Starch is one of the main components of wheat flour, which mainly fills in the gluten network structure during dough formation, and undergoes pasting during noodle cooking, conferring adhesion, chewiness, and so on.
Studies have shown that although protein is one of the determinants of noodle quality, the great physical properties of noodles originate from the pasting of starch rather than protein. The content and quality of starch have a significant effect on the quality of noodles, and the pasting characteristics and straight-chain starch content of starch have a significant correlation with the edible quality of noodles 6. The addition of a certain amount of exogenous starch in the production of noodles can make the gluten network structure fill more fully, which has a certain improvement effect on the quality of noodles.
Pasting characteristics of sweet potato starch and wheat flour blends
The results of the pasting characteristics of the blended flours with different ratios of sweet potato starch and wheat flour are shown in Figures 1 to 3.
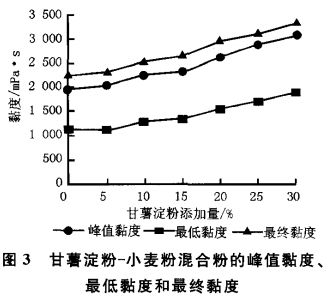
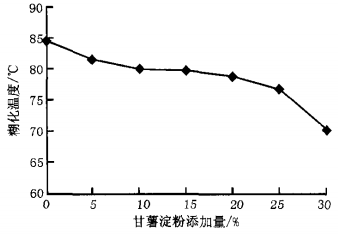
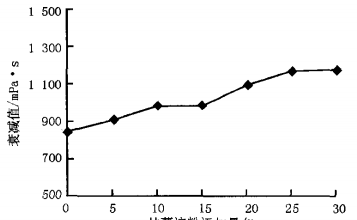
From Figures 1 to 3, it can be seen that with the increase of sweet potato starch addition, the pasting temperature of the blended flours gradually decreased, and the peak viscosity, the minimum viscosity, the final viscosity, and the attenuation value showed a gradual increase.
Comparison with the pasting characteristics of wheat flour and sweet potato starch revealed that, with the increase of sweet potato starch addition, the pasting characteristics of the blended flours were more and more similar to those of sweet potato starch, and more and more deviated from those of wheat flour.
This indicates that the sweet potato starch addition has a greater effect on the pasting characteristics of wheat flour, which can reduce the pasting temperature and increase the pasting viscosity of wheat flour. In addition, the increase of attenuation value during the pasting of mixed flours reflected that the hot paste was more susceptible to shear dilution and poor thermal stability.
Starch is a macromolecular material, a large number of hydrophilic groups in the molecule so that it has good hydrophilicity and water retention, so the addition of sweet potato starch can to a certain extent increase the rate of water absorption and water absorption during the pasting, and the pasting temperature of sweet potato starch is significantly lower than that of wheat flour, the pasting viscosity is significantly higher than the pasting viscosity of wheat flour, so increasing the amount of sweet potato starch will inevitably lead to the mixing of the flour pasting Therefore, increasing the addition of sweet potato starch will inevitably lead to the pasting of mixed flours with lower temperature and higher viscosity. In addition, it is believed that the reduction of the relative protein concentration in the mixed flour will weaken the degree of impediment to starch granule water absorption and pasting, thus increasing the pasting viscosity of the mixed flour.
Addition of sweet potato starch to pasta
Cooking Characteristics and Textural Properties
2.1 Cooking characteristics
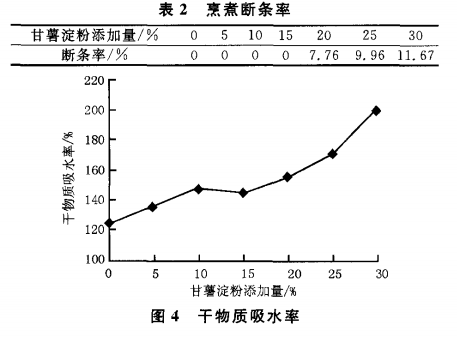
The results of cooking characteristics of noodles made from the mixture of sweet potato starch and wheat flour are shown in Table 2, Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. When the amount of sweet potato starch added reaches 20%, the noodles started to break during cooking, indicating that the internal structure of the noodles has been damaged to a certain extent; with the increase of the amount of sweet potato starch added, the breakage rate gradually increased.
When the noodles were cooked, the water absorption rate showed a gradual increase with the increase of sweet potato starch addition, which was consistent with the results of previous studies, which might be related to the good hydrophilicity and water-holding property of starch.
The cooking loss rate of noodles showed a tendency of decreasing and then increasing, which indicated that a small amount of sweet potato starch could reduce the cooking loss of noodles and stabilize the internal structure of noodles; however, the cooking loss rate increased significantly with the increase of sweet potato starch, which indicated that the proportion of sweet potato starch in the mixture exceeded a certain range, and it would have a certain negative effect on the cooking quality of noodles. As far as the results of this experiment are concerned, the addition amount of sweet potato starch should be controlled at about 15%.
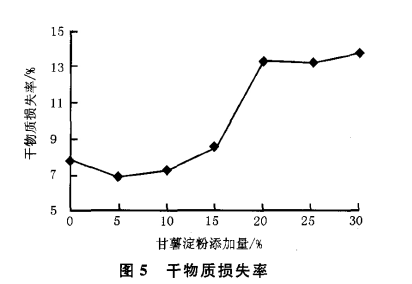
2.2 Textural properties of cooked noodles
With the increase of sweet potato starch, the hardness, cohesion and pulling force of noodles showed a tendency of increasing and then decreasing, indicating that a small amount of sweet potato starch can enhance the cohesive force of noodles and improve the quality of noodles; when the amount of starch added is more than a certain range, the hardness, cohesion and pulling force of noodles begin to decrease, and the quality of the noodles deteriorates.
A small amount of sweet potato starch is beneficial to improve the quality of noodles, but the amount of sweet potato starch added should be controlled within a certain range, and if too much is added, the quality of noodles will decline rapidly (the results of this experiment show that the amount of sweet potato starch added should not be more than 15%).
This trend may be mainly related to the dilution of gluten protein in wheat flour by sweet potato starch, and the destruction of the balance between gluten protein and starch.
When the amount of sweet potato starch is moderate, it is conducive to the further filling of the gluten network structure by starch, so that the gluten network can be fully expanded and the interaction between protein and starch can be enhanced to a certain extent; in addition, the addition of sweet potato starch will make the pasting temperature of the mixed flour lower, which is conducive to a better balance between the pasting of starch and the denaturation of protein, so that the structure of the gluten network can be better wrapped around the pasted starch.
And when the starch addition exceeds a certain range, the gluten network structure is weakened seriously, and the starch absorbs water and swells excessively, which leads to the disintegration of the gluten network structure as well as the dissolution of starch and protein fragments during cooking.
