Preparation of fucoidan nano selenium and its inhibition of tumor cell proliferation
At present, besides cardiovascular disease, cancer has become the second leading cause of human death. Due to its difficult treatment, long treatment cycle, and high treatment cost, it brings a heavy burden to people’s lives. Chemotherapy is one of the main methods for treating cancer in modern Western medicine, but due to the serious side effects and drug resistance of chemotherapy drugs, the treatment effect is not ideal. Therefore, developing a broad-spectrum anti-tumor drug with high efficacy and no toxic side effects is still an urgent problem to be solved.
Selenium (Se) is an essential trace element for the human body, playing an important role in the synthesis of glutathione peroxidase, thioredoxin reductase, and other enzymes. It participates in various life activities and is of great significance to human health. At the same time, selenium also has various functional activities such as antioxidant and anti-tumor. Research has found that cancer patients suffer from selenium deficiency in their bodies. Adequate intake of selenium can protect normal cells and reduce the occurrence of cancer. However, the safe dosage range of Se that can be used in organisms is very narrow, and it is easy to cause poisoning due to excessive use. Therefore, it is crucial to explore and develop safe forms of Se to reduce its toxicity. Research has found that compared to traditional forms of Se, selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) have lower toxicity and better bioavailability due to their unique size and surface effects. However, SeNPs have high activity due to the lack of neighboring coordinating atoms on their surface, making them extremely unstable at room temperature and prone to aggregation to form more toxic elemental Se. Therefore, dispersants are generally used in the preparation of SeNPs to increase their dispersibility. Polysaccharides have hydroxyl groups in their molecular structure, which can bind with Se through intermolecular hydrogen bonds to prevent the aggregation of SeNPs. Therefore, polysaccharides are often used to disperse SeNPs. At present, polysaccharides used as nano selenium modifiers that have been reported include astragalus polysaccharides, konjac glucomannan, etc.
Fucoidan (FD) is a natural water-soluble polysaccharide derived from brown algae, composed of sulfated fucoidan, mannose, arabinose, glucuronic acid, and other monosaccharides. Researchers have found that fucoidan has various functional activities such as anti-tumor, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects. However, there are currently no reports on the modification of nano selenium with fucoidan. Therefore, this article uses FD as a stabilizer to prepare fucoidan selenium nanoparticles (FD SeNPs) through redox reactions. Single factor and response surface experiments are used to optimize the preparation process parameters, and further structural identification and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation are studied, providing theoretical data support for the development and application of FD SeNPs as tumor cell inhibitors.
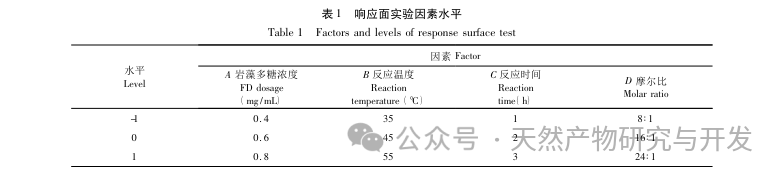
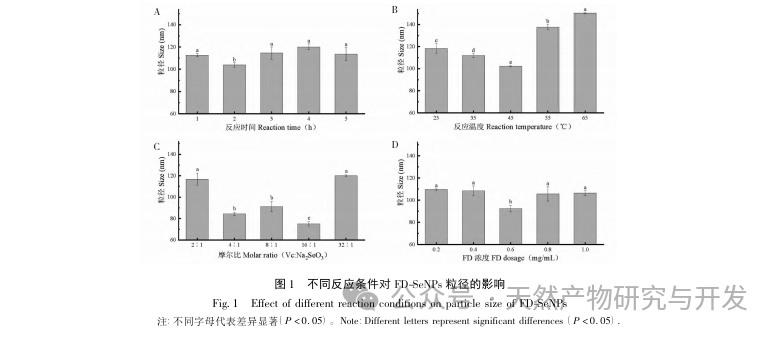
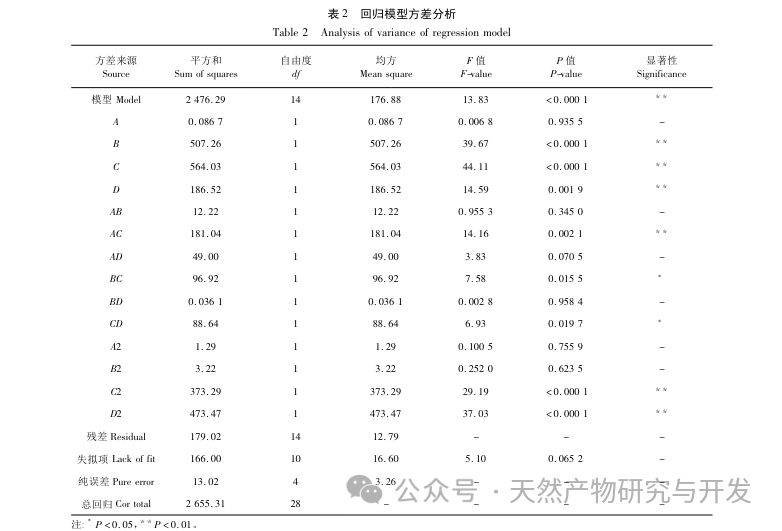
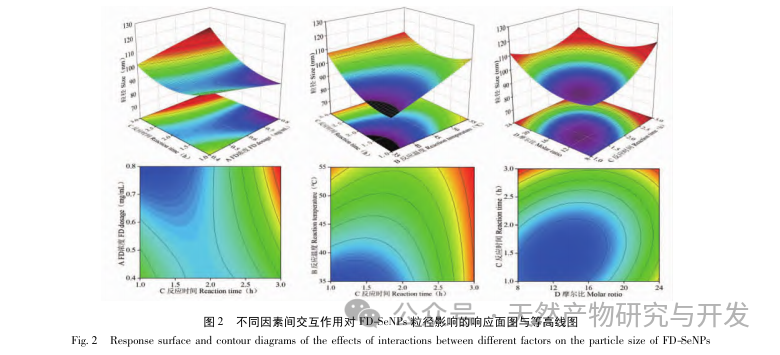
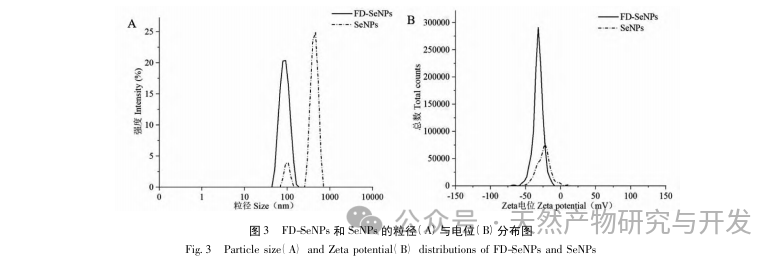

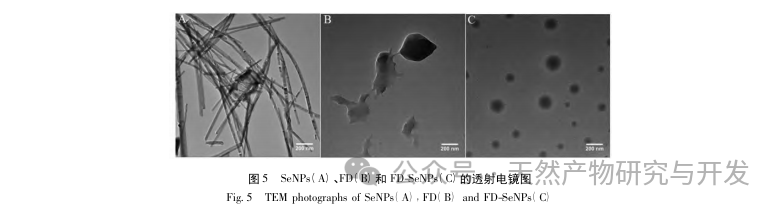
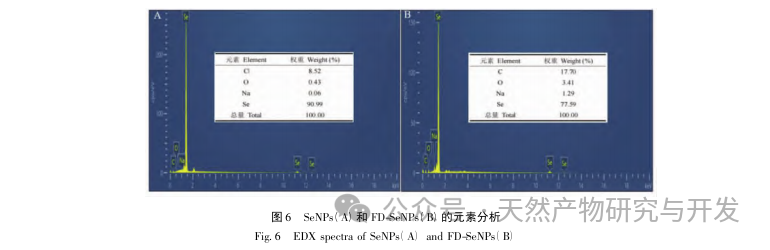
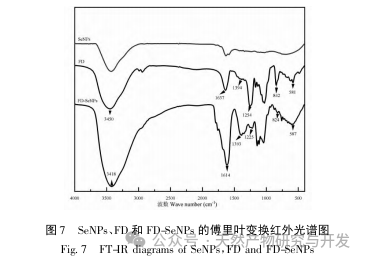
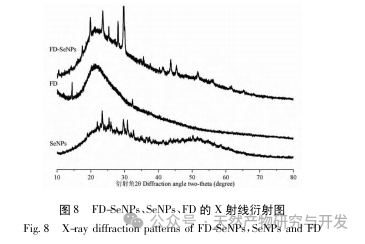
This article obtained the optimal preparation process parameters for FD SeNPs through single factor and response surface optimization experiments, which are a reaction temperature of 35 ℃, a reaction time of 1 hour, a molar ratio of ascorbic acid to sodium selenite of 14:1, and an FD concentration of 0.8 mg/mL. Under these conditions, the minimum particle size was measured to be (83.40 ± 0.55) nm, the potential was (-31.89 ± 0.47) mV, and the selenium content reached 29.93%. Further identification of its structure revealed that FD forms uniformly spherical nanoparticles on the surface of SeNPs through hydroxyl adsorption, indicating that the polar groups of polysaccharides can effectively inhibit the aggregation of SeNPs.
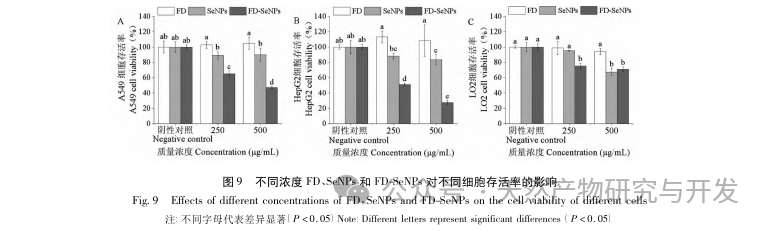
The current research has found that the anti-tumor mechanisms mainly include inhibiting tumor cell growth, inhibiting tumor cell metastasis or invasion, and enhancing the body’s immune regulatory ability to achieve anti-tumor effects. Research has shown that SeNPs using polysaccharides as templates can promote the expression of related apoptotic proteins and autophagy marker proteins, thereby inducing tumor cell apoptosis and autophagy. The in vitro anti-tumor experiment of this study found that FD modified SeNPs can significantly enhance the ability of SeNPs to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and have good cell selectivity, but its specific mechanism of action needs to be further studied.
