UPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS fingerprint and spectrum effect relationship of antibacterial activity of Jinlongdeng
Jin Deng Deng, also known as Suanjiang or Red Maiden, is the dried or fruiting calyx of Physalis alkekengi L. var. franchetii (Mast.) Makino, a plant in the Solanaceae family. Sour and bitter in taste, cold in nature, belongs to the lung and spleen meridians. It has the effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, promoting the throat and resolving phlegm, diuresis and clearing the lymphatic system. It is clinically used to treat sore throat, lung heat cough, and urinary incontinence. The chemical composition of Jinlongdeng is diverse, mainly including compounds such as bitters, flavonoids, sucrose esters, phenylpropanoids, alkaloids, etc. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that the alcohol extract and dichloromethane extract of Jinlongdeng have good inhibitory activity against Gram positive bacteria, Gram negative bacteria, and Candida albicans. Some components of sour bitters have also been proven to have significant antibacterial effects. At present, there are many studies on the antibacterial activity of Jinlongdeng both domestically and internationally, but its material basis is not yet very clear.
Traditional Chinese medicine itself has complex and diverse ingredients, and has the characteristics of multi-target and overall regulation when exerting its therapeutic effects. The relationship between traditional Chinese medicine spectrum and efficacy is based on the study of traditional Chinese medicine fingerprint spectrum, linking fingerprint spectrum with pharmacological effects, conducting research on spectrum efficacy relationship, and further clarifying the material basis for exerting pharmacological effects. At present, there is relatively little research on the fingerprint spectrum and spectral efficiency relationship of Jinlongdeng. Therefore, this study aims to explore the material basis of the antibacterial activity of Jinlongdeng from its spectrum effect relationship. By establishing mass spectrometry fingerprint spectra of 16 batches of Jin Deng lanterns from three different origins and determining their antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, grey correlation analysis was used to explore the correlation between characteristic peaks and their antibacterial activity, in order to clarify the material basis of their antibacterial activity and provide a basis for further development, utilization, and quality control research of Jin Deng lanterns.
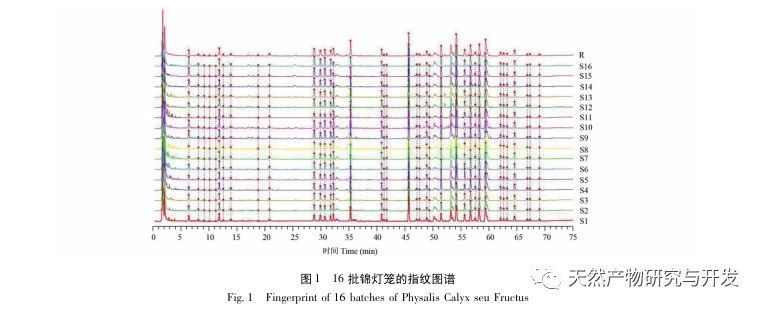




 In the early stage of this experiment, the effect of different concentrations of methanol (50%, 70%, 100%) on the extraction efficiency of Jinlongdeng medicinal materials was investigated, and it was found that the peak was highest when 70% methanol water extraction was performed. Meanwhile, during the investigation of mass spectrometry conditions, it was found that the total ion chromatogram in negative ion mode was more stable and the peak shape was more attractive. Therefore, the experiment was conducted in negative ion scanning mode.
In the early stage of this experiment, the effect of different concentrations of methanol (50%, 70%, 100%) on the extraction efficiency of Jinlongdeng medicinal materials was investigated, and it was found that the peak was highest when 70% methanol water extraction was performed. Meanwhile, during the investigation of mass spectrometry conditions, it was found that the total ion chromatogram in negative ion mode was more stable and the peak shape was more attractive. Therefore, the experiment was conducted in negative ion scanning mode.
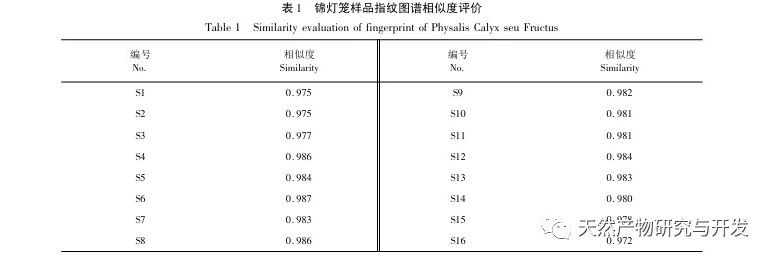
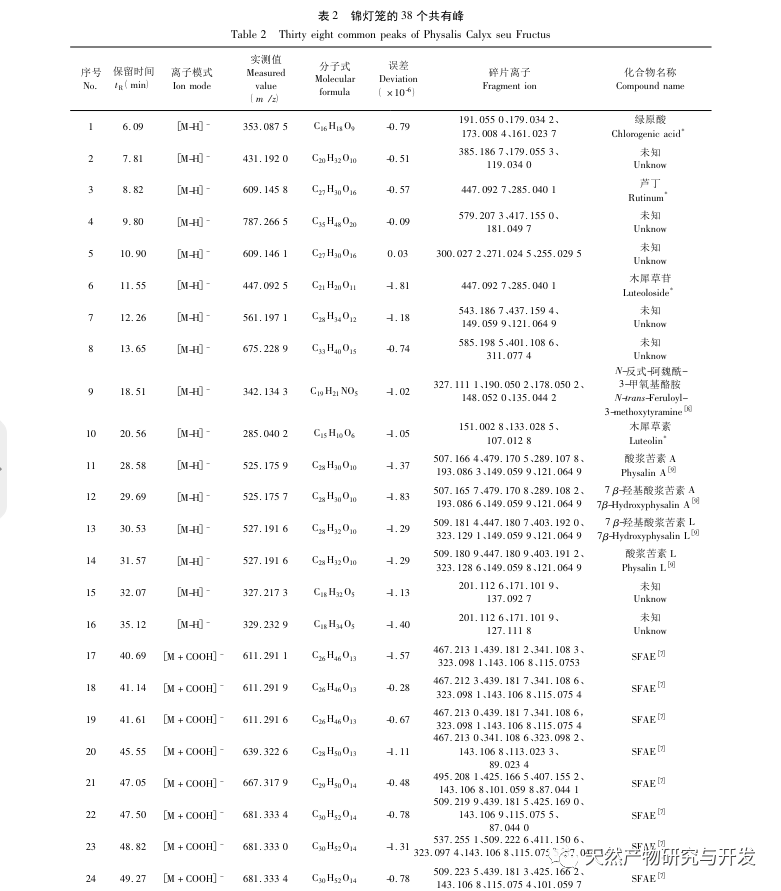
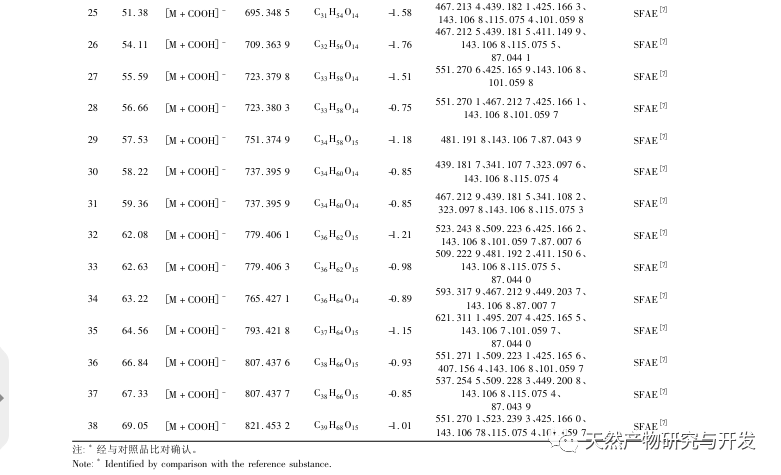
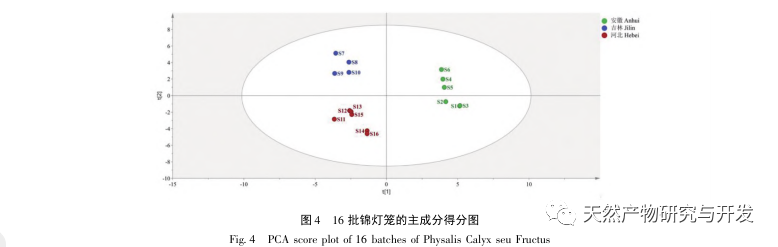
This study established fingerprint spectra of 16 batches of Jinlongdeng medicinal herbs, extracted 38 common peaks, and the similarity was above 0.95, indicating that the quality of Jinlongdeng medicinal herbs from different origins is relatively stable; Both cluster analysis and PCA analysis can cluster samples according to different origins, indicating that the growth environment of medicinal materials is a major factor causing quality differences.
At the same time, this study determined the antibacterial activity of 16 batches of Jin Deng lantern extracts against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. For the first time, fingerprint spectra were combined with pharmacological results, and grey correlation analysis was used to study the spectral efficacy relationship of Jin Deng lantern. The results showed that the antibacterial activity of Jinlongdeng may be the result of the combined action of multiple components. Among them, the characteristic peaks that contribute significantly to the antibacterial activity (correlation ≥ 0.85) are all composed of sucrose fatty acid esters, indicating that these components have a significant contribution to the antibacterial activity of Jinlongdeng.
In the past, scholars’ research on Jinlongdeng mainly focused on the complex chemical structure and significant biological activity of acid bitter compounds, while neglecting the study of sucrose fatty acid esters. The structural characteristics of sucrose fatty acid ester components are that sucrose serves as the parent nucleus and is linked to one or more fatty acid chain fragments through ester bonds. Modern pharmacological research has shown that this type of compound has significant antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, anti-tumor, insecticidal and other activities. At the same time, sucrose fatty acid esters have good biodegradability and toxicological properties, so their application prospects are broad and worthy of our attention.
In summary, this study successfully established the fingerprint spectrum of the extract of Lonicera japonica and studied its spectral effect relationship for the first time. The results showed that the sucrose fatty acid ester components were highly correlated with the antibacterial activity of Lonicera japonica. However, due to its unique structure, it was not possible to conduct in-depth analysis of its structure through mass spectrometry in this experiment. In the future, this type of component in Jin Deng will be isolated and purified to verify its antibacterial activity. Based on this, the structure-activity relationship will be summarized to provide reference for further research on the antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of Jin Deng.
