Study on the effect of steam explosion processing on the sugar components of fern based on PMP pre column derivatization HPLC method
Pteridium aquilinum, a plant in the Pteridium genus of the Pteridiaceae family, is widely distributed and has strong seasonality. It is harvested from March to June each year and is prone to aging and deterioration after harvesting. Traditional processing methods often use pickling and drying, which leads to a single variety of fern products on the market that require cooking before consumption, limiting the promotion of fern products. In recent years, in order to promote the development and utilization of fern resources, while ensuring the nutritional value and composition of fern itself as much as possible, a series of high value-added fern products have been developed by combining advanced processing and storage technologies at home and abroad, including paper fern, blanched fern, and steamed fern tea. Among them, steamed fern tea has a simple processing technology, convenient and fast consumption, and is more conducive to industrialization and product promotion. Steam explosion technology (referred to as “steam explosion”) refers to a thermal mechanical treatment method that places materials in a high temperature and high pressure environment, uses the generated water vapor to penetrate into the interior of the material, and after the internal and external pressures are balanced, instantly places all materials directly under atmospheric pressure to produce a “explosion” phenomenon. This technology can effectively break down the cell wall barrier of ferns, allowing the active ingredients to dissolve more efficiently and greatly shorten the brewing time. Some of the activities of plant materials treated by this technology, such as antioxidant, antibacterial, and inhibition of alpha glucosidase, are significantly enhanced.
The whole plant of fern can be used as medicine and is rich in various active ingredients such as polysaccharides, flavonoids, terpenes, etc. Among them, polysaccharides account for about 8% of the dry weight of fern and are one of its main active ingredients. Pteridium aquilinum polysaccharide is a heteropolysaccharide with a complex chain structure, multiple branches, and no triple helix structure. It has biological activities such as immune regulation, antibacterial activity, and regulation of gut microbiota. Studies have shown that the structure of polysaccharides has a significant impact on their biological activity. During the process of gas explosion, components such as cellulose and hemicellulose in plant raw materials undergo hydrolysis to produce soluble sugars, while reducing sugars and amino acids undergo Maillard reaction, causing changes in the structure of sugar components. At present, the commonly used analysis methods for carbohydrate components include thin-layer chromatography, capillary electrophoresis, and high-performance liquid chromatography. Among them, High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) has good stability, mature technology, and a wide range of chromatographic columns to choose from. However, due to the weak UV absorption of carbohydrate components, derivatization reagents are usually required to form derivatives with strong UV absorption. For example, derivatization reagent 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) can react with reducing sugars to produce strong UV absorption. This method is simple to operate, highly sensitive, and accurate, and is widely used in carbohydrate component analysis.
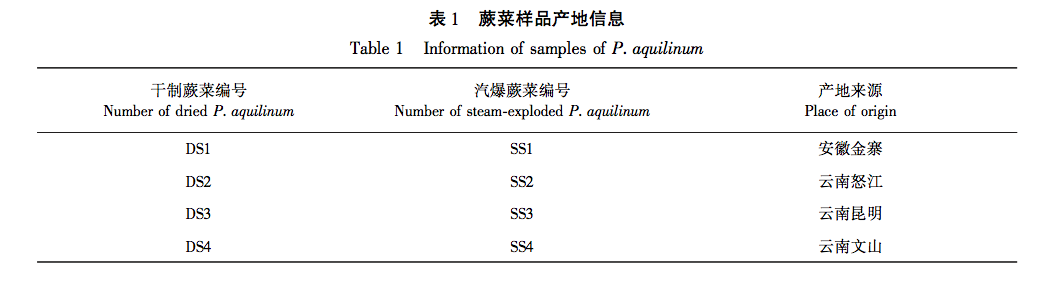
In recent years, domestic and foreign research has only reported the changes in the extraction rates of active ingredients such as polysaccharides, flavonoids, alkaloids, etc. in plant raw materials before and after steam explosion, but no study has been conducted on the effects of sugar components in ferns before and after steam explosion. In view of this, this study collected dried samples of fern from four different production areas and compared the total polysaccharide yield after treatment with the same steam explosion process. The PMP pre column derivatization HPLC method was used to establish a fingerprint spectrum, and the hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) and principal component analysis (PCA) methods were used in combination with similarity evaluation to identify the experimental data and evaluate the effect of steam explosion process on fern components. Five monosaccharide components were identified, and the free monosaccharide content and polysaccharide monosaccharide composition differences in each sample were determined to explore the effect of steam explosion process on the sugar components in fern, providing a basis for subsequent activity research and quality control of fern steam explosion processing. Reference.
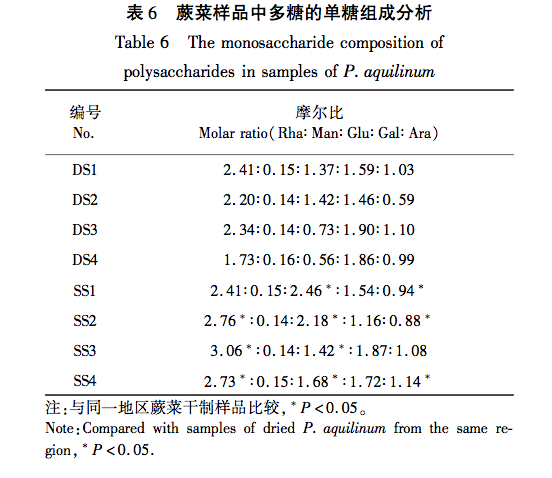
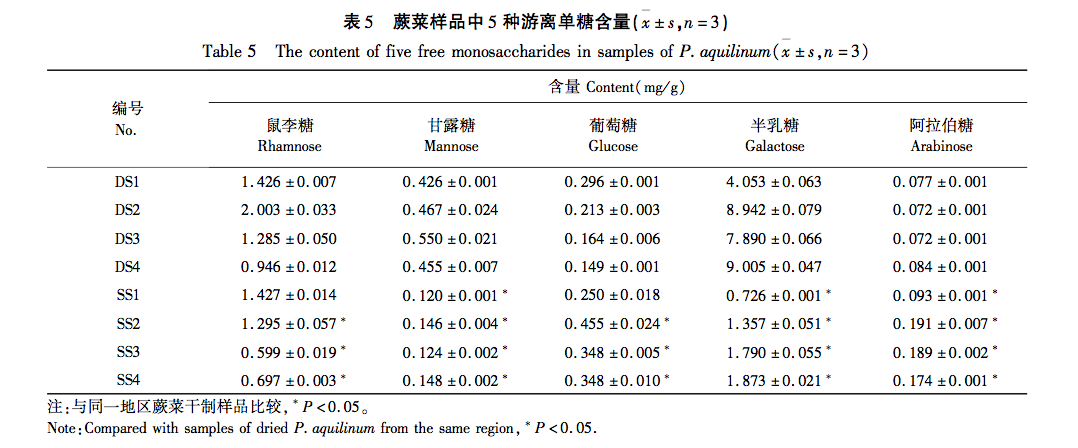

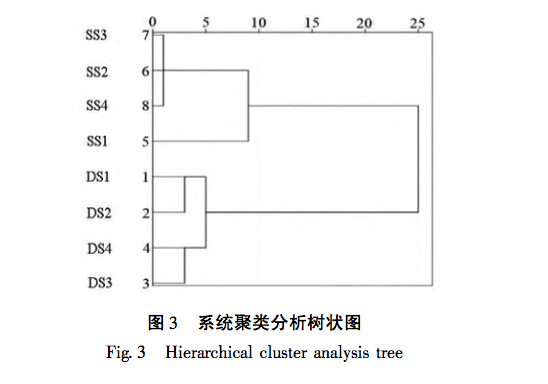
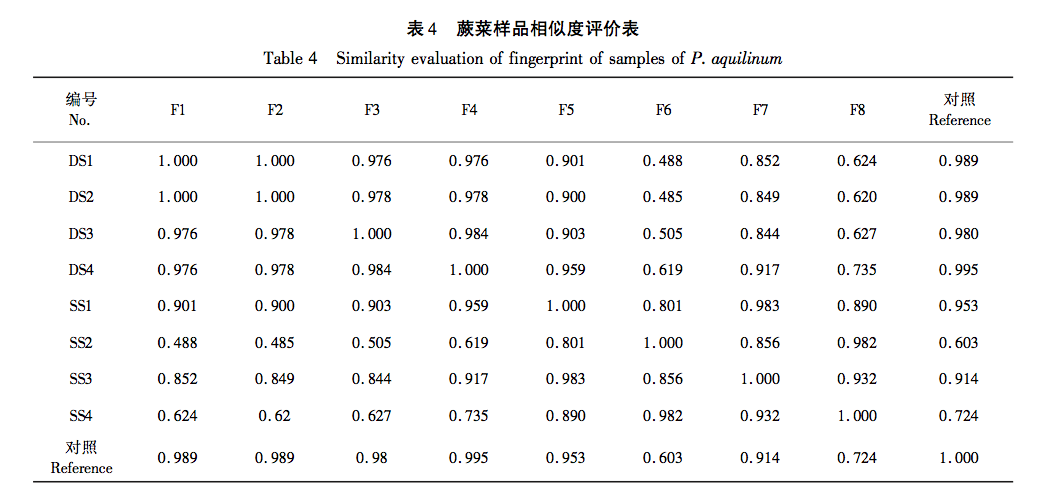
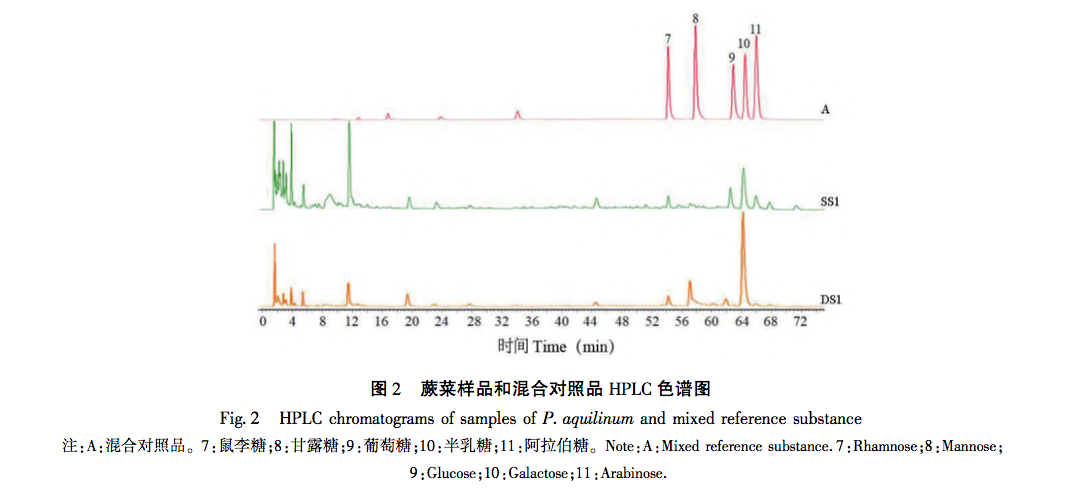
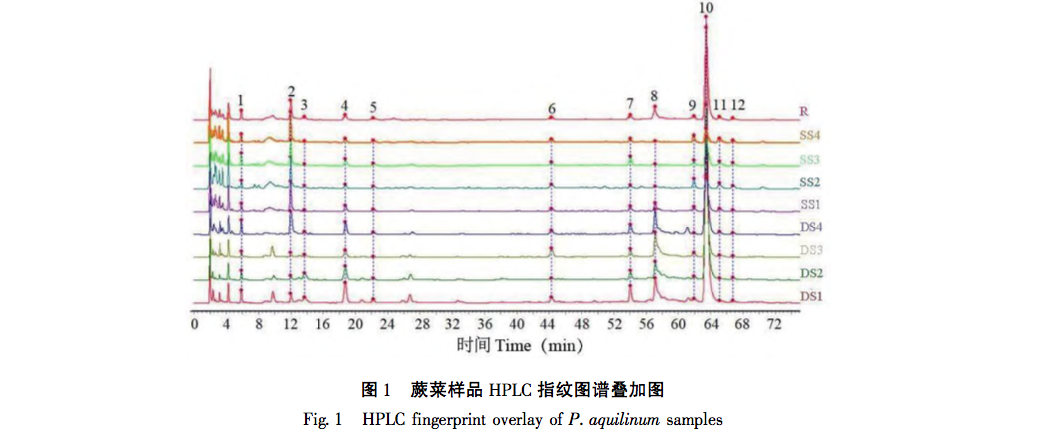
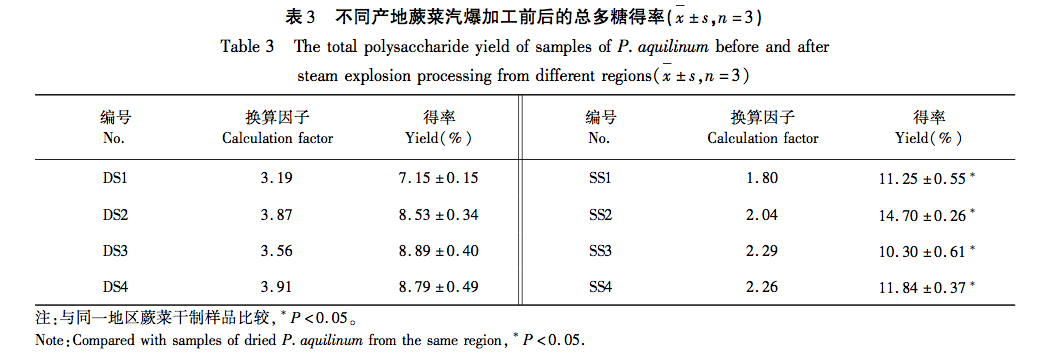
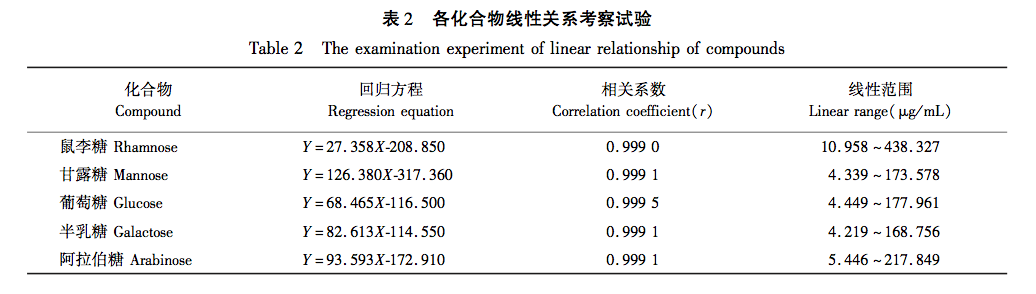 This study used dried fern samples from four different production areas as raw materials. After the same steam explosion process, the total polysaccharide yield of the samples was tested. It was found that the total polysaccharide yield of fern steam explosion samples increased significantly (P<0.05) by 55% compared to dried fern, confirming that steam explosion treatment can improve polysaccharide yield and obtain fern polysaccharides more efficiently. HPLC technology combined with PMP pre column derivatization was used to establish a fingerprint spectrum, and HCA and PCA methods were used to analyze the raw data. It was found that there was no significant change in the number of chromatographic peaks for both, and 12 common peaks were identified. HCA and PCA methods can effectively distinguish between dry processing and steam explosion processing of ferns; Simultaneously identifying 5 types of sugar components for free monosaccharide and monosaccharide composition determination, the results showed that compared with dried fern, the content of free monosaccharides in steamed fern decreased, including galactose, mannose, and xylose, while the content of glucose and arabinose increased; The average proportion of glucose and xylose in the monosaccharide composition of polysaccharides significantly increased (P<0.01), with increases of 1.64% and 0.94%, respectively. Through this study, it was found that steam explosion processing has a certain impact on the content and structure of sugar components in ferns, or may cause changes in their activity. This can provide reference for subsequent activity research and quality control of steam explosion processing of ferns.
This study used dried fern samples from four different production areas as raw materials. After the same steam explosion process, the total polysaccharide yield of the samples was tested. It was found that the total polysaccharide yield of fern steam explosion samples increased significantly (P<0.05) by 55% compared to dried fern, confirming that steam explosion treatment can improve polysaccharide yield and obtain fern polysaccharides more efficiently. HPLC technology combined with PMP pre column derivatization was used to establish a fingerprint spectrum, and HCA and PCA methods were used to analyze the raw data. It was found that there was no significant change in the number of chromatographic peaks for both, and 12 common peaks were identified. HCA and PCA methods can effectively distinguish between dry processing and steam explosion processing of ferns; Simultaneously identifying 5 types of sugar components for free monosaccharide and monosaccharide composition determination, the results showed that compared with dried fern, the content of free monosaccharides in steamed fern decreased, including galactose, mannose, and xylose, while the content of glucose and arabinose increased; The average proportion of glucose and xylose in the monosaccharide composition of polysaccharides significantly increased (P<0.01), with increases of 1.64% and 0.94%, respectively. Through this study, it was found that steam explosion processing has a certain impact on the content and structure of sugar components in ferns, or may cause changes in their activity. This can provide reference for subsequent activity research and quality control of steam explosion processing of ferns.
