Exploring the mechanism and efficacy verification of effective components of Scutellaria baicalensis on alcoholic liver disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Alcoholic liver diseases (ALD) have a wide clinical histological spectrum, including early simple hepatic steatosis, as well as mid to late stage alcoholic hepatitis, liver fibrosis, and alcoholic cirrhosis. The current best prevention and treatment method for ALD is still abstinence from alcohol, and clinical use of corticosteroids can only partially alleviate symptoms and provide short-term survival benefits. Currently, there are no corresponding specific drugs in clinical practice. According to the etiology, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations of ALD, traditional Chinese medicine divides ALD into three stages: the early stage of “wine stagnation” caused by dampness and heat, the middle stage of “wine addiction” caused by qi stagnation and blood stasis, and the late stage of “wine stagnation” caused by deficiency of positive qi. The treatment methods vary at different stages. In the early stage, the main focus is on soothing the liver and relieving depression, clearing heat and dampness. In the middle stage, the main focus is on promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis. In the later stage, the main focus is on strengthening the spleen and nourishing the liver and kidneys.
Scutellaria Radix is the dried root of Scutellaria baicalensis, a plant in the family Lamiaceae. It belongs to the category of heat clearing traditional Chinese medicine and has the effects of clearing heat and dampness, purging fire and detoxifying, stopping bleeding, and preventing miscarriage. It can be well used for the treatment of ALD in the early and middle stages. At the same time, combined with relevant studies on the liver protection of Scutellaria baicalensis, it can be found that Scutellaria baicalensis and its active ingredients can protect liver cells and reduce the degree of liver pathological damage by inhibiting oxidative stress response, suppressing inflammatory factor infiltration, reducing liver cell apoptosis, and regulating lipid metabolism. However, the pharmacological substance basis, action pathway, and mechanism of Huangqin in preventing and treating ALD are not yet clear. This study used network pharmacology, molecular docking technology, and in vitro cell experiments to preliminarily explore the active ingredients and corresponding pathways of action of Scutellaria baicalensis in preventing and treating ALD, in order to provide reference for in-depth research, new drug development, and clinical application of Scutellaria baicalensis and its active ingredients in preventing and treating ALD.

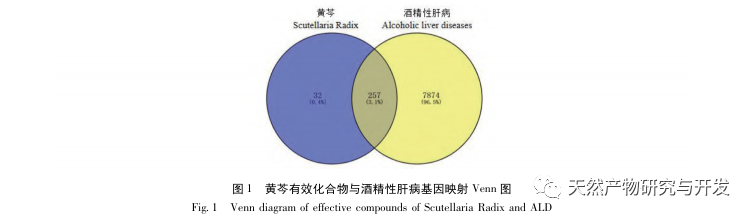


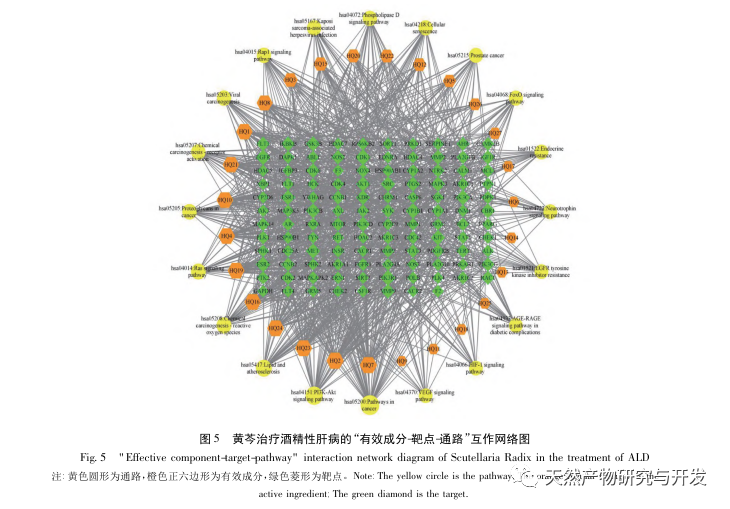
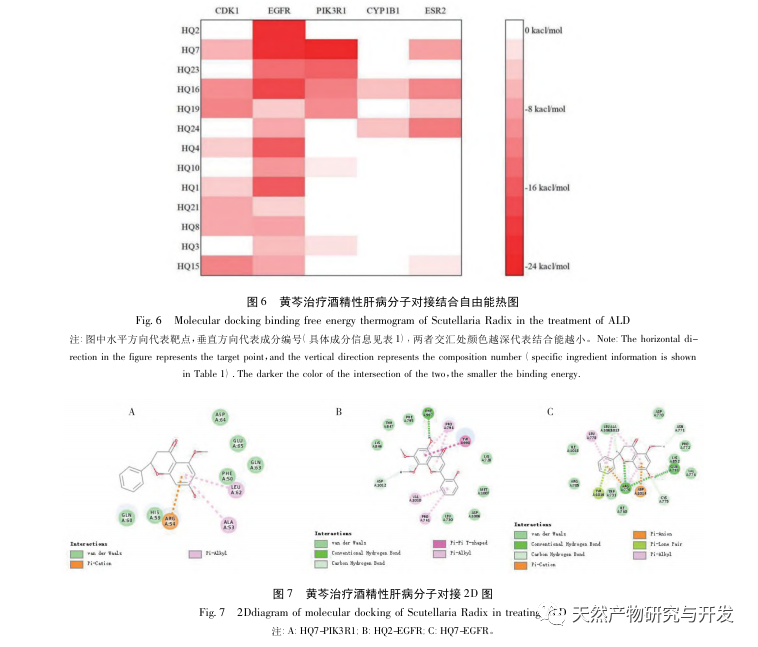
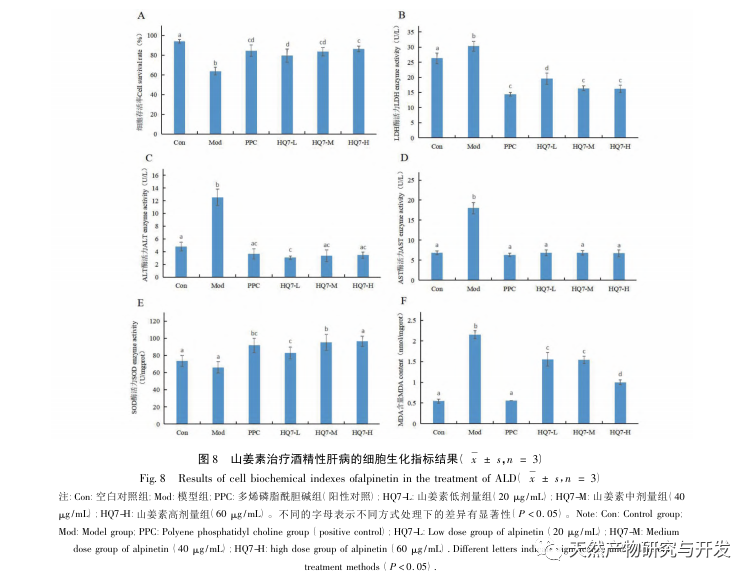
On the basis of the sustained good results in the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B and C in China, coupled with the rapid development of the economy and the widespread popularity of alcohol culture, the proportion of cases of liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and even patient deaths caused by ALD will continue to increase. There is no concept of “alcoholic liver disease” in the traditional Chinese medical system, but it can be classified according to its clinical manifestations, etiology and pathogenesis, and can correspond to “alcohol disease”, “alcohol injury”, “alcohol addiction”, “alcohol jaundice”, etc. The treatment methods mainly include strengthening the spleen and stomach, soothing the liver and promoting bile flow, clearing heat and dampness, and eliminating turbidity. The traditional Chinese medicine Scutellaria baicalensis belongs to the category of heat clearing and dampness drying drugs. Currently, Scutellaria baicalensis is mainly used in the early and middle stages of ALD. However, the pharmacological substance basis, action pathway, and mechanism of Scutellaria baicalensis in preventing and treating ALD are not yet clear, so it has certain research value.
Through the application of network pharmacology techniques, it can be found that the key core targets in protein interaction networks are SRC, AKT1, and PIK3R1. These three proteases may be structurally activated in almost all types of cancer through the activation of upstream signaling molecules or mutations in pathway components. Among them, SRC, as the first discovered carcinogenic gene, is involved in the phosphorylation of downstream target proteins in numerous signaling pathways. It has different pathways for regulating cell survival, adhesion, proliferation, motility, and angiogenesis. In addition, the constitutive activity of SRC can also promote and maintain the reprogramming of inflammation and cellular metabolism, thereby synchronizing with the development of the tumor microenvironment and actively maintaining tumor growth. AKT1, as a central member of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, can be activated by PIK3R1 encoding the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) regulatory subunit alpha (p85-ALPHA). Combined with the protein-protein interaction PPI diagram in this study, it can once again confirm the close upstream and downstream relationship between the two.
Among the top 20 signaling pathways obtained by KEGG enrichment, most of them also belong to the “carcinogenesis pathway”, indicating that Scutellaria baicalensis mainly treats ALD by preventing or inhibiting liver cell carcinogenesis. EGFR, as a typical tyrosine kinase receptor of the ErbB family, is highly expressed in the liver. After drinking alcohol, EGFR can be activated under the condition of binding to angiotensin II and its receptor AT1R. At the same time, EGFR can act as a hub of the Ras-Raf-1-MAP2K/MEK-MAPK/ERK cell signaling pathway, stimulating abnormal expression of PIK3R1 protein and affecting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is closely related to many inflammatory diseases and is considered one of the key signaling pathways in tumors. Previous studies have confirmed that Scutellaria baicalensis can promote the phosphorylation of p-PI3K, p-Akt, and Glut2 by upregulating the mRNA expression of IRS1, PI3K, Akt2, and Glut2, thereby overcoming damage to the PI3K/Akt insulin signaling pathway and actively improving hepatitis. Comparing the pathogenic factors of ALD, it can be found that it, like cardiovascular disease (CVD), includes inflammation, adipokines, dysbiosis of gut microbiota, oxidative stress, and psychological stress. Some studies have also shown that there is a direct relationship between ALD and CVD, and put forward the concept of liver heart axis, and combined with this study to screen the lipid and atherosclerosis signal pathways, suggesting that the treatment of ALD should not only focus on the liver itself, but also consider the impact of cardiovascular on it.
Comparing the binding energies in molecular docking, it can be found that resveratrol can be one of the key active ingredients in Scutellaria baicalensis for treating ALD. Shanjiangsu is widely present in ginger plants, and pharmacological experiments have confirmed its anti-cancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and endothelial repair effects. The human body mainly relies on microsomal CYP2E1 for alcohol metabolism, during which a large amount of intermediate products such as acetaldehyde and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced. On the one hand, acetaldehyde can form adducts with proteins and DNA, directly exerting carcinogenic toxicity. On the other hand, the accumulation of ROS can also cause changes in DNA structure and function, leading to cell cycle disorders and affecting gene transcription, translation, and other functions, thereby initiating or promoting cellular carcinogenesis. Research has shown that resveratrol can act as a signaling molecule to activate related pathways, effectively inhibiting cellular carcinogenesis while clearing ROS. Combined with in vitro cell experiments, it can be found that after administering different concentrations of mountain ginger extract, alcohol induced damage to liver cells can be effectively reduced, and related biochemical indicators ALT and AST are also significantly improved. Combined with the results of MAD and SOD, it suggests that resveratrol may exert its effect by increasing the enzyme activity of SOD to inhibit the oxidative stress response of the liver. However, its antioxidant effect may be far inferior to its anti-cancer effect, and further experimental research is needed.
In summary, this experiment preliminarily predicted the 27 active ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis through network pharmacology, indicating that a single traditional Chinese medicine can also be considered as a small-scale compound. Meanwhile, the 27 active ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis can exert therapeutic effects on ALD through 257 gene targets, among which the key core targets include SRC, AKT1, PIK3R1, etc. The enrichment analysis of KEGG signal pathway suggested that Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi could play a role in ALD through the pathways affecting cancer, PI3K Akt signal pathway, lipid and atherosclerosis and other signal pathways. Through molecular docking technology, while verifying the results of network pharmacology, the best effective ingredient for treating ALD with Scutellaria baicalensis was screened as kaempferol. Through in vitro cell experiments, it can be found that mountain ginger extract can significantly improve the alcohol induced damage status of rat liver cell BRL 3A. The results of this experiment can provide some theoretical basis for the treatment of ALD with Scutellaria baicalensis, but further exploration of the specific mechanism of action of Scutellaria baicalensis in treating ALD still requires a large number of pharmacological mechanism experiments.
