Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors among women in the world, and it is also the main cause of cancer related deaths among women. The risk of breast cancer is related to many factors, such as age, genetics, reproductive factors and obesity. At present, hormone therapy, surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the main strategies for the treatment of breast cancer. However, because breast cancer is a complex and highly heterogeneous disease, multi drug resistance and serious side effects limit the therapeutic effect of these treatment methods. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop more effective and safer anti breast cancer drugs. In cancer treatment, traditional Chinese medicine and natural products have the advantages of multi-level, multi pathway, multi-target, high efficiency, and minimal side effects, demonstrating good anti-tumor effects. While traditional Chinese medicine and its active compounds have the characteristics of definite curative effect, small toxic and side effects, rich targets and diverse mechanisms against breast cancer. Anti breast cancer drugs from traditional Chinese medicine have good prospects for development and application.
Solanum nigrum L. is a medicinal plant in the Solanaceae family, widely distributed in Europe, Asia, and the Americas. Longkui has anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, and antiepileptic effects. Its main bioactive components include steroidal saponins, alkaloids, phenols, and polysaccharides. Modern research shows that Solanum nigrum and its active ingredients (mainly steroids, organic acids, lignans and others) can be used to treat different types of cancer, such as liver cancer, cervical cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, etc. Solanum nigrum methanol extract can induce autophagy and apoptosis of breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468. Solanum nigrum water extract and ethanol extract have cytotoxicity to breast cancer cell line MCF-7, and induce apoptosis and cycle arrest of MCF-7 cell line. In addition, Solanum nigrum can also play an anti breast cancer role through epigenetic modulation. Diosgenin is a kind of natural steroid saponin from Dioscorea plants, which has good anti-tumor activity. Research shows that diosgenin can inhibit the migration of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by inhibiting Vav2 activity, and affect the migration behavior of cells, revealing that diosgenin may have anti metastasis potential. Although the above research has made some progress, the material basis, action targets and detailed molecular mechanism of Solanum nigrum against breast cancer are not completely clear. Based on the technical methods of network pharmacology and molecular docking, this study constructed a multi-level and multi angle “drug target pathway disease” network relationship, and verified it by combining in vitro cell experiments. It was clear that the effective component of Solanum nigrum could inhibit the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells in breast cancer and induce cell apoptosis, and preliminarily explored the molecular mechanism of action of diosgenin, providing a reference for further research of Solanum nigrum in the treatment of breast cancer.




Solanum nigrum is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Modern pharmacology has found that Solanum nigrum has various biological activities, most of which are concentrated in the field of anti-tumor. Studies have shown that its active ingredient, diosgenin, can exert anti-tumor effects by regulating various cellular signaling pathways, and is closely related to many important molecular targets such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
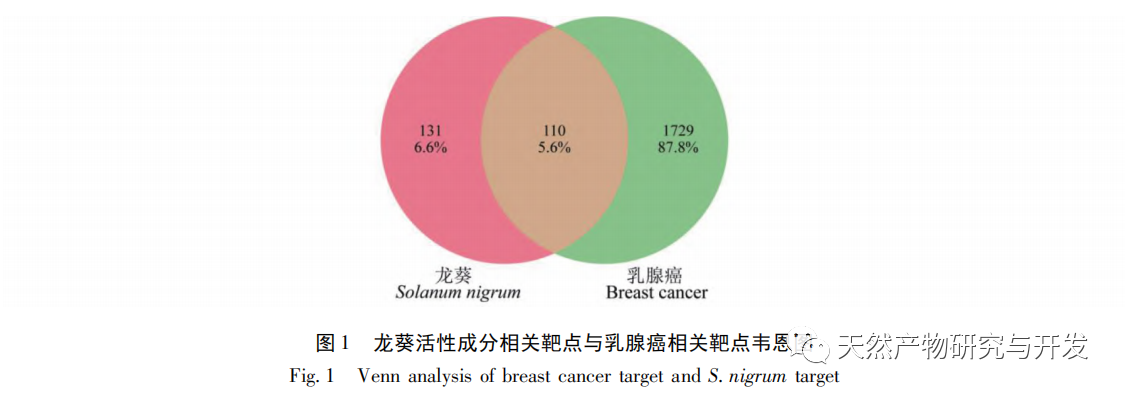
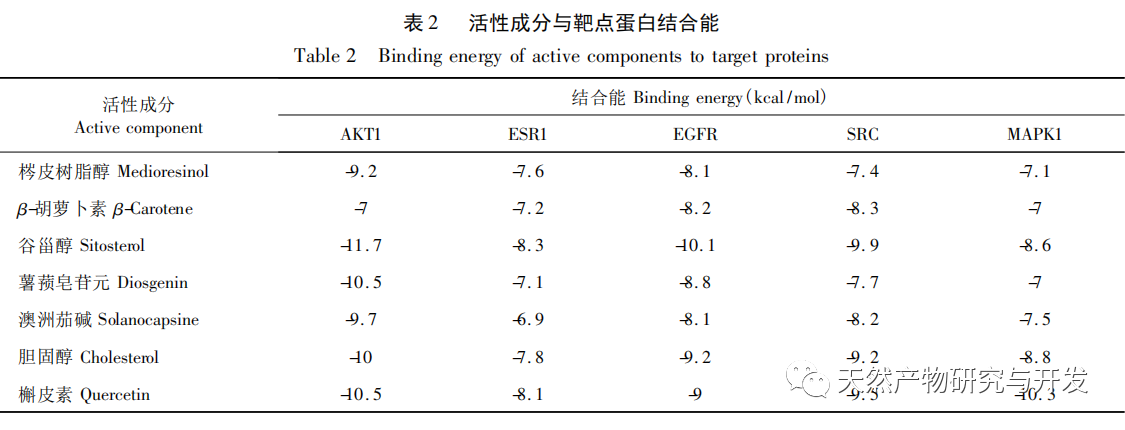
Through the analysis of TCMSP database of network pharmacology, this study screened seven effective active ingredients, namely, fraxinol, β – carotene, sitosterol, diosgenin, solanine, cholesterol and quercetin. The intersection was obtained by mapping the relevant targets of the active ingredients of Solanum nigrum with the breast cancer disease target introduction line software VENNY 2.1. At the same time, the PPI network analysis showed that there was close relationship between these intersection targets. Studies have shown that quercetin, Australian solanine, and sitosterol have pharmacological effects such as inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and inducing tumor cell apoptosis. Diosgenin can promote the apoptosis of breast cancer MCF-7 cells and Skp2 cells. From this, it can be seen that the active ingredients of Solanum nigrum, such as quercetin, solanine, sitosterol, and dioscin, can exert anti-tumor effects.
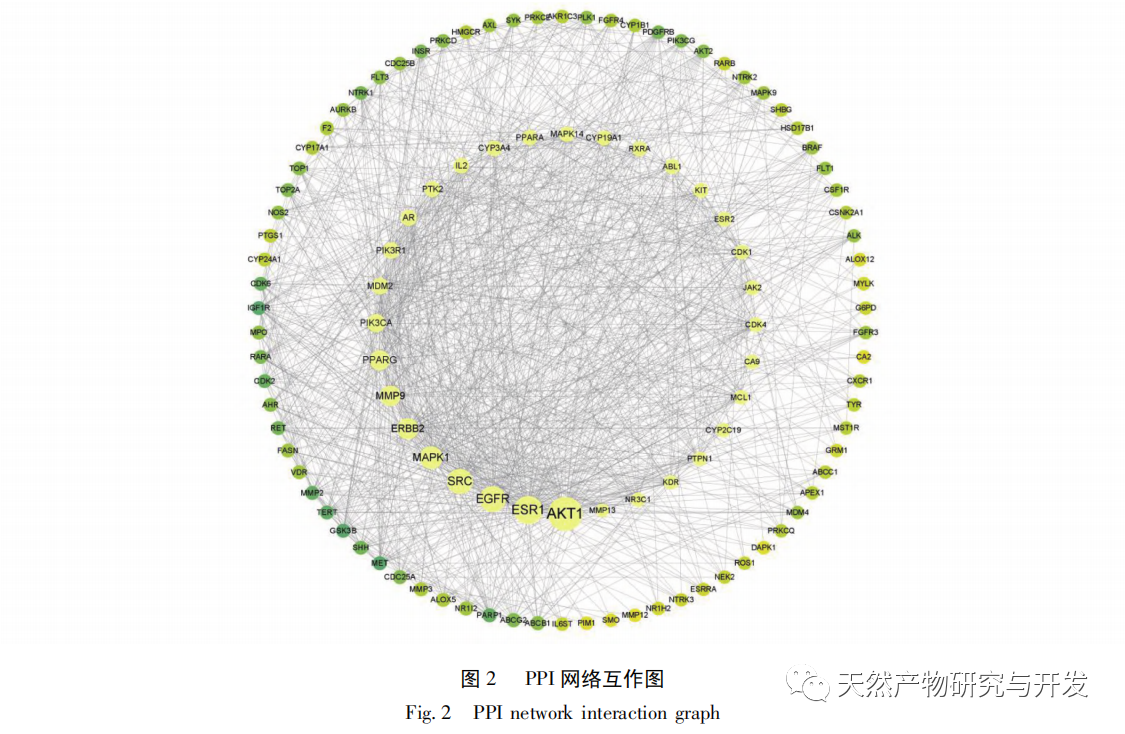
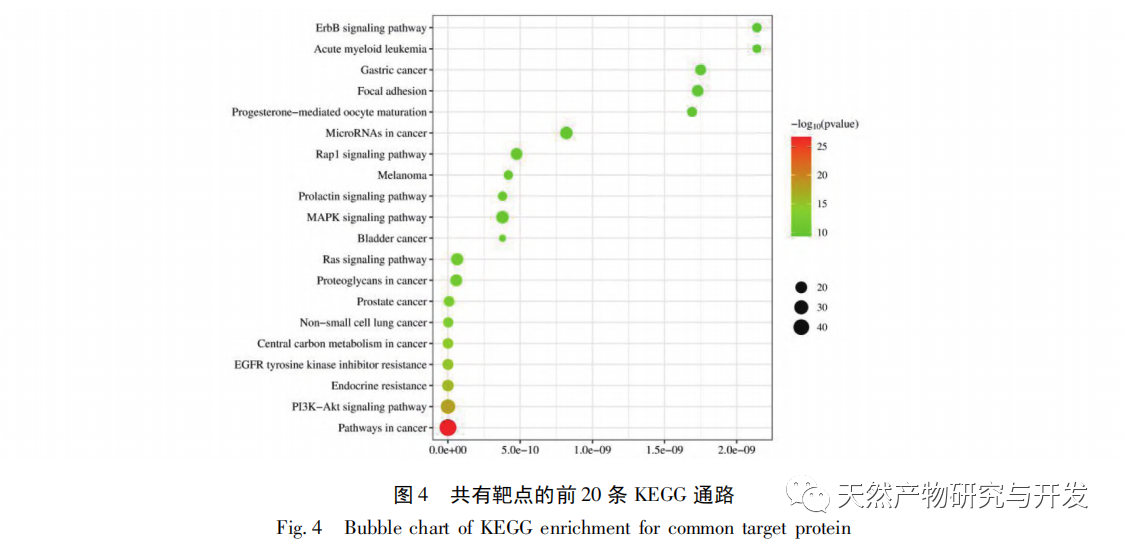
According to the compound target network diagram, 110 targets were obtained after the intersection of Solanum nigrum and disease targets. Further screening found that ERBB2, EGFR, KIT, SRC, ESR1, AKT1, MAPK1, PIK3CA, etc. were the target proteins of the effective ingredients of Solanum nigrum in the treatment of breast cancer. Among them, resveratrol, diosgenin, and quercetin all act on AKT1 and EGFR targets, and AKT (serine/threonine kinase) and EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) play important roles in cell proliferation, migration, and metabolism. Therefore, targeting AKT and EGFR is a very attractive treatment strategy for breast cancer. The results of this study indicate that AKT1 and EGFR and other targets play an important role in the development of breast cancer, and may be potential targets of Solanum nigrum in the treatment of breast cancer. GO enrichment analysis shows that the target genes of Solanum nigrum against breast cancer involve biological processes such as positive regulation of kinase activity, binding protein serine/threonine kinase activity, positive regulation of MAPK cascade, positive regulation of PI3K signal, ATP binding, etc. These key processes play an important role in Solanum nigrum’s treatment of breast cancer. The KEGG results showed that a total of 137 signaling pathways were enriched, including cancer pathway, PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway, Rap1 signaling pathway, etc.
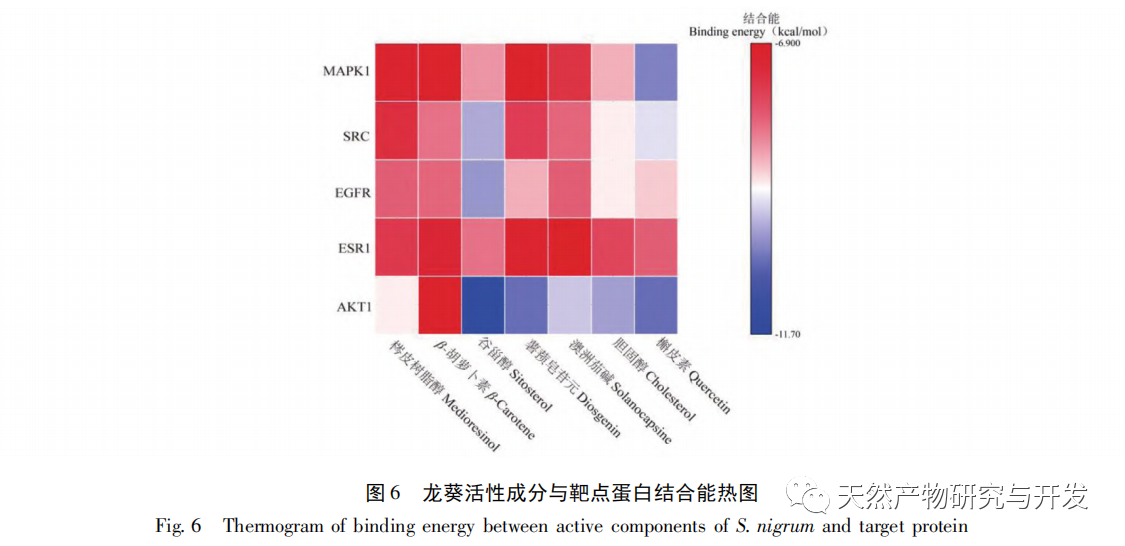
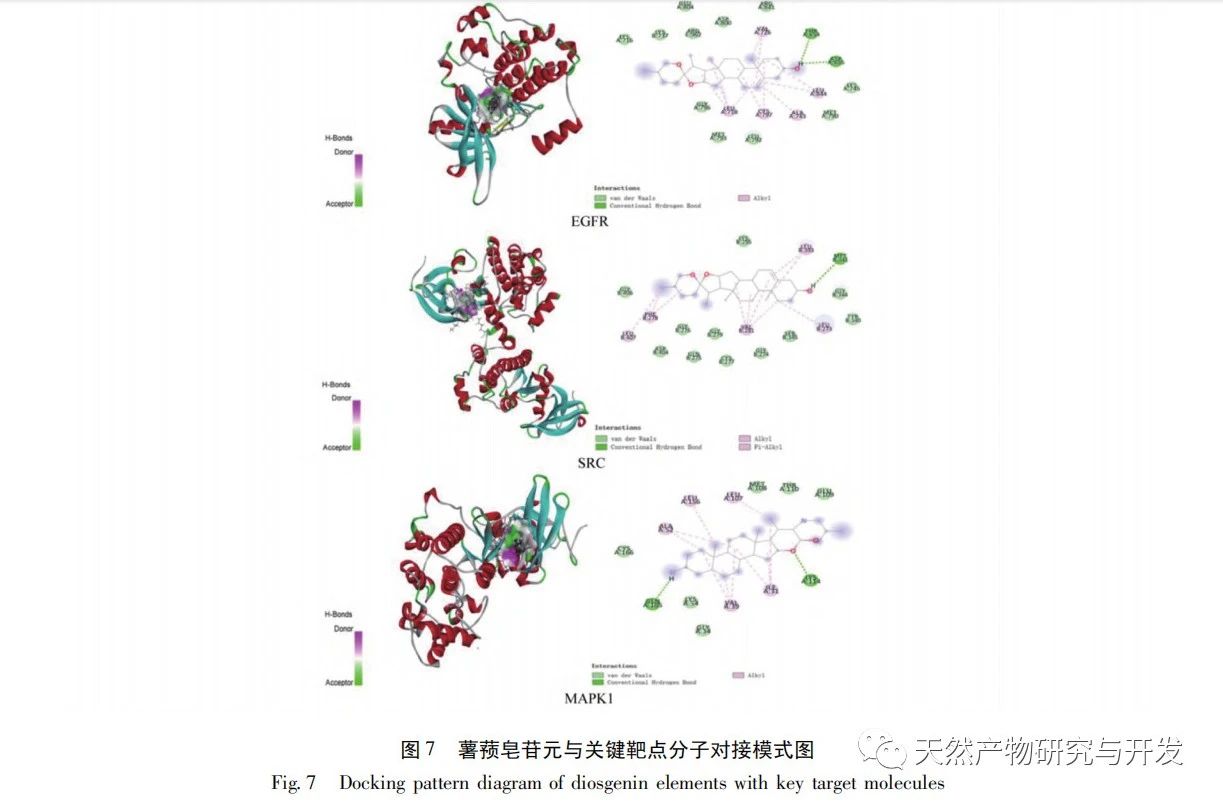
Molecular docking technology was used to explore the affinity between the key active components and target proteins of Solanum nigrum. The results showed that the active components such as quercetin, sitosterol and diosgenin had good binding activity with the target AKT1, EGFR, ESR1, SRC and MAPK, reflecting that the main mechanism of the main active components of Solanum nigrum, sitosterol and quercetin in the treatment of breast cancer may be closely related to the above active components and targets. Solanum nigrum may have a certain therapeutic effect on breast cancer through multiple targets and multiple signal pathways.
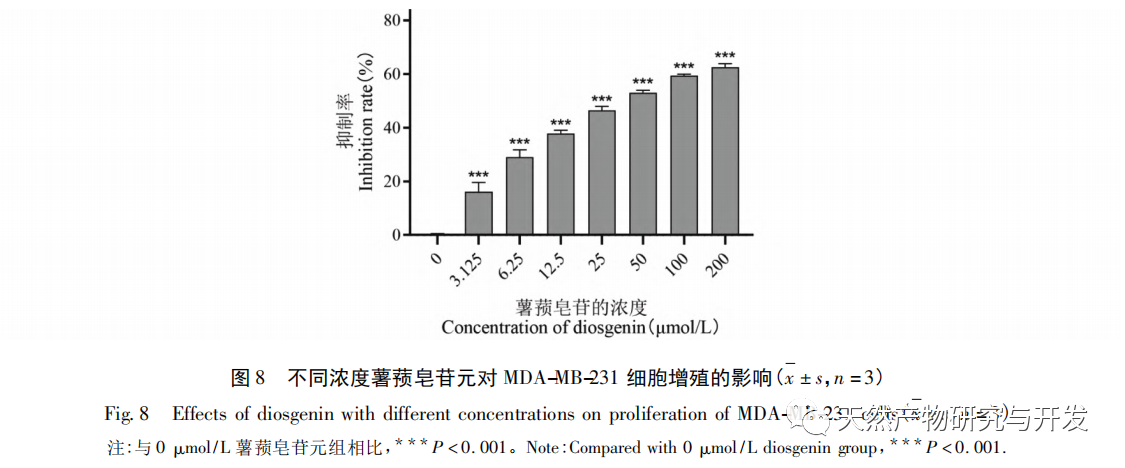
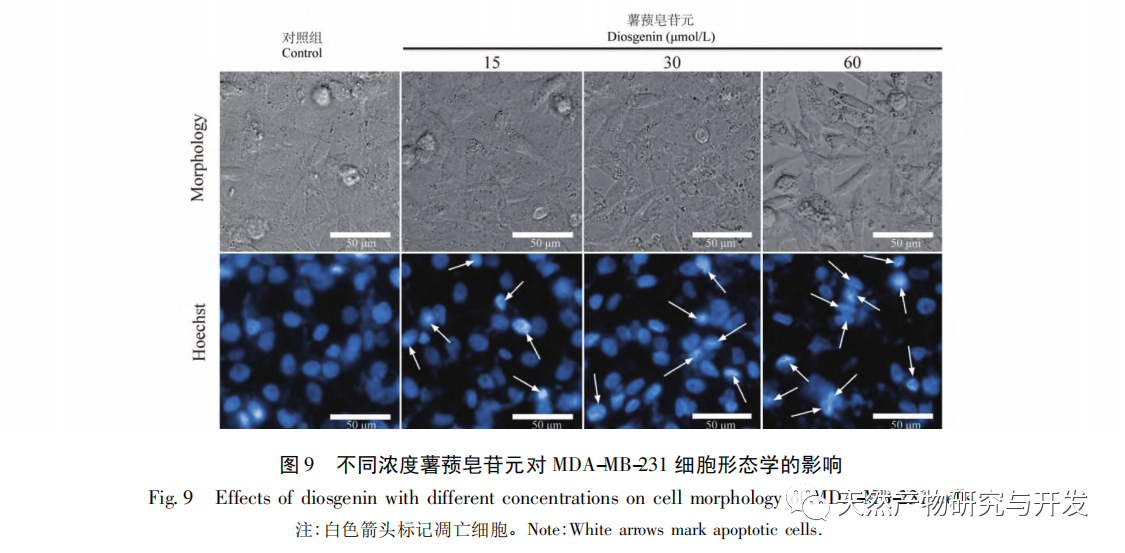
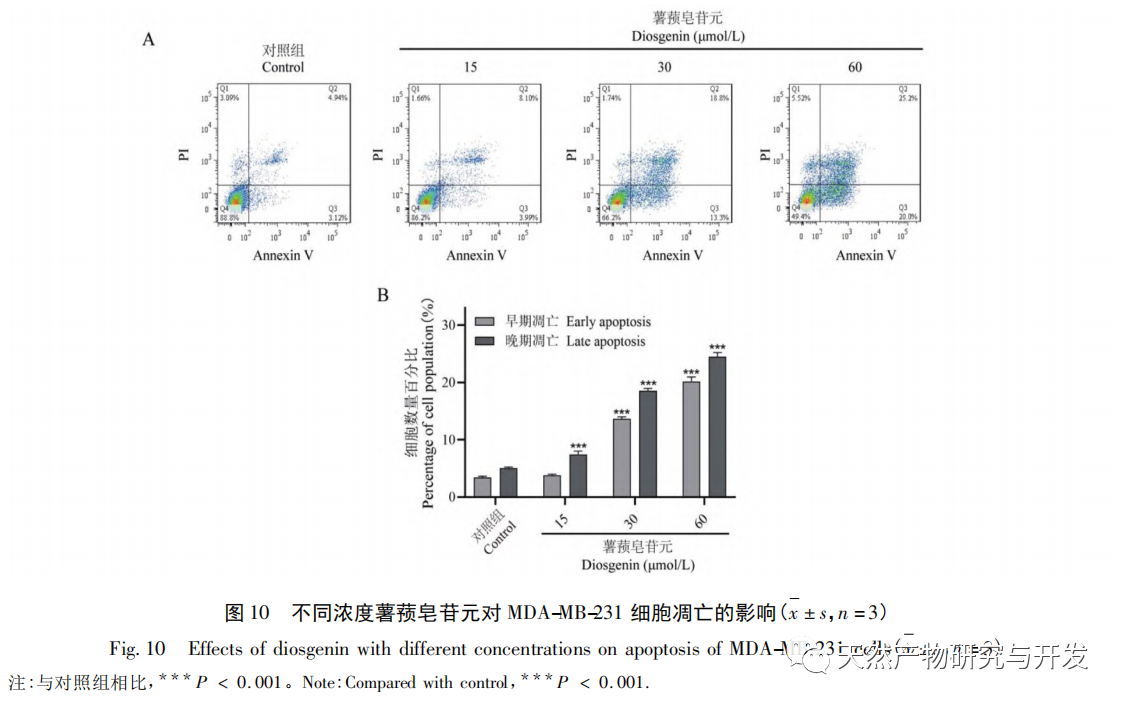
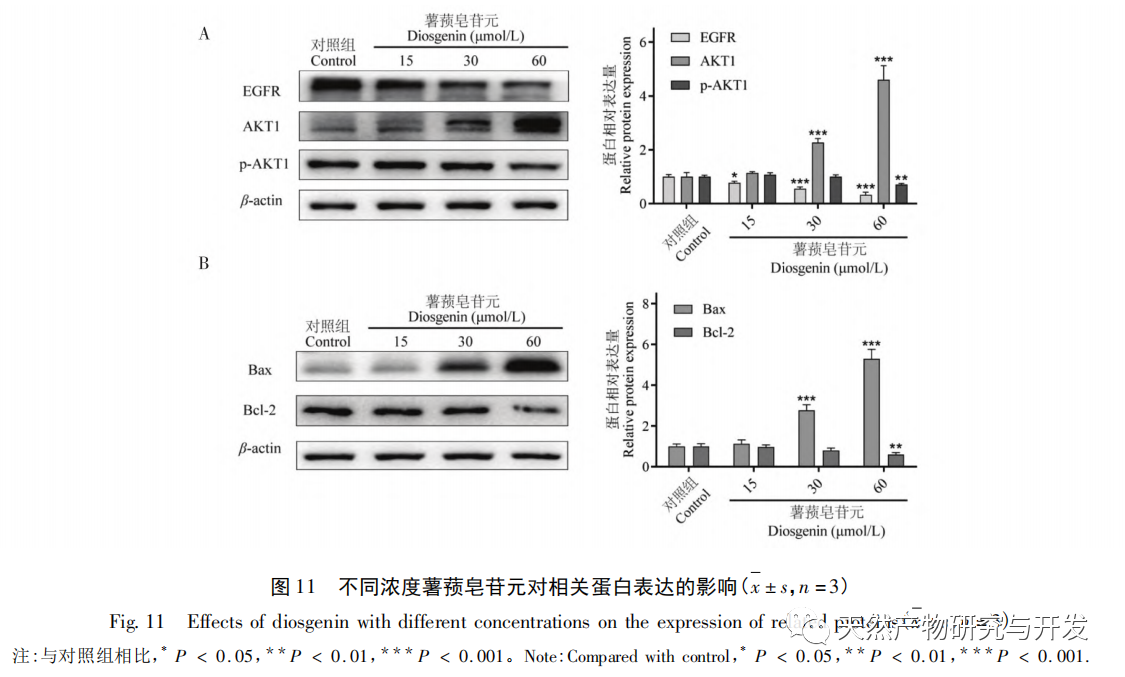
Based on the results of molecular docking research, the main active ingredient of Solanum nigrum, Diosgenin, was selected for anti-tumor experiments, and the regulatory effect of Diosgenin on its predicted targets EGFR and AKT1 was verified. To explore the potential mechanism of diosgenin against breast cancer. The experimental results showed that dioscin can inhibit the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells and induce apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells. Dioscin can downregulate the expression of EGFR protein and upregulate the expression of AKT1 protein in cells. It is worth noting that dioscin can downregulate the phosphorylation level of AKT, and at the same time, it can upregulate the expression of pro apoptotic protein Bax and downregulate the expression of anti apoptotic protein Bcl-2.
To sum up, this study applied the network pharmacology data platform to analyze and screen the main active ingredients of Solanum nigrum, and analyzed the multi-component, multi target, multi pathway mechanism of Solanum nigrum in treating breast cancer, and carried out experimental verification in vitro. The results showed that Solanum nigrum may act on AKT1, EGFR and other targets to play a role in treating breast cancer, providing ideas and basis for further in-depth research on the related mechanism of Solanum nigrum in treating breast cancer and subsequent clinical application research of Solanum nigrum.
