What are the applications of phosphates in food processing?
Properties of Phosphates and Their Role in Food Processing Phosphates have two main functions in food processing: one is as a quality improver to improve the organization and taste of food; the other is that they can be used as mineral nutrient enhancers.
The role of phosphate in food processing is mainly based on the following characteristics of phosphate: 1. Buffering: the PH value of phosphate from moderate acidity (PH ~ 4) to strong alkaline (PH ~ 12), when different phosphates in different ratios with different buffers can be obtained PH value stabilized in the PH4.5-11.7 between the different levels of buffer.
In the PH value range of most foods (PH3.5-7.5), phosphate can be used as an efficient PH regulator and PH stabilizer to make the food taste more delicious. The strongest buffering effect is orthophosphate, for polyphosphate, with the increase of chain length, the buffering ability will be weakened.
2. Water-holding effect: Polyphosphates are hydrophilic water-holding agents, which can well stabilize the water contained in food. The good or bad water-holding property is related to the type of polyphosphate, addition amount, PH value of food, ionic strength and other factors. For meat products and seafood, the best water-holding capacity is pyrophosphate, followed by tripolyphosphate, with the increase of chain length, the water-holding capacity of polyphosphate will be weakened.
3. Polyanion effect: polyphosphate is a polymerization dielectric, and has the characteristics of inorganic surfactants, can make the water insoluble substances dispersed or form a stable suspension to prevent the suspension of adhesion, cohesion.
Because polyphosphates can make the water-soluble gel of protein form a kind of gel film on the fat globules, so that the fat can be more effectively dispersed in water, and thus they are widely used in the phosphorylation of starch, dispersion of pigment, emulsification of food products (dairy products, ice cream, salad, sauce, etc.) as well as used as dispersion stabilizers of sausage, minced meat products, and minced fish products. For straight-chain polyphosphates, its emulsifying and dispersing ability increases with the increase of chain length. 4.
4. chelating effect: polyphosphates are easy to form soluble complexes with metal cations in solution, thus reducing the hardness of water, inhibiting oxidation, catalysis, discoloration, decomposition of vitamin C caused by Cu2+, Fe3+ and other metal cations, to prevent and delay the oxidation of fats, preventing the corruption of meat, poultry, fish, maintaining the color and lustre of food products in order to prolong the shelf life.
Chelating ability of polyphosphate to metal ions (g/100g polyphosphate)
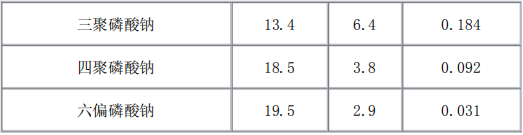
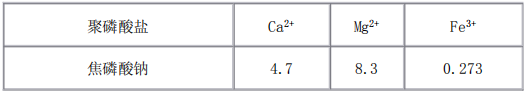
The chelating effect of polyphosphates depends on the length of the chain and PH value. Generally speaking, long-chain polyphosphates have strong chelating ability for light metal ions, and increase with the PH value; short-chain polyphosphates have strong chelating ability for heavy metal ions, but with the increase of PH value, the chelating effect is weakened.
5. Protein effect: phosphate on protein, gliadin has enhanced the role of protein, thus can improve the hydration of meat products and water retention, improve the water permeability, promote the softening of food and improve the quality of food, maintain the flavor of food. At the same time, phosphate in dairy products can prevent the coagulation of milk when heated, to prevent the separation of casein and fat water. 6.
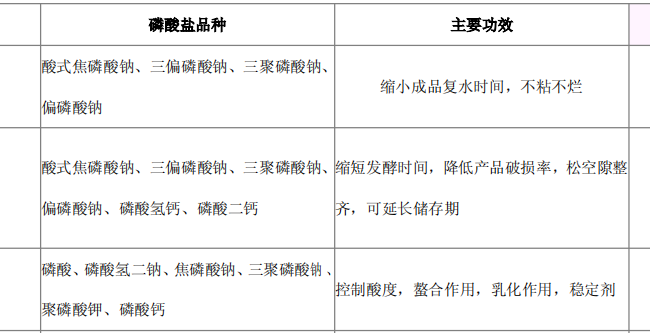
6. puffing effect: acidic phosphate (such as acid sodium pyrophosphate, calcium phosphate) is usually used as a puffing agent for bakery products puffing acid, and bicarbonate reaction for the baking process to provide the required carbon dioxide gas.
7. Anti-caking effect: tricalcium phosphate is often used as an anti-caking agent to improve the free-flowing properties of powdered or hygroscopic foods. Tricalcium phosphate has a large specific surface area, which can combine more water; and its special spherical crystal structure can produce the “ball effect”, so that the powder has good free flow performance.
8. Extend the shelf life of food: polyphosphate can enhance the storage stability of food, extend the shelf life of products. This effect is mainly based on: (1) PH regulation; (2) bacteriostatic effect: microbial cell growth must rely on divalent metal cations, especially Ca2+ and Mg2+, and phosphate can chelate with these metal cations, and it can reduce the stability of the cell wall in cell division, but also reduce the thermal stability of many cells, thus effectively inhibiting the growth of bacteria.
The bacteriostatic effect of polyphosphates is related to their type (chain length), content, pH value, salt content, nitrite content and other factors. Generally speaking, as the chain length increases, the antibacterial effect increases.
9. Mineral Nutritional Enhancement: Calcium phosphate, magnesium phosphate, iron phosphate, zinc phosphate are often used as mineral enhancers in food processing. The addition of iron and zinc phosphate to gastric juice can enhance the biopharmaceutical effect of gastric juice due to its better solubility and does not promote the occurrence of natural oxidation.
Application of phosphate in food
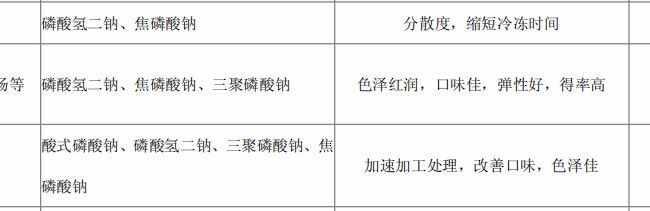
1.1 In order to improve the quality of meat products, usually add phosphate in the processing of meat products, its role is to: a. Improve the bonding of meat products, improve the slicing performance of meat products; b. Improve the water holding capacity of meat, so that meat products in the processing and cooking process can still maintain its natural moisture, reduce the loss of nutrients in the meat, preserving the tenderness of the meat products, to improve Improve the water holding capacity of meat, so that meat products can still retain their natural moisture during processing and cooking, reduce the loss of meat nutrients, preserve the tenderness of meat products, and improve the rate of finished products; c. Control the PH value of meat products in the most suitable range for protein blooming and the best color of meat products; d. Enhance the performance of emulsification and emulsion stability, and effectively prevent the separation of fat and water; e. Seal the metal cations to slow down oxidation reactions in the processing of meat products, which effectively reduces the rate of rancidity of the products, inhibits the decoloration and rancidity of meat products, and extends the shelf life of meat products; f. Improve the processing performance of meat products, and increase the production capacity. f. Improve the processing performance of meat products and increase the production efficiency.
1.2 The water holding capacity of meat generally refers to the water of the meat and the water added to the meat in the process of processing to maintain the ability to hold water, the level of water holding capacity is directly related to the texture of the meat products and the rate of finished products, the addition of phosphate can effectively improve the water-holding capacity of meat products. How to use phosphate and other additives reasonably without affecting the flavor of meat products, maximize the water retention and adhesion of meat products, reduce the cooking loss of meat products, has been an important issue in the research and development of meat products.
1.3 Reasonable use of phosphate in meat processing: in practical application, according to the type of meat products, texture requirements, production processes, raw materials, etc. Combined with the characteristics of various phosphates to choose the appropriate type of phosphate and the amount of addition.
Added pyrophosphate meat products, the natural water retention capacity of muscle proteins can be restored and enhanced, polyphosphate in the muscle enzymes can be quickly converted to pyrophosphate, and thus can achieve the same effect.
Although the water retention effect of pyrophosphate is the best, but its solubility is too poor, so most of the cases can not be used alone, but often and the solubility of the better long-chain polyphosphate or potassium phosphate together with the compound use. In addition, in order to play a variety of phosphate and phosphate and other additives between the synergistic effect, often use a variety of complex meat improver.
a. For sausage and minced meat products, pyrophosphates and medium chain length polyphosphates are commonly used and are added in dry powder form during chopping. The pH of the complex phosphates used is usually around 7, and sometimes complex phosphates with a pH higher than 9 are used.
b. Compound phosphates for saline injection must meet the following requirements: 1) good solubility in ice brine; 2) high dissolution rate; 3) good stability in ice brine.
The PH value of the compound phosphate used is generally 8.5-9.5. In order to achieve the best muscle protein activation effect in the preparation of ice brine for injection, it is best to dissolve the phosphate in ice water first, and then add salt, and this order can not be reversed in general.
c. The added amount of mixed phosphate is generally 0.1-0.4%, but the dosage should be strictly controlled. If the added amount is too high, it will damage the original flavor of meat and affect the color due to the rise of PH value.
2. Application in seafood processing: 2.1 Phosphate as a water retention agent with excellent performance, PH regulator and antifreezing agent is used in a large number of seafood, especially frozen seafood processing, and its role is to: a. Effectively improve the seafood’s water-holding capacity, so that the meat juice is richer, and effectively maintain the nutrients and water; b. Inhibit the oxidation of fat, and effectively extend the shelf life of seafood; c. Reduce the loss of droplets after defrosting, and reduce the cooking time. c. Reduce the droplet loss after thawing and reduce the weight loss in boiling; d. Maintain the natural color and flavor of seafood; e. Synergize with sugar to effectively prevent the protein of minced fish from freezing and denaturing.
2.2 In the processing of frozen shrimp, fish and shellfish, the products are usually immersed in 3-10% compound phosphate solution for treatment (temperature less than 10 ℃), the concentration of the immersion solution and the immersion time according to the type of shrimp, fish and shellfish, size and fishing time to decide. Reasonable selection of compound phosphate for soaking should take into account the following factors: a) can effectively improve the water holding capacity of seafood; b) good solubility in iced water; c) can be quickly dissolved in iced water; d) good stability in iced water. The PH value of the compound phosphates used is generally higher than 9. 2.3 The compound phosphates added to frozen surimi in general are mainly sodium pyrophosphate, sodium tripolyphosphate and sodium hexametaphosphate, and the amount of the added phosphates is 0.1-0.3% of the surimi.
3. Application of phosphates in pasta products 3.1 Application in bakery products: Acid phosphates (e.g., acid sodium pyrophosphate, calcium hydrogen phosphate) are usually used as bulking acid in the bulking agent of bakery products, and react with bicarbonate to provide carbon dioxide gas for the baking process. Different phosphates have different dough reaction rates (ROR) and can be selected according to the desired baking effect (puff volume, pore structure, flavor). In addition, phosphate can also be used as flour conditioner, dough improver, buffer and yeast nutrient.
3.2 Phosphate as a noodle quality improver is widely used in the processing of instant noodles and ordinary noodles, its main role is to: a. Increase the degree of starch dextrinization, increase starch water-absorbing capacity, so that the water holding capacity of the dough increases, so that the instant noodles rehydrated quickly, easy to brew; b. Enhance the gluten protein absorption and swelling properties, to improve its elasticity, so that the noodle texture smooth and gluten, resistant to cooking and soaking; c. Phosphate excellent buffering effect can stabilize the dough PH. c. The excellent buffering effect of phosphate can stabilize the PH value of dough, prevent discoloration and deterioration, and improve the flavor and texture; d. Phosphate can be complexed with metal cations in dough, and it has a “bridging” effect on glucose groups to form cross-links of starch molecules, so that the starch colloidal viscoelastic characteristics can be maintained after rehydration of high-temperature cooked and deep-fried noodles e. Improve the glossiness of noodles. 4;
4. Application in dairy products: phosphate is used as stabilizer and emulsifier for UHT-sterilized milk, cream products, condensed milk, milk powder, coffee mate, milk drink, cheese products, its role is: a. Buffer and PH stabilization; b. Interaction with proteins: dispersion of food ingredients, stabilization of emulsification system, enhancement of casein water-binding capacity, and effectively prevent the separation of protein, fat and water; c. Chelation of polyvalent metal ions. Chelate polyvalent metal ions, so that in the heating process and storage process protein agglutination and precipitation phenomenon is greatly reduced, thus improving the thermal stability and storage stability of milk. And can effectively delay the occurrence of lactose coagulation phenomenon. 5.
5. Phosphates are also widely used in the following food processing fields: ◎ Beverages: used as acidity regulator, stabilizer and mineral nutrient fortifier; ◎ Potato products: used as stabilizer and color retainer; ◎ Rice products: to improve the elasticity of the products and improve the texture of the products; ◎ Seasoning and instant soup: stabilizer, acidity regulator; ◎ Humidity-absorbent powdered food: to prevent clumping and to improve the free-flowing performance; ◎ Starch products and modified starch; ◎ Infant food: to prevent clumping, to enhance the free-flowing performance; ◎ Starch products and modified starch; and Starch products and modified starch; ◎ Baby food, functional food: mineral nutritional enhancer.