The effect of resveratrol on proliferation, migration, and invasion of endometrial cancer HEC-1A cells
Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is the most common tumor in the female reproductive tract, second only to breast cancer, lung cancer and colorectal cancer. In the world, there are about 380000 new cases of endometrial cancer every year, and about 89000 people die of endometrial cancer every year, with its incidence rate increasing year by year. At present, the specific pathogenesis of endometrial cancer is still unclear, and its risk factors are related to obesity, metabolic syndrome, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome and other diseases that lead to endometrial hyperplasia caused by high estrogen status. Early endometrial cancer can be treated with surgery alone or surgery combined with adjuvant chemoradiotherapy, with a 5-year overall survival rate of 74% to 91%. Patients diagnosed with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer have a poor prognosis and low survival rate, with a five-year overall survival rate of approximately 15%. Conventional therapies such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy are expensive and prone to serious side effects. With the emergence of issues such as tumor recurrence and metastasis, as well as chemotherapy resistance, there is an urgent need to find easily accessible, low side effect, and low-cost alternative drugs to treat EC. Therefore, understanding the intrinsic mechanisms of tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion is of great value for exploring new methods for treating EC patients.
Piceatannol (PIC), with the chemical formula C14H12O4, is a natural polyphenolic compound widely distributed in plants such as passion fruit, passion flower, white tea, and Japanese tiger flowers. Research has shown that PIC has anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune regulatory effects similar to resveratrol, and plays an important role in cancer prevention and treatment due to its multi-target nature. Some studies have shown that PIC has chemopreventive activity and can block the migration and invasion of prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, etc. Abnormal activation of the Wnt/β – catenin signaling pathway can promote the occurrence and development of various malignant tumors, and regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Research has found that PIC can also act as an inhibitor of the Wnt/β – catenin pathway and an inducer of apoptosis in myeloma cells. At present, there are no research reports on the anti-tumor effect of PIC on endometrial cancer, and its mechanism of mediating the action of endometrial cancer cells is still unclear. This experiment aims to explore the preliminary anti-tumor mechanism of PIC by observing its effects on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of endometrial cancer cells, providing theoretical and experimental basis for the search for new strategies for treating endometrial cancer.
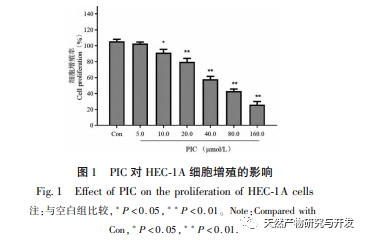
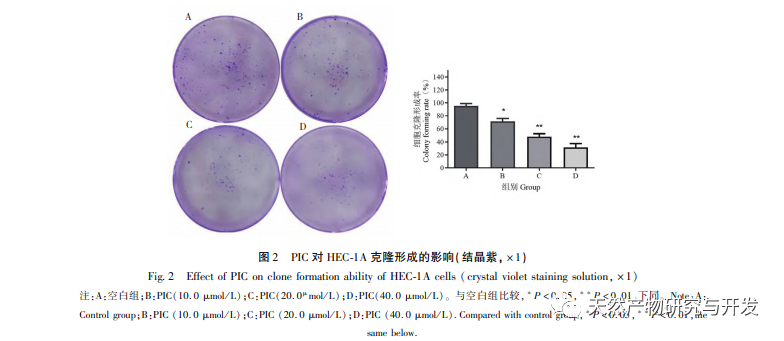
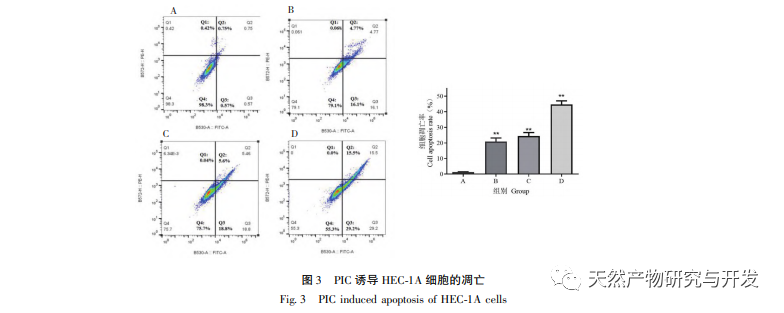
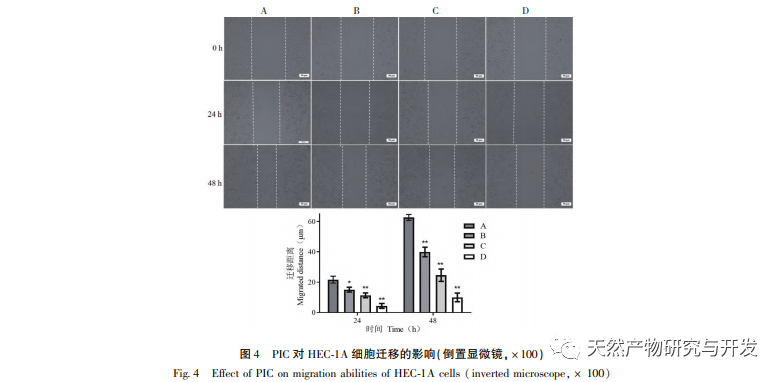
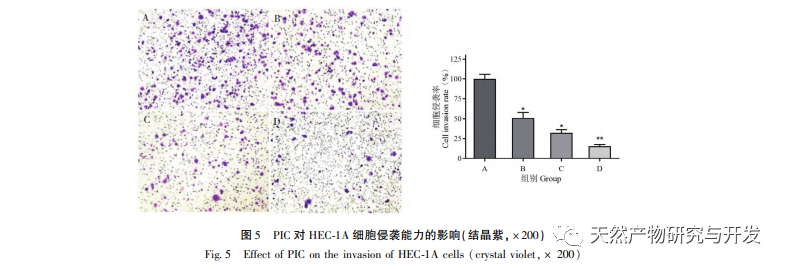
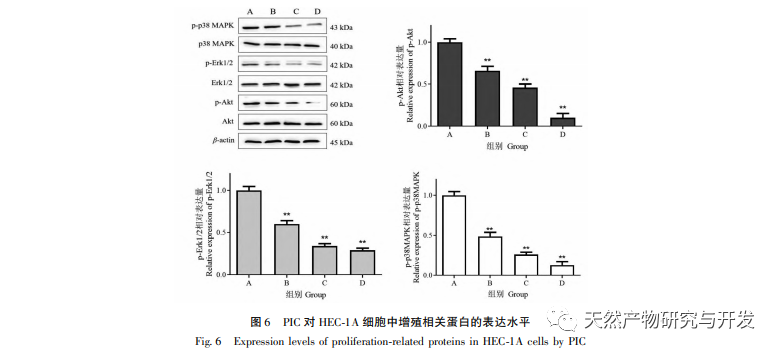
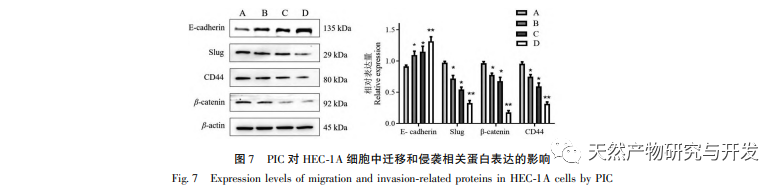
Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a crucial process in tumor metastasis, endowing cells with strong migratory and invasive embryonic programs. Under normal circumstances, EMT plays a crucial role in wound healing, while in abnormal cases, it promotes tumor metastasis. Research has confirmed that EMT is involved in the occurrence, metastasis, anti apoptosis, and invasion processes of endometrial cancer tumor cells. Research has shown that the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway are abnormally activated in EC. During the process of cell transformation from normal to malignant, EMT is regulated by the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, while the Wnt signaling pathway induces EMT in tumor cells, thereby affecting tumor invasion and metastasis. In this study, we found that PIC can upregulate the expression level of the epithelial like marker E-cdaherin in endometrial cancer HEC-1A cells, and downregulate the expression levels of the transcription inhibitory factor Slug and key effector molecules β – catenin and CD44 proteins in the Wnt signaling pathway. The results indicate that PIC can inhibit the Wnt signaling pathway to induce EMT transformation in endometrial cancer cells, thereby suppressing the migration and invasion of HEC-1A cells.
Research reports indicate that PIC has the potential to regress tumors, induce apoptosis, and inhibit angiogenesis, invasion, migration, and metastasis. Our previous research found that PIC can inhibit the proliferation, block cell cycle and induce apoptosis of triple negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468 by inhibiting Wnt/β – catenin signaling pathway, and has a good anti triple negative breast cancer effect. Another study showed that PIC inhibited the metastasis and invasion of breast cancer MCF-10A cells by inhibiting the Hras induced AKR phosphorylation, MMP-2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activities and down regulating the expression of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5) – triphosphate (PI3K), and played its anti breast cancer role. The in vitro results of this study found that PIC has a significant drug concentration dependent inhibitory effect on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of endometrial cancer cells HEC-1A. The activation of the MAPK signaling pathway is related to the occurrence and development of tumors, and is involved in regulating cell growth, differentiation, survival, and death. Erk and p38MAPK proteins are key effector molecules of the MAPK signaling pathway. Yan et al. found that PIC inhibits the phosphorylation of Erk1/2 and Akt proteins by affecting the MAPK and AKT signaling pathways, thereby suppressing RANKL induced osteoclast generation and bone resorption. At the molecular level, this study further demonstrated that PIC can inhibit the phosphorylation of proliferation related proteins Akt, Erk1/2, and p38MAPK in HEC-1A cells, effectively suppressing the proliferation, migration, and invasion of endometrial cancer cells.
In summary, the results of this study indicate that PIC can effectively inhibit the proliferation of endometrial cancer cells HEC-1A, induce cell apoptosis, and significantly reduce the migration and invasion ability of HEC-1A cells. Its mechanism may be related to the inhibition of Akt, Erk1/2, and p38MAPK phosphorylation in the Akt/ERK/MAPK signaling pathway, downregulation of the expression levels of invasion and migration proteins β – catenin, CD44, and Slug, and upregulation of E-cdaherin protein expression levels. It has been preliminarily confirmed that PIC has inhibitory effects on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of endometrial cancer cells. However, this experiment only conducted preliminary in vitro studies at the cellular level, and the specific molecular mechanism of its anti endometrial cancer effect still needs further clarification through in vivo studies.
