What are the differences between the various types of sterilization techniques used in food plants?
Food Heat Treatment
As one of the most important methods used in food processing and preservation to improve food quality and extend the storage period of food. Its main role is to kill pathogenic bacteria and other harmful microorganisms, passivate enzymes, destroy unwanted or harmful components or factors in food, improve the quality and characteristics of food, as well as improve the availability of nutrients in food, digestibility and so on. Of course, there are certain negative effects of heat treatment, such as a greater impact on the heat-sensitive components, but also the quality and characteristics of the food to produce undesirable changes in the process consumes more energy.
First, industrial cooking is often used as a kind of pretreatment for food processing, mainly to improve the sensory quality of food. Cooking is usually boiled, stewed (stew), baked (baked), fried (fried), baked and other forms.
Second, baking and roasting (Baking) and baking (Roasting) is basically the same unit of operation, they are high temperature heat to change the edible properties of food. The difference between the two is that baking is mainly used for pasta products and fruits, while grilling is mainly for meat, nuts and vegetables. Baking can also achieve a certain sterilization and reduce the role of food surface moisture activity, so that products have a certain degree of preservation, but the storage period of baked goods is generally shorter, combined with refrigeration and packaging can be appropriate to extend the storage period.
Third, deep-frying is mainly to improve the quality of food consumption and the use of a heat treatment means. Through deep-frying can produce fried food unique color, aroma and texture. Frying treatment also has a certain sterilization, enzyme and reduce the role of food moisture activity. The storability of fried food is mainly determined by the water activity of the food after frying. But fried food in the storage period is easy to occur during the phenomenon of oil and grease ha defeat.
Fourth, hot blanching is also known as scalding, bleaching, killing, pre-cooking. Mainly used in vegetables and some fruits, to maintain the original color, usually vegetables and fruits frozen, dried or canned before a pretreatment process.
Thermal sterilization
Is to kill microorganisms for the main purpose of heat treatment form.
1, according to the different types of microorganisms to be killed can be divided into pasteurization and commercial sterilization. (1) pasteurization, also known as low-temperature disinfection, cold sterilization method, the use of lower temperatures can kill germs and keep the items in the nutrients in the flavor remains unchanged, often defined as the need to kill a variety of pathogenic bacteria in the heat treatment method, is currently mainly used in the processing of milk, not only to kill the health of the pathogenic bacteria can be harmful to health but also to make the milk quality as little as possible to change.
(2) Commercial sterilization, also called commercial asepsis, in which all pathogenic bacteria and toxin-forming microorganisms have been destroyed, as well as other microorganisms (if present) that can grow and form spoilage in the product under normal handling and storage conditions. Commercially aseptic foods may contain very small amounts of bacterial spores, but such spores do not normally multiply in the food. However, if such spores are dissociated from the food and given special environmental conditions, they can still show vitality, mostly in canned and bottled foods.
2, sterilization methods are usually divided into pressure, temperature, time, heating medium and equipment, and sterilization and canning sealing relationship, etc., the pressure can be divided into atmospheric sterilization and pressurized sterilization; sterilization of the heating medium can be hot water, water vapor, water vapor and air mixtures and flames, etc..
(1) hygrothermal sterilization with steam, hot water as the heat medium, or directly with steam jet heating sterilization method. The use of heat converters (such as boilers) will be burning heat into hot water or steam as a heating medium, and then heat exchanger will be hot water or steam heat transfer to the food, or steam directly into the food to be heated by spraying.
(2) Atmospheric pressure sterilization is a method of killing microorganisms by denaturing proteins with hot steam. Moist heat penetration, sterilization effect is better than dry heat. Mainly use water (also use water vapor) as the heating medium, the sterilization temperature is 100℃ or below 100℃, used for acidic food or low acidic food sterilization which does not require high degree of sterilization. The cans are under atmospheric pressure when sterilized, which is suitable for metal cans, glass jars and cans with soft packaging materials as containers. There are intermittent and continuous sterilization equipment.
① Boiling or circulation steam sterilization: the temperature of atmospheric pressure boiling water and steam is 100℃, generally 30-60min can kill bacterial propagules, but not completely kill the spores. This method is suitable for items that can not be autoclaved.
② low-temperature gap sterilization (pasteurization): first 60-80 ° C heating 1h, and then placed in 20 ~ 25 ° C preservation of 24h (or overnight at room temperature), so that the residual spores sprouted into propagules, and then sterilized with the above conditions, and so repeated three times. This method is suitable for items that do not tolerate high temperatures or high temperatures easily deteriorate, but it is very time-consuming.
(3) high-pressure steam sterilization using saturated water vapor as a heating medium, sterilization cans in saturated steam, sterilization temperature is higher than 100 ℃, used for low acidic food sterilization. As the air in the sterilization equipment is exhausted during sterilization, it is conducive to maintaining a consistent temperature. In the higher sterilization temperature is higher than 121 ℃, cooling is generally used in air counterpressure cooling. Sterilization equipment has intermittent and continuous, cans in the sterilization equipment have static and rotary. Rotary sterilization equipment can shorten the sterilization time.
(4) high-pressure boiling sterilization using air pressurized water as a heating medium, sterilization temperature is higher than 100 ℃, mainly used for glass jars and soft materials for the container of low-acid canned sterilization. Sterilization (including cooling) when the can is submerged in water to make heat transfer uniform, and to prevent container breakage due to too large a pressure difference between inside and outside the can or too drastic a change in temperature. Good circulation of air and water should be maintained during sterilization to make the temperature uniform. Sterilization equipment is mainly intermittent, but cans can be kept rotating during sterilization. When soft cans are sterilized, special trays (racks) are needed to place the soft cans to facilitate the circulation of the heating medium.
(5) air-pressurized steam sterilization is the use of steam as a heating medium, while adding compressed air to the sterilization equipment to increase the pressure outside the tank, reduce the pressure difference between inside and outside the tank. Mainly used for glass bottles and soft cans of high-temperature sterilization. Sterilization temperature is above 100℃, and the sterilization equipment is intermittent. Its control requirements are strict, otherwise it is easy to cause sterilization sterilization equipment temperature distribution is uneven.
(6) flame sterilization using flame direct heating of cans, is a kind of atmospheric pressure, high temperature short-term sterilization. Sterilization of cans after preheating in the high-temperature flame (temperature of 1300 ℃ or more) rolled over, a short period of time to reach high temperatures, maintained for a short period of time, cooled by water spray. Food in the can may not need soup as a convective heat transfer medium, the contents of the solids content is high. However, due to high pressure in the can when sterilized, generally only used for small metal cans. This method of sterilization temperature is more difficult to control (generally to join the determination of the heat radiated from the can to determine).
(7) hot canning sealing sterilization is heat treatment of food before canning, and then immediately seal the food while hot canning, the use of residual heat of the food to complete the sealing of the cans after the sterilization or secondary sterilization to meet the requirements of sterilization and then cooling the cans. It is mainly used for the sterilization of acidic foods such as juice and sauce. Sterilization equipment is mostly used in tube or sheet type, the degree of cleanliness and sterility of the canning container is required to be higher, and the cans are mostly inverted after sealing in order to ensure the sterilization of the can lid.
(8) Pre-sterilization aseptic canning is to make the food in the pre-sterilization process to achieve sterilization requirements, and then cooled to room temperature, in aseptic state into the sterilized aseptic containers and sealing (canning). Mostly used for liquid and semi-liquid food sterilization. Pre-sterilization is done in a heat exchanger and takes a short time. Aseptic canning can be done in aseptic packaging equipment or systems, and is a continuous high-temperature short-time or ultra-high-temperature instantaneous sterilization method. It is suitable for flexible packaging materials and metal and plastic containers. Non-thermal sterilization
Sterilization process of food temperature does not rise or rise very low, both conducive to maintaining the physiological activity of the functional components of food, but also conducive to maintaining the color, aroma, taste and nutrients. Non-thermal sterilization technology mainly includes physical sterilization and chemical sterilization. Non-thermal physical sterilization is the use of physical means (such as electromagnetic waves, pressure, light, etc.) for sterilization, chemical sterilization is through chemical reagents to achieve sterilization.
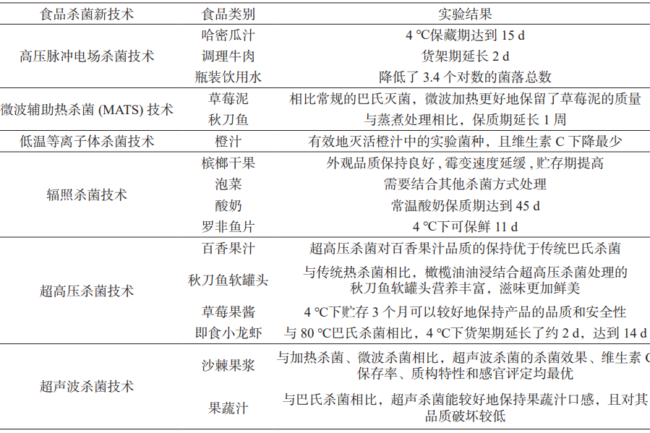
First, ultra-high pressure (UHP) sterilization technology refers to the sealing of food in flexible containers placed in water or other liquids as the pressure transfer medium in the pressure system, by more than 100MPa pressure treatment, in order to achieve sterilization, inactivation of enzymes and improve the functional properties of food and other effects.
Second, high-voltage pulsed electric field (PEF) sterilization is the use of strong electric field pulses of dielectric resistance break the principle of food microorganisms to produce inhibition, with a short processing time, low energy consumption, delivery of fast, uniform and so on, and thus is expected to be widely used in food sterilization.
Third, pulsed light sterilization is a continuous broadband spectrum of short and strong pulse, inhibit food and packaging material surfaces, transparent beverages, solid surfaces and microorganisms in the gas.
Fourth, magnetic sterilization is in the experimental development stage of non-thermal sterilization technology. Studies have shown that the use of 6000 magnetic strength, the food will be placed between the N pole and the S pole, after continuous oscillation, without heating, you can achieve 100% sterilization effect, the composition of food and flavor without any impact. It can be applied to beverages, condiments and various packaged solid foods.
Fifth, the induction electron sterilization is a linear induction electron gas pedal with electricity as the energy source of ionizing radiation produced by the microbial DNA and cell changes, and then passivate and kill harmful microorganisms.
Six, semiconductor photocatalytic sterilization semiconductor photocatalytic technology applied to the field of sterilization, especially the depth of water treatment, opened up a new world in the field of sterilization. This sterilization is through the biological life activities in the process of electron gain and loss and the result. Thus, the control of appropriate photocatalytic conditions, you can achieve a good sterilization effect.
Seven, microwave sterilization for food sterilization microwave frequency is often 2450 megahertz. Microwave lethal effect on microorganisms have two factors, namely, thermal effect and non-thermal effect. Thermal effect refers to the material absorption of microwave energy, the temperature rises so as to achieve the effect of sterilization. Non-thermal effect refers to the electromagnetic field formed by microwave polar molecules of living organisms to produce a strong rotational effect, so that the microbial nutrient cell inactivity or destruction of microbial cells within the enzyme system, resulting in the death of microorganisms.
Microwave sterilization is characterized by strong penetration, energy saving, high heating efficiency and wide application range. And microwave sterilization is easy to control, uniform heating, food nutrition, composition and color, aroma, taste by sterilization is basically close to the natural quality of food. Microwave sterilization is mainly used for meat, fish, soy products, milk, fruit and beer.
Eight, ultraviolet sterilization is the use of ultraviolet light irradiation material, so that the surface of the microbial cells within the nucleoprotein molecular structure changes and cause death. Ultraviolet light can only be transmitted along the straight line, the lamp from the surface of the object shall not exceed 1 m, and should reach a sufficient irradiation dose (kill bacterial spores should reach 100000UW.s/cm²), used for air disinfection requires not less than 1.5W per square meter, the irradiation time of not less than 30min, the lamp from the ground is less than 2 m. Lamps are generally life of 1,000 hours every half a year to monitor the intensity of radiation Once every six months to monitor the radiation intensity, less than 70uw/cm² should be replaced. However, ultraviolet sterilization by the relative humidity, when the relative humidity in the clean room > 60%, the sterilization effect is significantly weakened, relative humidity > 80%, should not be used.
Nine, resistance sterilization technology is the use of electric current through the food, food in the polar molecules in the electrode polarity of the high-frequency changes, constantly rotating friction and heat generation, to kill the role of living organisms.
X. Ozone sterilization uses the principle of high-voltage discharge to produce ozone, which destroys the structure of viruses and bacteria, thus achieving the purpose of disinfection. The advantage is that the gas diffusion is uniform, permeability is good, overcoming the problem of sterilization of ultraviolet sterilization exists in the dead zone of disinfection, there is no disinfectant residue. Ozone acts slowly, generally need 60-120min to achieve the purpose of disinfection, and ozone will irritate the human respiratory tract, causing discomfort. Although most of the microbial effect is ideal, but the effect of fungi is not ideal, for example, mold.
Eleven, irradiation sterilization technology irradiation is the use of X-rays, γ-rays or accelerated electron rays on the penetration of food in order to achieve the death of food microorganisms and pests in a cold sterilization disinfection method. Irradiated food or organisms will form ions, excited state molecules or molecular fragments, and then these products interact with each other to generate compounds different from the original substance. Will also occur a series of biochemical effects, resulting in pests, insect eggs, microorganisms, proteins, nucleic acids and promote biochemical reactions in the body of the enzyme is damaged, inactivated, and then terminate the food erosion and growth of the aging process, to maintain quality and stability.
Twelve, high-voltage electric field pulse sterilization technology high-voltage electric field pulse sterilization is generated between the two electrodes instantaneous high-voltage, pulsed electric field effect on food. High-voltage electric pulse treatment can destroy the cell membrane of bacteria, change its permeability, thus killing the cells. High-voltage electric pulse sterilization is usually carried out at room temperature, and the treatment time is tens of milliseconds. Therefore, compared with fresh food, the food processed in this way has little change in physical properties, chemical properties, nutrients, and no difference in flavor and taste. And sterilization effect is obvious, to achieve the requirements of commercial sterility, especially for heat-sensitive food, has a broad application prospects.
Thirteen, membrane filtration sterilization technology with the development of materials science, a variety of materials can be used for the separation of the membrane appeared one after another, membrane separation technology has been widely used in food, biopharmaceutical and other industrial production, such as the extraction of biochemical substances, the preparation of pure water, juice concentration. Membrane separation process is roughly divided into two types according to the different driving force.
One is to pressure as the driving force of the membrane process, such as ultrafiltration, micro-vacuum filtration, reverse osmosis; the other is to power as the driving force of the membrane process, called ion exchange, such as electrodialysis. Membrane filtration sterilization technology has the advantages of less energy consumption, operation at room temperature, suitable for heat-sensitive materials, process applicability, etc. Its application prospects are broad, and it is now widely used in the filtration and sterilization of food, biochemicals, pharmaceuticals, dairy products, fruit juices and so on. Food engineering sterilization technology is also a lot, such as chlorine dioxide sterilization technology, chlorine sterilization technology, electronic sterilization technology, heating and pressurization and sterilization technology, heating and chemicals and sterilization technology, heating and radiation and sterilization technology, electrostatic sterilization technology, etc., these technologies are being studied and applied.
Fourteen, ultrasonic sterilization technology ultrasound is a frequency greater than 10kHz sound waves. Ultrasonic waves are longitudinal waves like ordinary sound waves. Ultrasound and sound transmission medium interaction contains a huge amount of energy, when encountered with the material to produce rapid alternation of compression and expansion, this energy in a very short period of time is enough to play a role in killing and destroying microorganisms, but also able to produce such as homogenization of food, catalytic ageing, cleavage of macromolecular substances and other roles, with other physical sterilization methods are difficult to obtain the effect of multiple, so that it can better Improve food quality and ensure food safety.
Fifteen, low-temperature plasma sterilization technology low-temperature plasma sterilization technology is an emerging in the traditional heating sterilization technology after the food non-heating sterilization technology, the technology has a low temperature, short time, small damage, fewer residues and no pollution and other advantages. Compared with the traditional heat sterilization technology, low-temperature plasma technology in the sterilization process has a safe and efficient, as well as the generation of active substances can be highly effective sterilization and is not easy to residue and other characteristics.
Sixteen, high hydrostatic pressure technology High Hydrostatic Pressure Technology (High Hydrostatic Pressure, HHP) is the use of water as a medium to transfer pressure to the product, the role of non-covalent bonds, destroy the structure of the polymer material, causing material modification, in order to achieve inactivation of most of the pathogenic bacteria and spoilage bacteria, so that proteins, starch and other large molecules of material denaturation and inactivation of the purpose, and for small molecules of material such as polyphenols, vitamins, amino acids and other substances. substances such as polyphenols, vitamins, amino acids, flavor substances, etc. have less effect. Food Processing