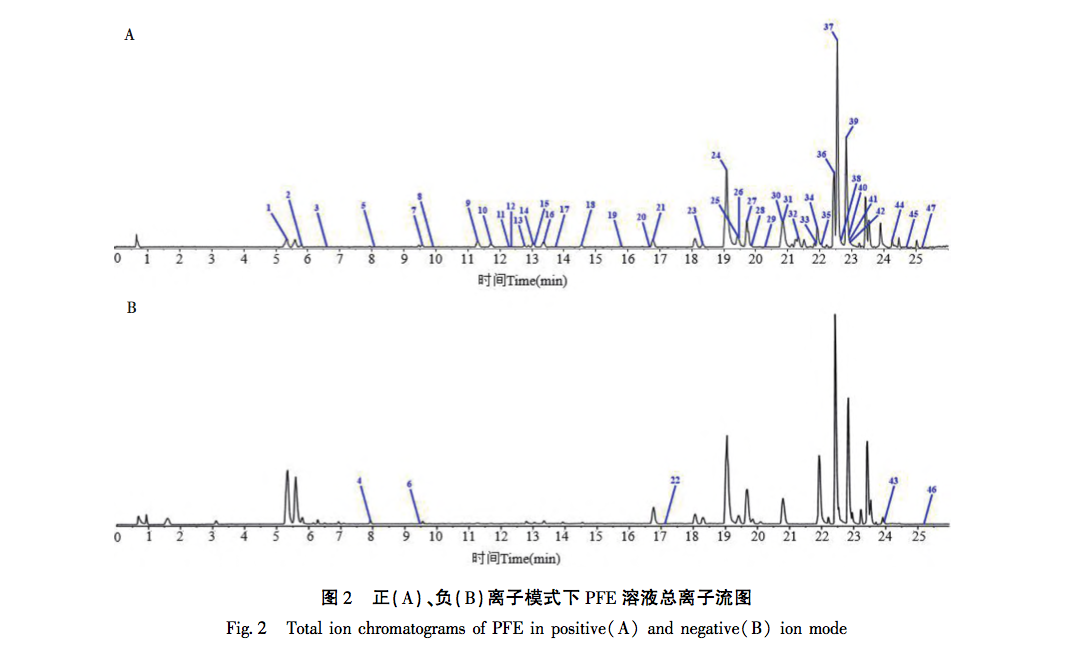
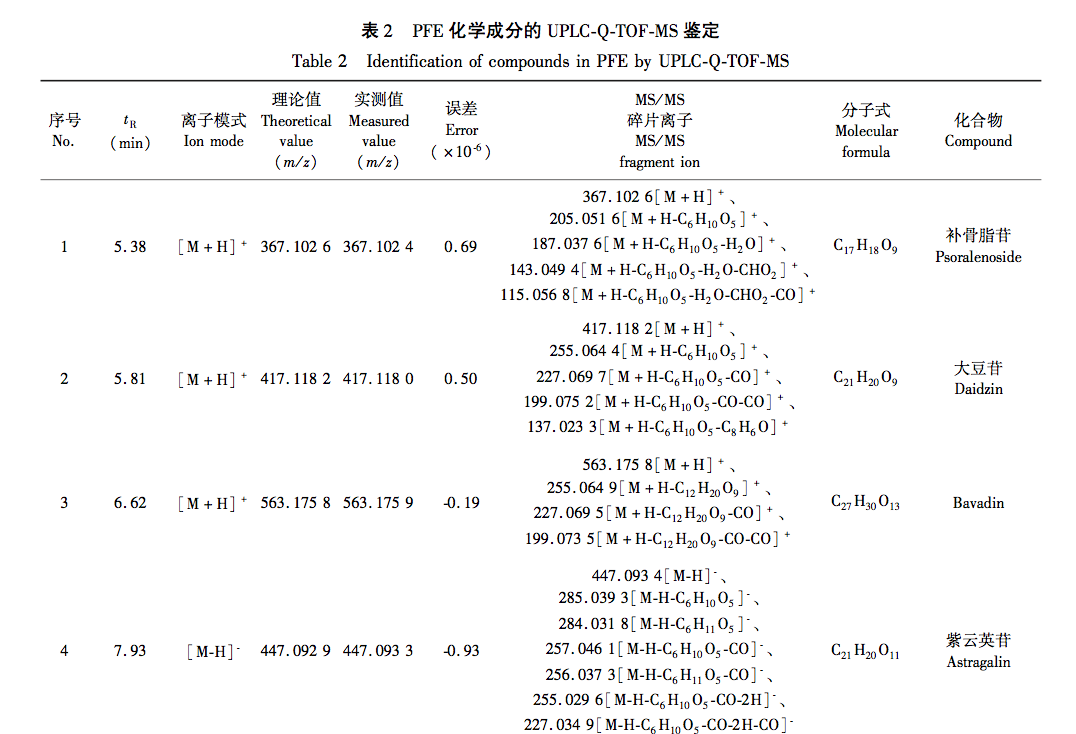

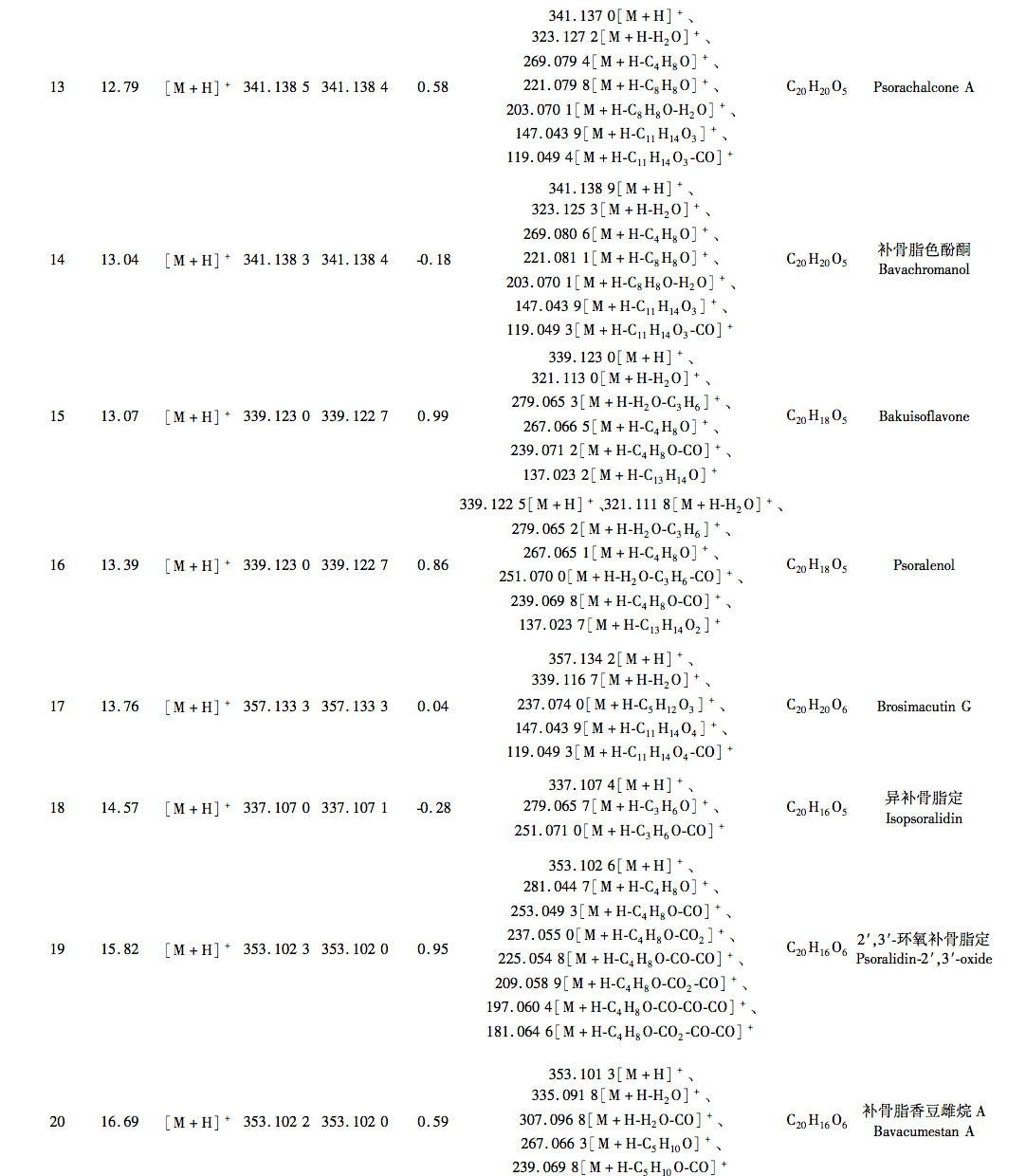

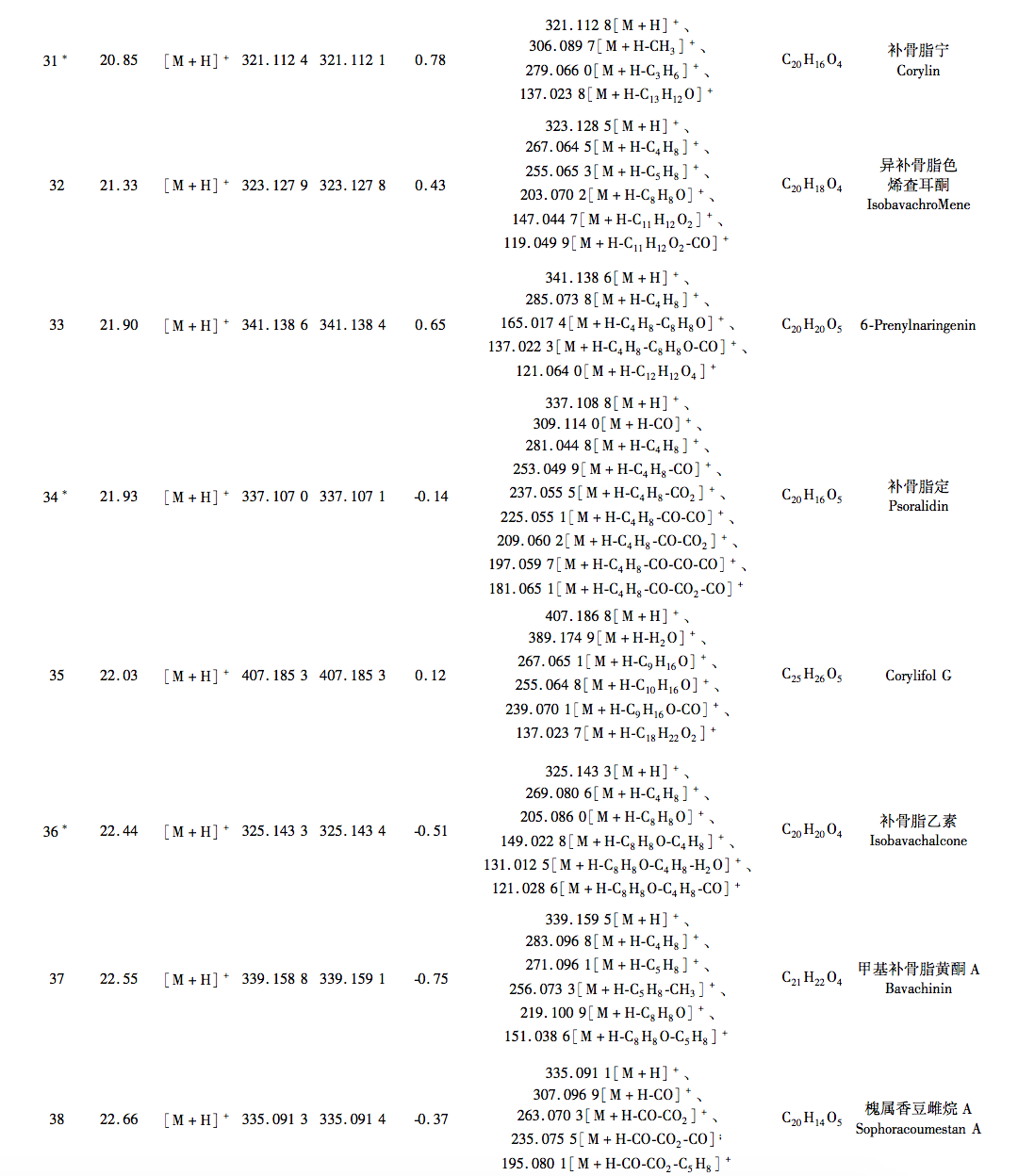
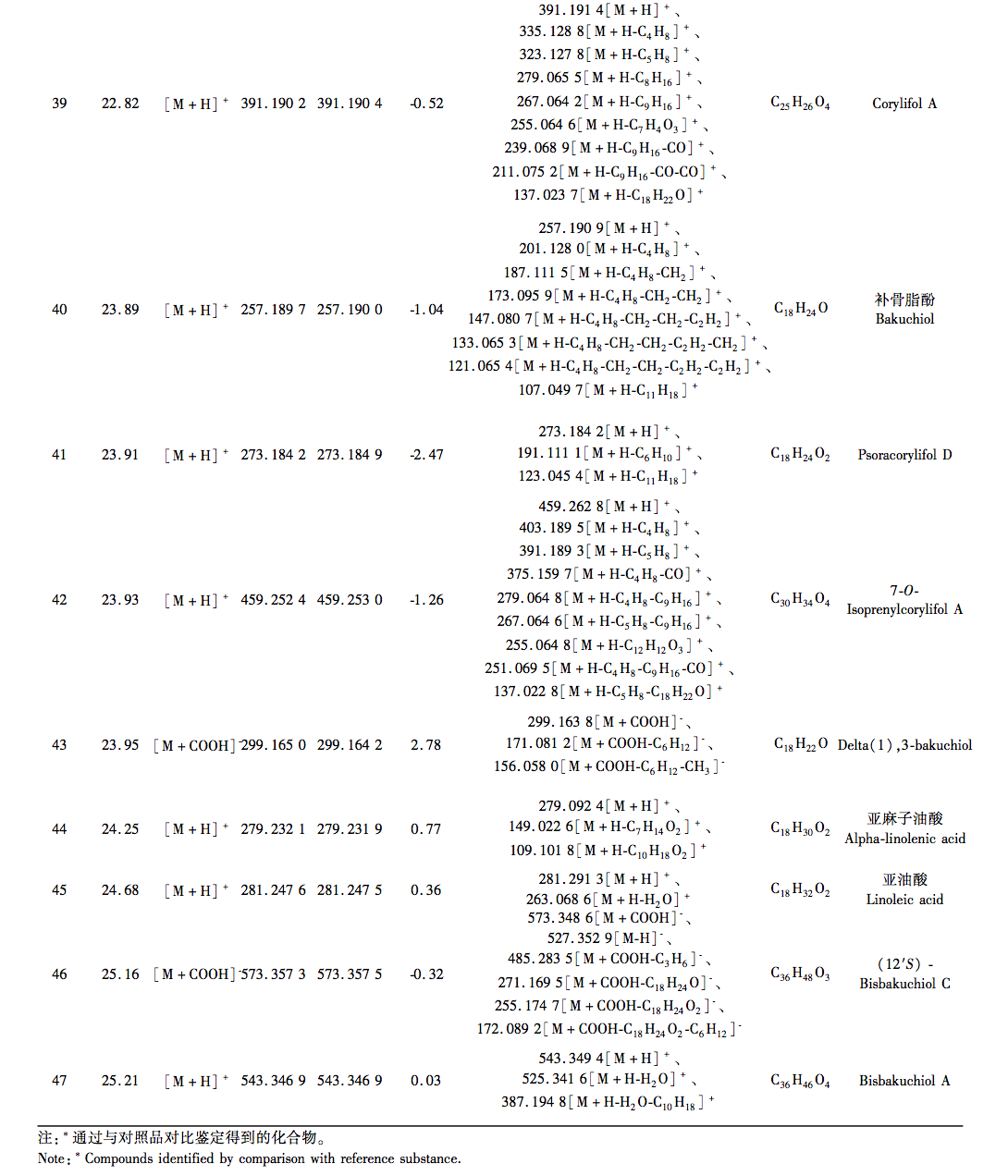
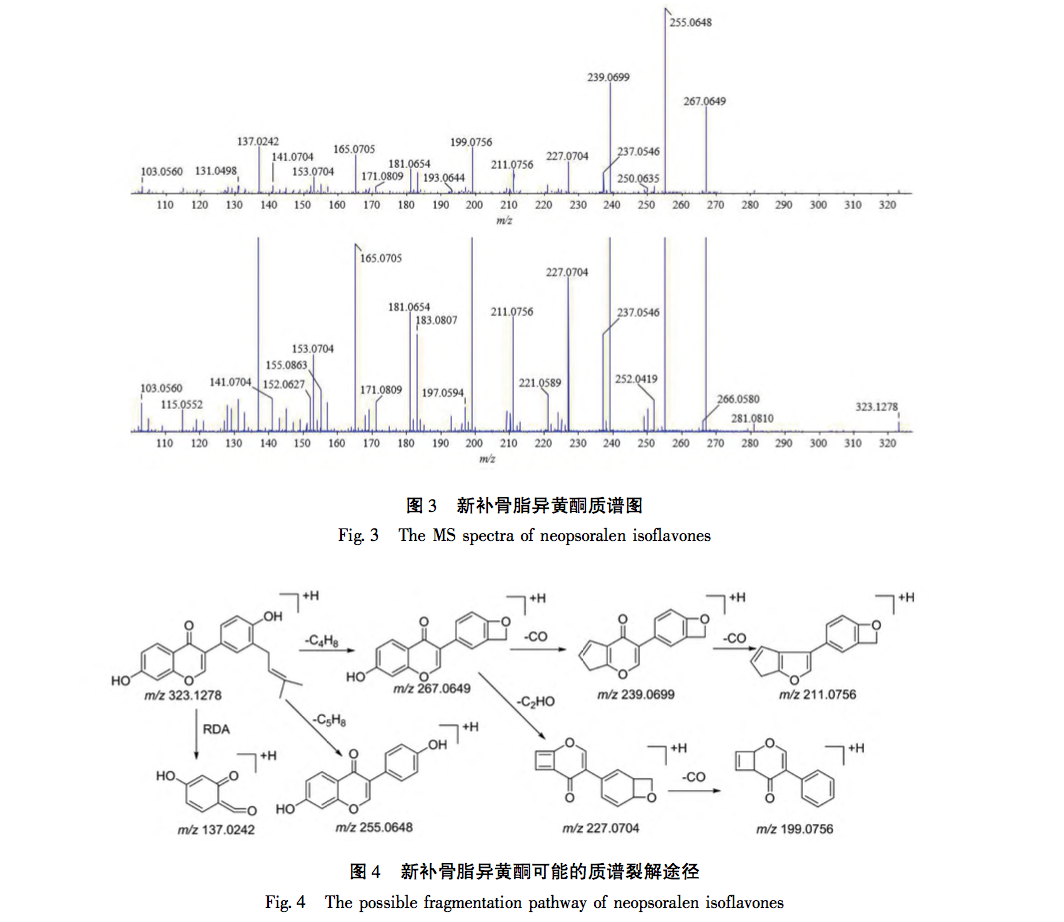
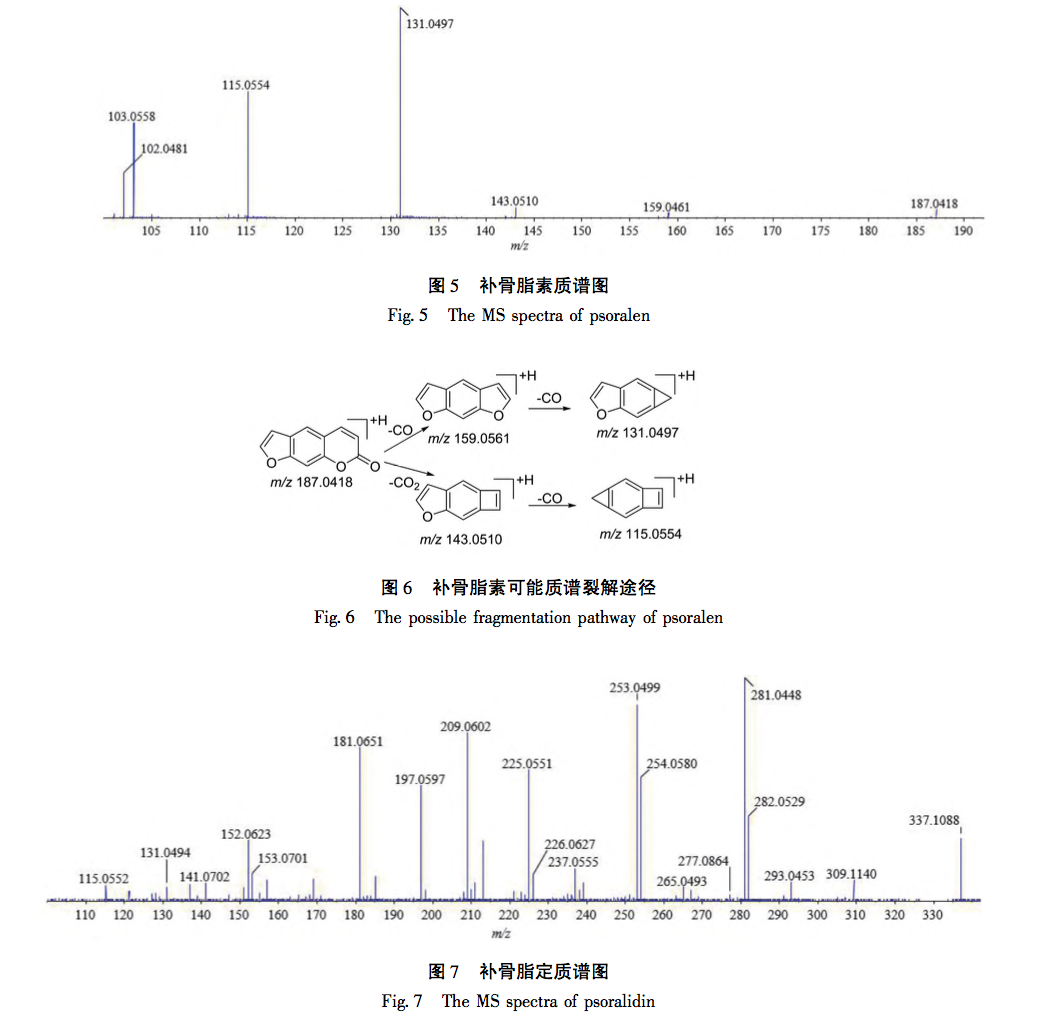
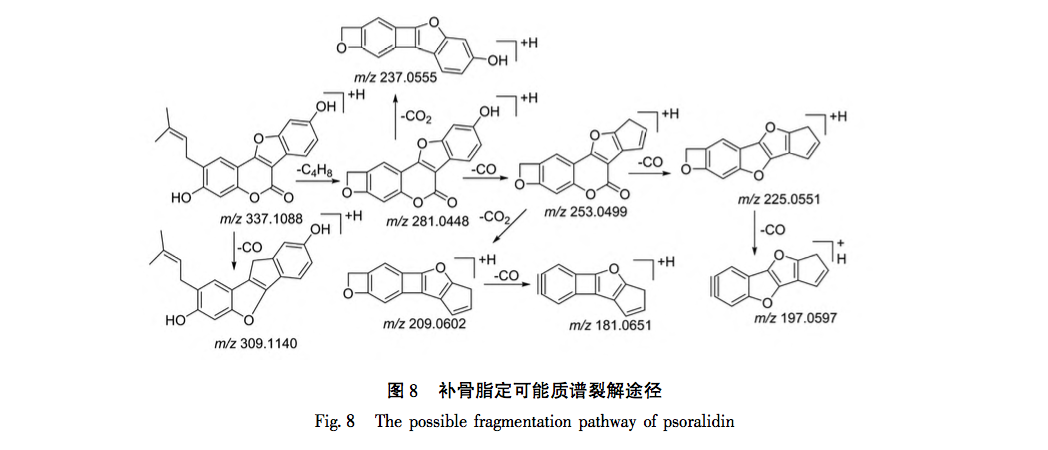
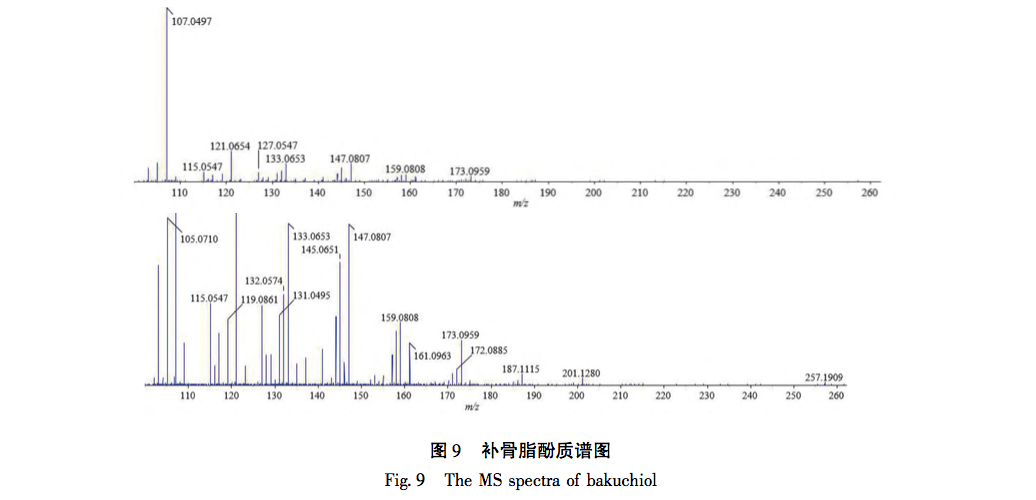

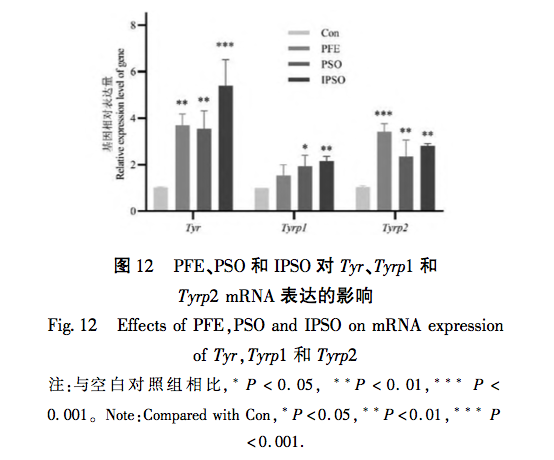 According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and ancient and modern herbal books, Fructus Psorale is a traditional Chinese medicine with proven efficacy in treating vitiligo. Most medical institutions use Fructus Psorale in tinctures, with ethanol concentrations ranging from 30% to 100%. Therefore, based on literature and practical applications, this study selected 65% ethanol as the extraction reagent. This study used UPLC-Q-TOF-MS technology to identify the chemical components in PFE. A total of 47 chemical components were identified, mainly flavonoids (27) and coumarins (10). The identified coumarin chemical components PSO and IPSO may be the main effective chemical components for treating vitiligo. Benzofurans (such as psoralen and isopsoralen) can also be converted into PSO and IPSO in the body to exert their effects. PSO and IPSO are also quality control components for bone fat medicinal materials specified in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Therefore, PFE and these two chemical components were selected for cell experiments. Preliminary exploration of the mechanism of action showed that qRT PCR results showed that compared with the control group, PFE significantly increased the expression of Tyr and Tyrp2 mRNA in B16-F10 cells, while other treatment groups could increase the expression of Tyr, Tyrp1, and Tyrp2 mRNA to varying degrees, with statistical differences, indicating that PSO, IPSO, and other potentially unknown compounds in Fructus Psorale may exert therapeutic effects on vitiligo by increasing tyrosinase content. However, there are also literature reports that PSO acts on human melanoma cell line A375, inhibiting the activity of the tyrosinase promoter; Downregulating the expression levels of Tyr, Tyrp1, and Tyrp2 mRNA and inhibiting melanin production, contrary to the results of this experiment, may be due to different research subjects or the bidirectional regulation of melanin production by PSO in different concentration ranges. Further research is needed to draw more rigorous and accurate conclusions. For the treatment of vitiligo with psoralen, PSO and IPSO are the main active ingredients, which can be used as quality control indicators for this drug or formulations containing this traditional Chinese medicine.
According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and ancient and modern herbal books, Fructus Psorale is a traditional Chinese medicine with proven efficacy in treating vitiligo. Most medical institutions use Fructus Psorale in tinctures, with ethanol concentrations ranging from 30% to 100%. Therefore, based on literature and practical applications, this study selected 65% ethanol as the extraction reagent. This study used UPLC-Q-TOF-MS technology to identify the chemical components in PFE. A total of 47 chemical components were identified, mainly flavonoids (27) and coumarins (10). The identified coumarin chemical components PSO and IPSO may be the main effective chemical components for treating vitiligo. Benzofurans (such as psoralen and isopsoralen) can also be converted into PSO and IPSO in the body to exert their effects. PSO and IPSO are also quality control components for bone fat medicinal materials specified in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Therefore, PFE and these two chemical components were selected for cell experiments. Preliminary exploration of the mechanism of action showed that qRT PCR results showed that compared with the control group, PFE significantly increased the expression of Tyr and Tyrp2 mRNA in B16-F10 cells, while other treatment groups could increase the expression of Tyr, Tyrp1, and Tyrp2 mRNA to varying degrees, with statistical differences, indicating that PSO, IPSO, and other potentially unknown compounds in Fructus Psorale may exert therapeutic effects on vitiligo by increasing tyrosinase content. However, there are also literature reports that PSO acts on human melanoma cell line A375, inhibiting the activity of the tyrosinase promoter; Downregulating the expression levels of Tyr, Tyrp1, and Tyrp2 mRNA and inhibiting melanin production, contrary to the results of this experiment, may be due to different research subjects or the bidirectional regulation of melanin production by PSO in different concentration ranges. Further research is needed to draw more rigorous and accurate conclusions. For the treatment of vitiligo with psoralen, PSO and IPSO are the main active ingredients, which can be used as quality control indicators for this drug or formulations containing this traditional Chinese medicine.
