Study on the anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of Sophora alopecuroides on lipopolysaccharide induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells
Inflammation is a defensive response that occurs when the body is attacked or infected by harmful internal and external stimuli such as pathogens. It triggers an immune response to protect the body. When the immune system is excessively or continuously activated, it can lead to a series of inflammation related diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, tumors, etc., ultimately resulting in permanent or temporary inflammation. Macrophages play a central role in the initiation, maintenance, and alleviation of inflammatory responses, and their sustained accumulation and activation are indicative of chronic inflammation. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) can activate macrophages and promote their secretion of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF – α), interleukin-1 β (IL-1 β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), nitric oxide (NO), etc. The excessive release of these inflammatory mediators can lead to organ damage and chronic diseases. NF – κ B plays an important role in regulating processes such as cell apoptosis and inflammatory response, and is an important target for anti-inflammatory therapy.
Sophora alopecuroides L, also known as Sophora alopecuroides, is a plant belonging to the Leguminosae family of the Sophora genus. It is distributed in various provinces in northwest China and Central Asian countries, and has the functions of clearing heat and detoxifying, relieving pain and inflammation, drying dampness and stopping dysentery. It is an important medicinal plant in the northwest region of China. Sophora alopecuroides mainly contains alkaloids, flavonoids, organic acids, polysaccharides, volatile oils, steroids, phenols and other components. Alkaloids have anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antibacterial and immune regulating effects, flavonoids have anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antioxidant effects, and polysaccharides have immune regulating and anti-tumor functions, which can effectively improve the body’s immunity and play an important role in anti-tumor and immune promotion. The above studies are all based on a certain chemical composition group of Sophora alopecuroides, and traditional Chinese medicine has the characteristics of multi-component, multi-target, and multi pathway combined effects, which can achieve the same or even better therapeutic effect with lower drug doses, including effective part compatibility and effective ingredient compatibility. Therefore, it is necessary to explore whether different chemical composition groups of Sophora alopecuroides can enhance efficacy. This article uses LPS induced RAW 264.7 cells as an inflammatory model for screening anti-inflammatory drugs in Sophora alopecuroides, and explores the conventional water decocting extract (WDE), water ultrasonic extract (WUE), 75% ethanol reflux extract (ERE), 75% ethanol ultrasonic extract (EUE), as well as the total alkaloids extract (TAE), total flavonoids extract (TFE), total polysaccharides extract (TPE) of Sophora alopecuroides and their nine combinations of different effective parts. The anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of action of (1:1:1, 1:2:2, 1:3:3, 2:1:2, 2:2:3, 2:3:1, 3:1:3, 3:2:1, 3:3:2).
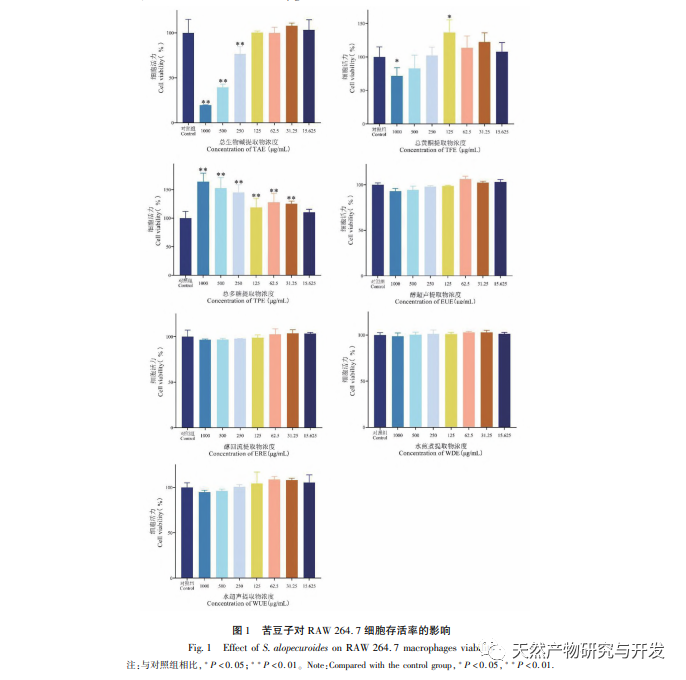
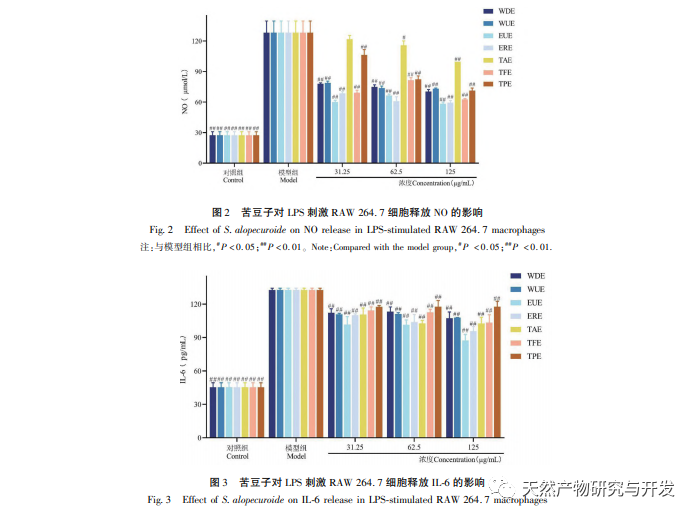
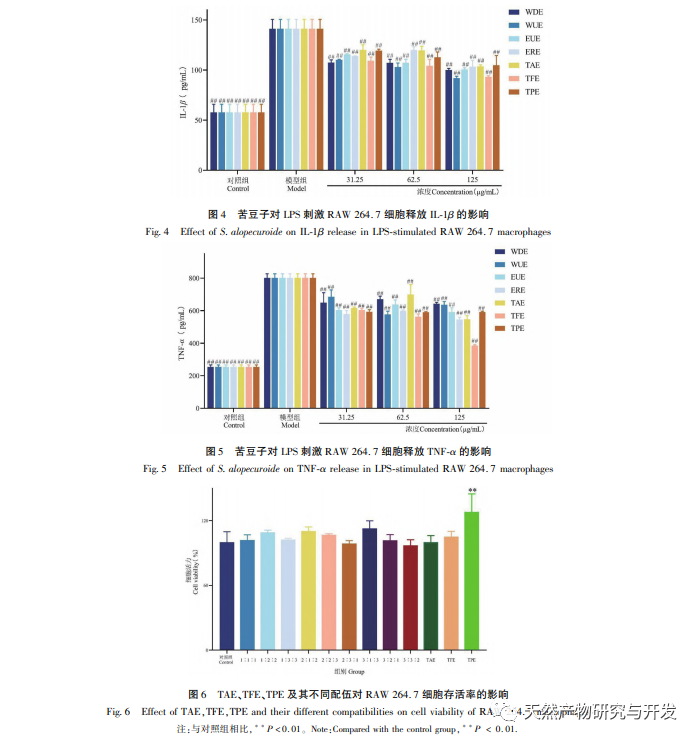
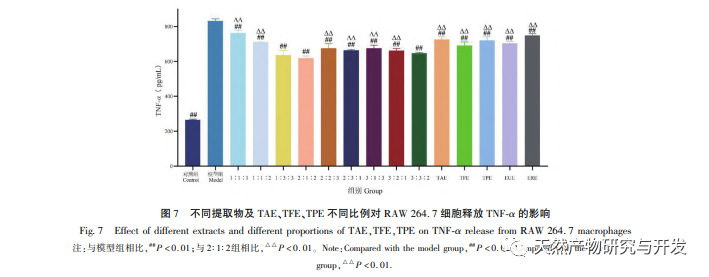
Macrophages participate in the immune response of the body. When stimulated by LPS, macrophages trigger signaling pathways (such as NF – κ B) to promote the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as NO, TNF – α, IL-1 β, IL-6, etc. Excessive production of NO is closely related to the occurrence of inflammation. An increase in the levels of TNF – α and IL-6 can promote the secretion of more pro-inflammatory cytokines by cells. IL-6 is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine that can induce the activation of B cells and T cells, and participate in the immune response of the body. IL-1 β is upregulated in acute or chronic inflammation. The results of this study found that after LPS treatment of RAW 264.7, the release of NO, TNF – α, IL-6, and IL-1 β significantly increased, indicating the successful establishment of an in vitro inflammation model. Sophora alopecuroides WDE, WUE, EUE, ERE and their TAE, TFE, TPE can all inhibit the production of NO, TNF – α, IL-6, and IL-1 β in RAW 264.7 cells stimulated by LPS, among which TFE, EUE, ERE The inhibitory effect of TAE is more significant After blending TFE and TPE in different ratios, it was found that they could inhibit the release of TNF – α to varying degrees. Among them, except for the 1:1:1 and 1:1:2 combinations, the other seven combinations had better inhibitory effects on the release of TNF – α than when acting alone. The 2:1:2 combination had the best inhibitory effect, demonstrating a significant synergistic effect.
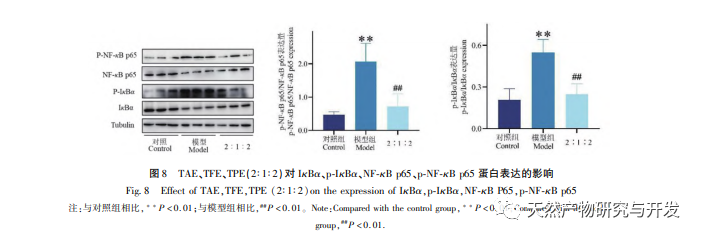
To explore the molecular mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of Sophora alopecuroides, this study used WB to detect the expression of key proteins IkB α, NF – κ B p65, and p-IkB α, p-NF – κ B p65 in the NF – κ B signaling pathway. NF – κ B is a key regulatory factor in inflammation, which can regulate the transcription of many key inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF – α, etc. LPS binds to TLR4 receptors to activate the NF – κ B signaling pathway, which is an important link in inducing macrophages to release inflammatory mediators. When cells are stimulated, the inhibitory protein IkBa that binds to NF – κ B is rapidly phosphorylated to p-IkB α under the action of IkB α kinase, releasing active p-NF – κ B p65 into the nucleus, thereby promoting the synthesis and secretion of inflammation related factors. In recent years, there have been extensive reports on the anti-inflammatory effects of alkaloids, flavonoids, and polysaccharides. For example, studies have found that Sophora flavescens alkaloids can alleviate LPS induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages by inhibiting IkB α phosphorylation and p-NF – κ B p65 nuclear translocation. Zhao et al. found that Sophora flavescens total alkaloids may alleviate dextran sulfate induced colitis by inhibiting NF – κ B activation. Studies have shown that flavonoids in traditional Chinese medicine can reduce the phosphorylation levels of proteins IkB α and p65 in the NF – κ B signaling pathway to exert anti-inflammatory effects. Li et al. found that Sophora flavescens total flavonoids can exert immunomodulatory effects on ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, and Cistanche polysaccharides can inhibit the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. NF – κ B MAPK and STAT3 activation are used to inhibit LPS induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages, while Qu et al.’s study showed that polysaccharides from Pinus koraiensis can inhibit LPS induced inflammation by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. At present, there is relatively little research on the effects of the combination of alkaloids, flavonoids, and polysaccharides on inflammation. This study found that when the combination of TAE, TFE, and TPE in Sophora alopecuroides was used, the phosphorylation of NF – κ B p65 and IkB α proteins was significantly reduced, and the expression of p-IkB α and p-NF – κ B p65 proteins was inhibited. This indicates that the combination of Sophora alopecuroides total biomass, total flavonoids, and total polysaccharides can alleviate LPS induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages by inhibiting the activation of the NF – κ B pathway.
In summary, this study mainly compared the anti-inflammatory activity of conventional WDE, WUE, EUE, ERE and their different effective parts TAE, TFE, TPE and nine combinations (1:1:1, 1:2:2, 1:3:3, 2:1:2, 2:2:3, 2:3:1, 3:1:3, 3:2:1, 3:3:2) of Sophora alopecuroides in vitro. It was found that the combination of TAE, TFE, TPE (2:1:2) had the best inhibitory effect on LPS induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells, and it exerted anti-inflammatory effects in vitro by inhibiting the activation of the NF – κ B inflammatory pathway. This experiment only completed the screening of anti-inflammatory drugs at the cellular level, and only screened the compatibility combinations of different pharmacological parts of Sophora alopecuroides. However, there are still problems such as complex chemical composition, unclear pharmacological components and material basis of their effects, which require further research.
