Isolation, purification, and in vitro inhibition of tumor cell proliferation by Qigui polysaccharides
The combination of Huangqi and Danggui is the most commonly used and representative tonifying qi and nourishing blood medicine in clinical practice. In the database of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions, the frequency of compatibility between Huangqi and Danggui is as high as 2632 times. Huangqi and Danggui are combined in a ratio of 5:1 to form Danggui Buxue Tang, which is a well-known formula for replenishing qi and generating blood. It is widely favored by traditional Chinese medicine researchers for its refined formula and precise therapeutic effect. Qi Gui medicine pairs can also be used as basic medicine pairs in combination formulas. There are no formulas such as Huangqi Danggui Jianzhong Tang, Buzhong Yiqi Tang, Guipi Tang, Shengyu Tang, Buyang Huanwu Tang that do not use Qi Gui medicine pairs. Clinical applications and research are mostly focused on this medicine pair. Modern pharmacological research has shown that Qigui medicine has effects such as promoting hematopoiesis, immune regulation, cardiovascular protection, and anti-tumor effects. Qigui medicine has a significant anti-tumor effect, showing significant inhibitory effects on colon cancer, lung cancer, leukemia, and other cancers.
Polysaccharides are abundant in Qigui medicinal herbs and are common macromolecular active ingredients in Huangqi and Danggui. They have effects such as improving anemia, anti-aging, anti fibrosis, and anti-tumor. Polysaccharides are important active ingredients in Qi Gui medicine for exerting blood replenishing effects. Compared with non polysaccharide components, the polysaccharide component of Danggui Buxue Tang has a stronger blood replenishing effect, which can significantly promote bone marrow hematopoiesis, accelerate blood cell differentiation and maturation, and increase the number of peripheral red blood cells in mice with blood deficiency. Moreover, Danggui polysaccharides have particularly significant blood replenishing activity. Qigui polysaccharides can also enhance immune and antioxidant functions, regulate the aging cell cycle and telomerase activity, delay cell aging, and alleviate oxidative damage in renal tissue of aging model mice. In addition, Qigui polysaccharides have a protective effect on CCl4 induced liver fibrosis injury and cyclophosphamide induced spleen and thymus injury. Polysaccharides are one of the main active substances in the anti-tumor effect of Qigui medicine, and the polysaccharides of Huangqi and Danggui, which make up Qigui medicine, have significant inhibitory effects on various tumors. Astragalus polysaccharide has significant effects on lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, etc. It can play an anti-tumor role by directly inhibiting the proliferation of tumor cells, inducing apoptosis and cycle arrest, activating the immune system, and regulating the inflammatory microenvironment. Angelica polysaccharides have outstanding effects on leukemia, melanoma, colon cancer, liver cancer, etc. They can exert anti-tumor effects by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, enhancing immunity, regulating autophagy, and inhibiting tumor cell invasion and migration. Domestic and foreign scholars have conducted extensive and in-depth research on the polysaccharide structures in the single herbs Huangqi and Danggui that make up the Qigui medicinal pair. At present, 34 homogeneous polysaccharides have been isolated from Astragalus membranaceus and 39 homogeneous polysaccharides have been isolated from Angelica sinensis. The primary structures of these polysaccharides, including molecular weight, monosaccharide composition, sugar residue composition, glycosidic bond configuration, and connection sequence, have been analyzed. However, current research on Qigui polysaccharides mostly involves optimizing the extraction process, and there are few reports on the related research of Qigui homogeneous polysaccharides. There has been no systematic study on the anti-tumor activity of Qigui drugs on polysaccharides. There have been no reports on whether Qigui medicine has a significant inhibitory effect on tumor cell proliferation in the novel structural polysaccharide. Based on previous research and relevant literature reports, this study isolated six types of Astragalus polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus medicinal pairs, and selected single herb Angelica polysaccharides or Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides that had significant inhibitory effects on human colon cancer cells HCT116, lung cancer cells A549, and leukemia cells K562. The proliferation inhibitory and apoptosis inducing effects of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides on three types of tumor cells were investigated, and it was found that two types of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides could significantly inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of HCT116 cells and A549 cells. This study provides a scientific basis for the development and further application of health products based on “Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides” and “Astragalus membranaceus Angelica medicinal pairs” with potential anti-tumor activity.
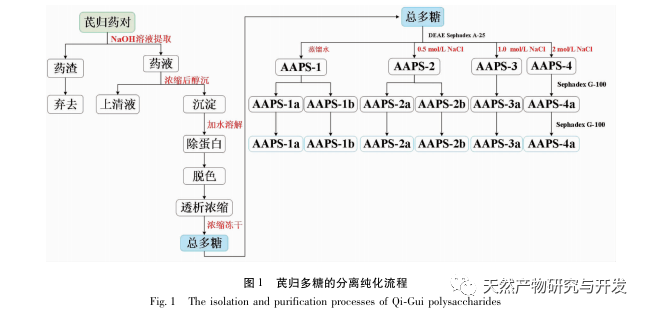
 Polysaccharides are composed of multiple monosaccharide units connected by glycosidic bonds and are one of the most abundant and important biological polymers in nature. Since the first report of the anti-tumor effect of shiitake mushroom polysaccharides in the journal Nature in 1969, the research and application of polysaccharides as drugs have attracted widespread attention from scholars at home and abroad. Traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharides have outstanding pharmacological activities in immune regulation, anti-tumor, anti diabetes, anti-oxidation, anti-virus, cardiovascular protection and neuroprotective activities, and are hot spots in the research field of active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine in recent years. At present, hundreds of highly purified “active polysaccharides” with significant pharmacological effects have been obtained from traditional Chinese medicines such as Ganoderma lucidum, ginseng, astragalus, Angelica sinensis, and wolfberry.
Polysaccharides are composed of multiple monosaccharide units connected by glycosidic bonds and are one of the most abundant and important biological polymers in nature. Since the first report of the anti-tumor effect of shiitake mushroom polysaccharides in the journal Nature in 1969, the research and application of polysaccharides as drugs have attracted widespread attention from scholars at home and abroad. Traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharides have outstanding pharmacological activities in immune regulation, anti-tumor, anti diabetes, anti-oxidation, anti-virus, cardiovascular protection and neuroprotective activities, and are hot spots in the research field of active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine in recent years. At present, hundreds of highly purified “active polysaccharides” with significant pharmacological effects have been obtained from traditional Chinese medicines such as Ganoderma lucidum, ginseng, astragalus, Angelica sinensis, and wolfberry.
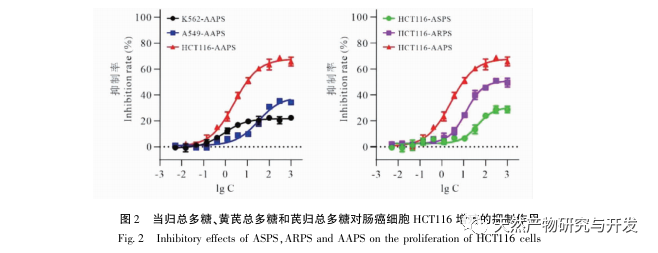
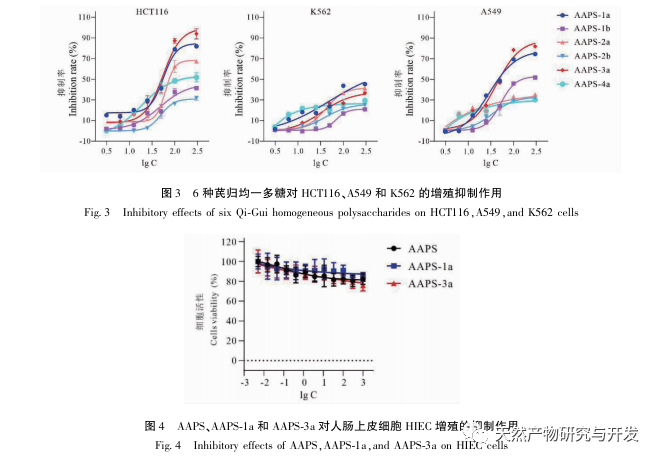
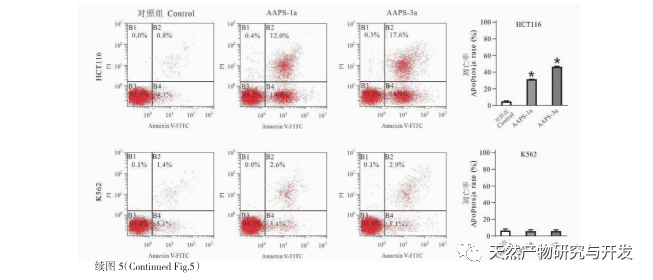
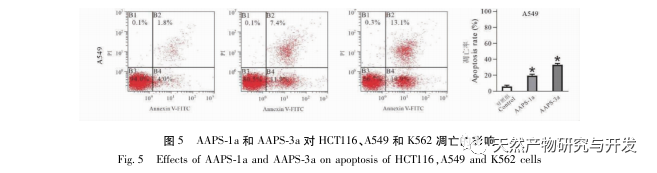
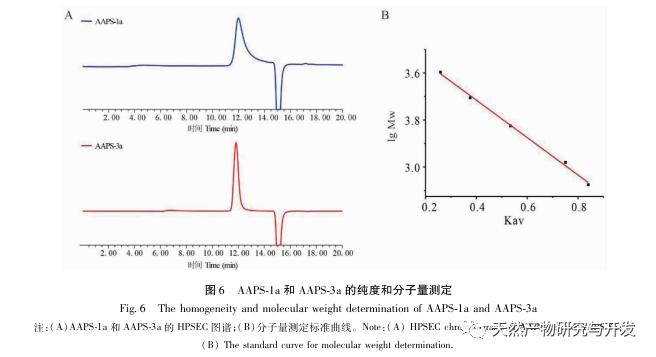
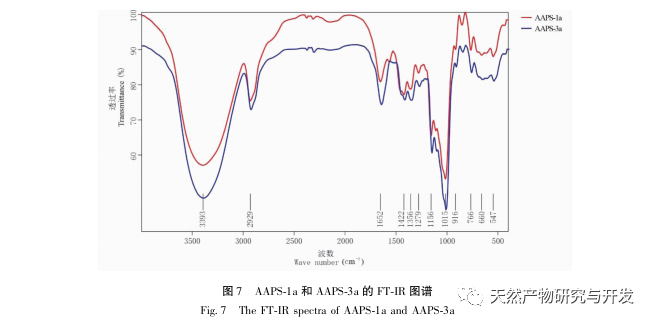
Compared with single ingredient polysaccharides, compound polysaccharides can combine the biological activities of various single ingredient polysaccharides to achieve synergistic effects. In addition, compound polysaccharides are affected by the source of medicinal materials, processing techniques, compatibility effects, and extraction methods, and their purity and structural characteristics are different from those of single herb polysaccharides. How to effectively and fully separate and purify traditional Chinese medicine compound polysaccharides based on the research of single herb polysaccharides, and clarify their structural basis and mechanism of action, has become one of the hotspots and difficulties in the study of Chinese medicine active substances in recent years. The uniform polysaccharide structure obtained from traditional Chinese medicine formulas such as Sijunzi Tang is different from that of single herb polysaccharides. Research has found that Qigui medicine has significant anti-tumor activity against polysaccharides, but the structural basis and mechanism of action of Qigui polysaccharides in anti-tumor treatment are still unclear. It has not been reported whether the structure and activity of the polysaccharide components in Qigui medicine are different from those of single herbs. In this study, total polysaccharides of Astragalus membranaceus (AAPS) were isolated from Astragalus membranaceus and screened for their tumor cell proliferation inhibitory activity. It was found that AAPS had a significant inhibitory effect on colon cancer cell proliferation. After further separation and purification of AAPS, it was found that two types of Qigui polysaccharides, AAPS-1a and AAPS-3a, can significantly inhibit the proliferation of human colon cancer cell line HCT116 and lung cancer cell line A549, and induce their apoptosis. Preliminary structural analysis indicates that AAPS-1a and AAPS-3a are homogeneous polysaccharides of Qigui with molecular weights of 7.3 × 105 and 8.5 × 104 Da, respectively. In summary, AAPS-1a and AAPS-3a are active Qigui homogeneous polysaccharides with potential anti-tumor effects. This study provides a research basis for the subsequent study of the anti-tumor substance basis and structure-activity relationship of Qigui polysaccharides, and provides important methods, ideas, and experimental evidence for the research of the macromolecular substance basis of traditional Chinese medicine formulas.
