Chemical Composition Analysis of Mango Kernel Based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS
Mangifera indica L. is a plant species in the family Anacardiaceae, and its fruit, mango, is the most traded, exported, and consumed tropical fruit worldwide. Mango kernels, which account for 20% to 60% of the total weight of mangoes, are often discarded as waste. However, mango kernels are one of the commonly used medicines in Tibetan and Mongolian medicine. The “Chinese Materia Medica: Mongolian Medicine Volume” records that they have the effects of promoting digestion, reducing phlegm, and promoting qi circulation. They are used for food stagnation, loss of appetite, cough, hernia, orchitis, and other conditions. The “Drug Standards of the Ministry of Health – Tibetan Medicine” records that it has the effects of nourishing yin and kidney, and is commonly used for kidney deficiency. Research has shown that the chemical components of mango kernels are mainly polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, and saponins, which have significant antioxidant activity and can be used as a substitute for cocoa butter in cosmetics, food, pharmaceuticals, and other fields. However, the pharmacological substance basis of mango seeds used in Tibetan and Mongolian medicine to treat diseases such as dietary stagnation and kidney deficiency is not yet clear. Therefore, further comprehensive and systematic qualitative analysis of the chemical composition of mango seeds is needed.
Traditional chemical analysis methods, from the extraction and separation of chemical components to structural identification, are often time-consuming and labor-intensive, and the structural analysis of the obtained components is also very difficult. The ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) technology has the advantages of high separation ability, high sensitivity, and high resolution, which can quickly achieve the analysis of drug chemical components. It is increasingly widely used in the field of qualitative analysis of natural drug chemical components. To further elucidate the pharmacological substance basis of mango seeds, this study intends to use UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS for rapid qualitative analysis of the chemical components of mango seeds, in order to provide reference for subsequent research on mango seeds and the rational development and application of resources.
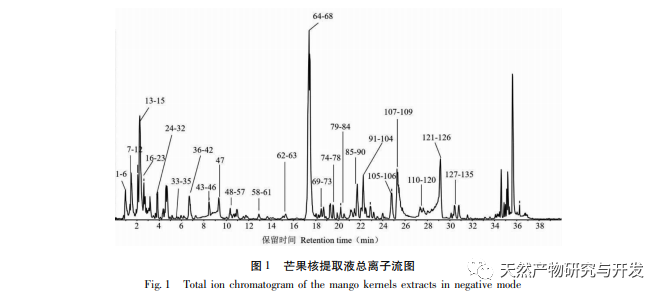
 In daily life, mango kernels are often discarded as a byproduct of mango processing, resulting in resource waste and environmental pollution. Therefore, in order to improve the value of mango kernels, this study used UPLC-Q-TOFMS/MS technology to systematically and comprehensively analyze the chemical components in the alcohol extract of mango kernels. To provide a basis for the development of innovative functional foods and in-depth research in fields such as medicine for mango kernels.
In daily life, mango kernels are often discarded as a byproduct of mango processing, resulting in resource waste and environmental pollution. Therefore, in order to improve the value of mango kernels, this study used UPLC-Q-TOFMS/MS technology to systematically and comprehensively analyze the chemical components in the alcohol extract of mango kernels. To provide a basis for the development of innovative functional foods and in-depth research in fields such as medicine for mango kernels.
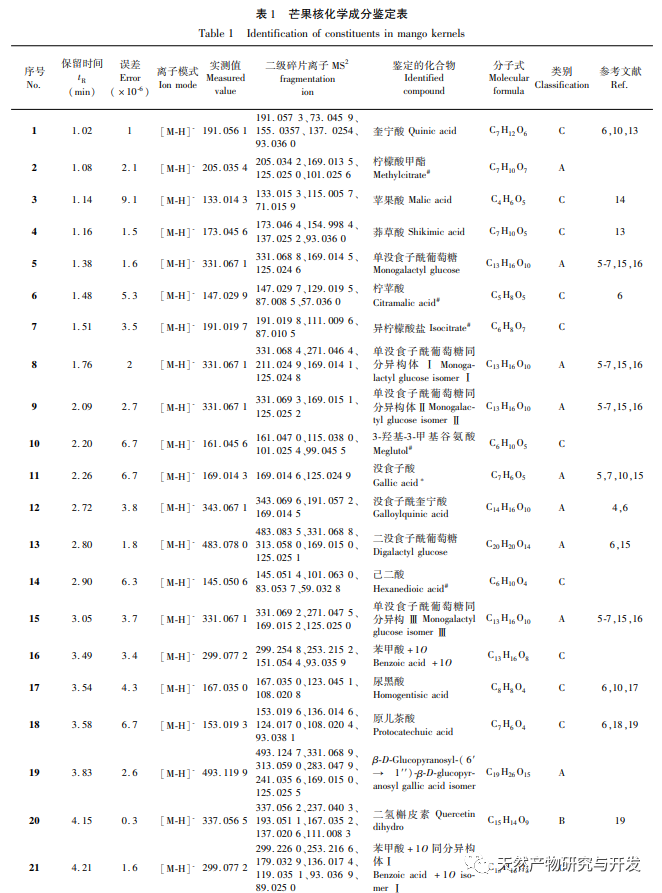
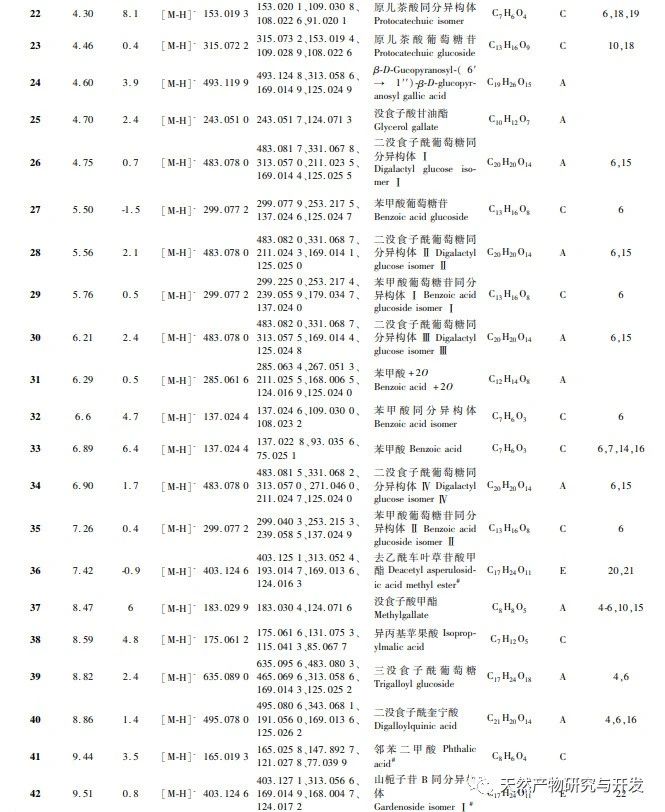
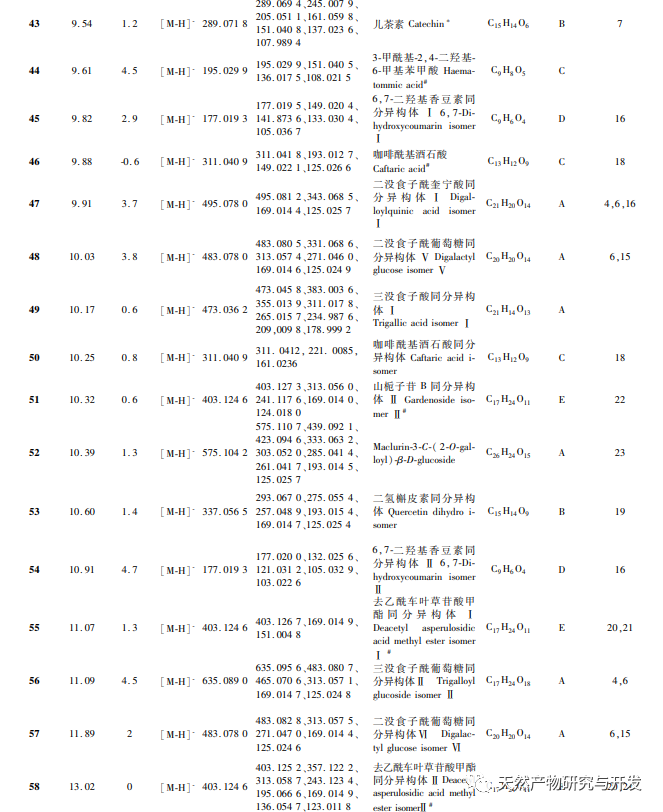
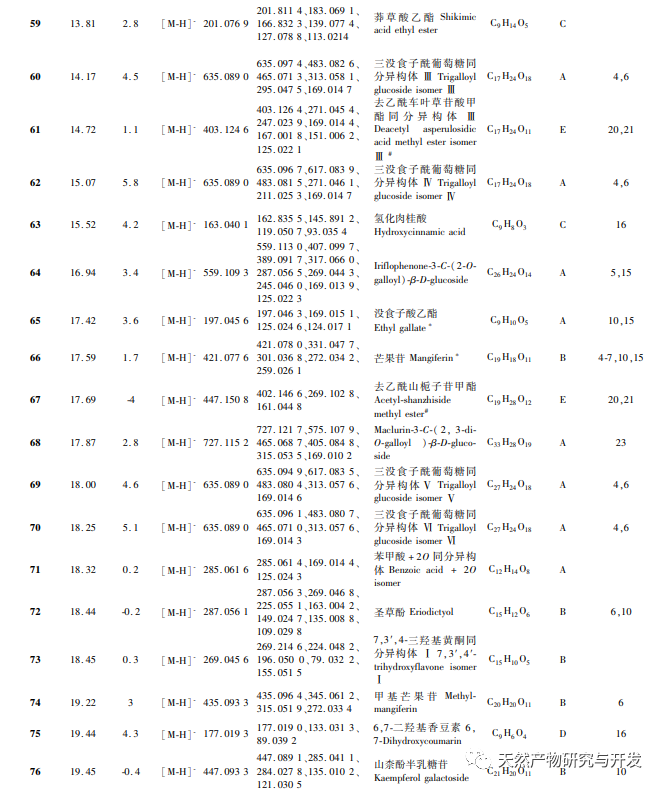
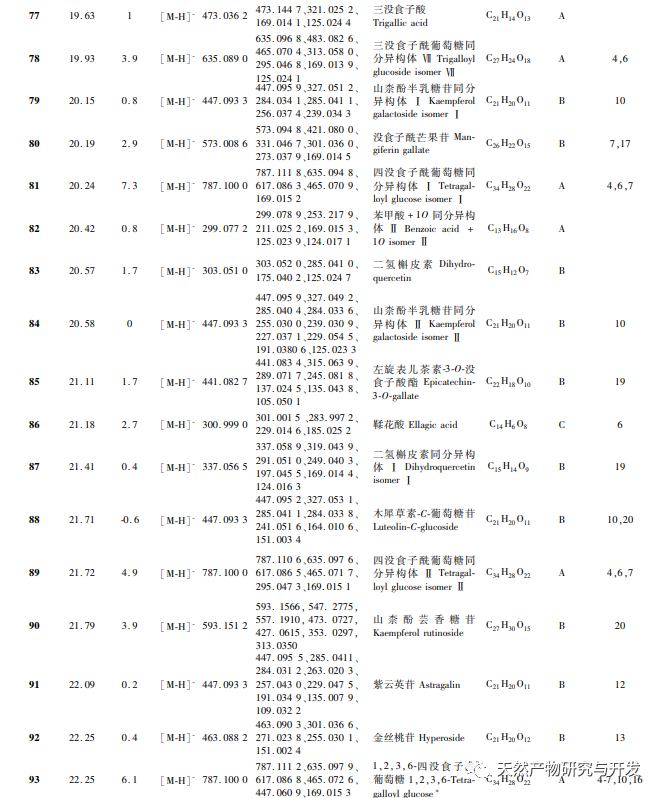
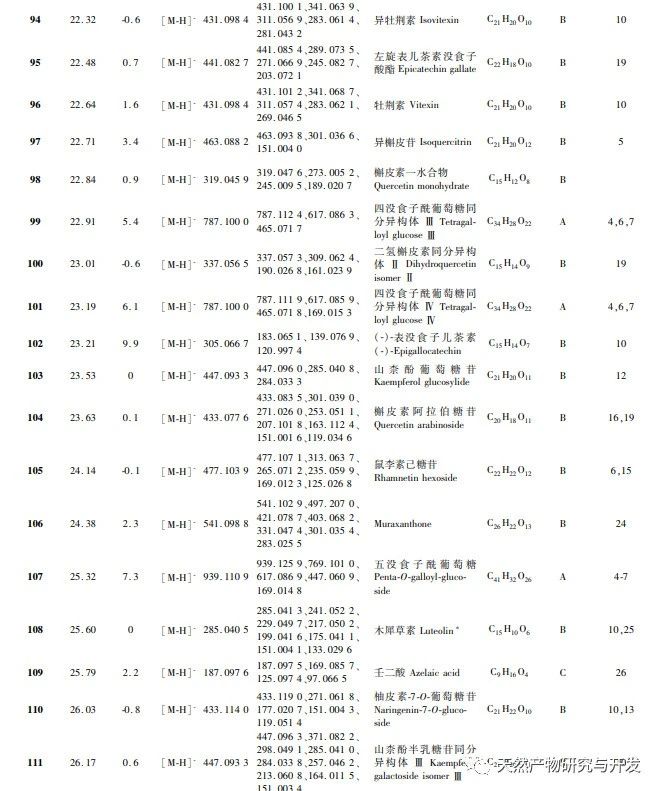
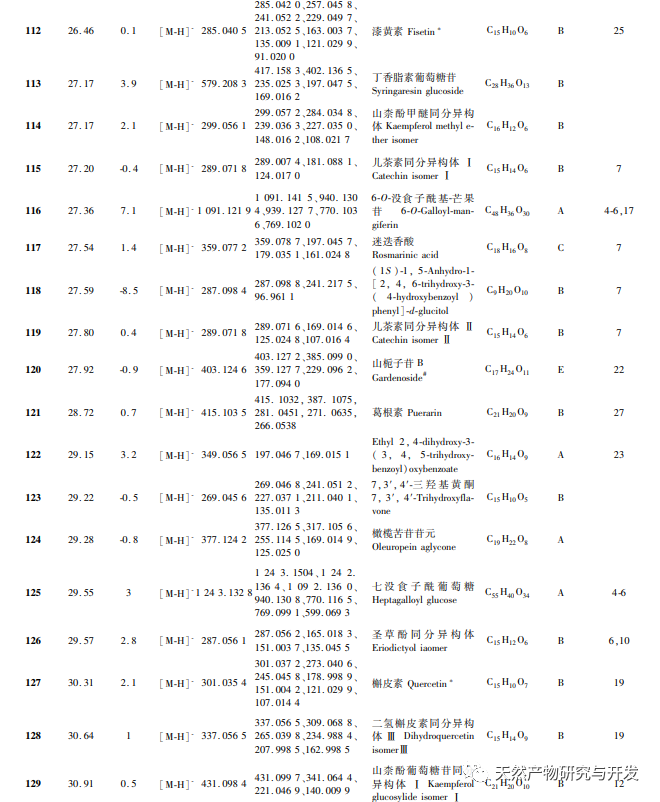
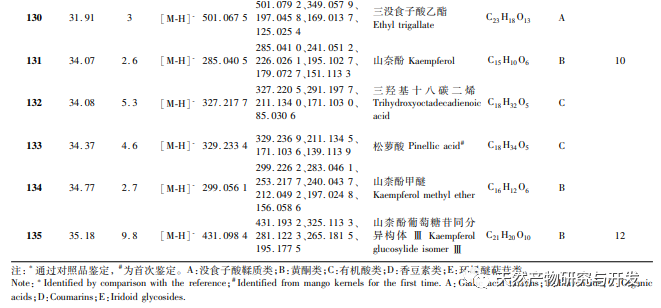
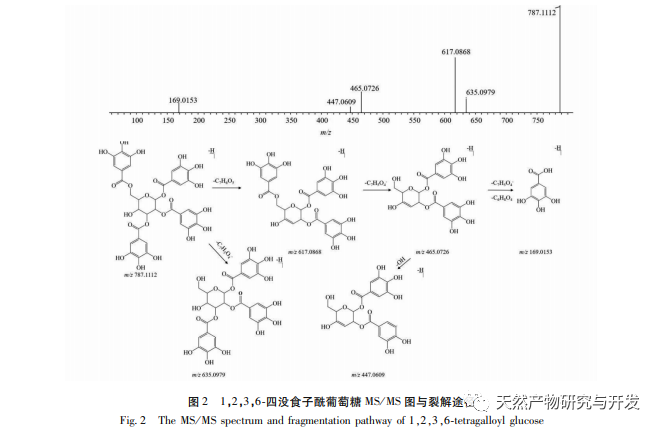
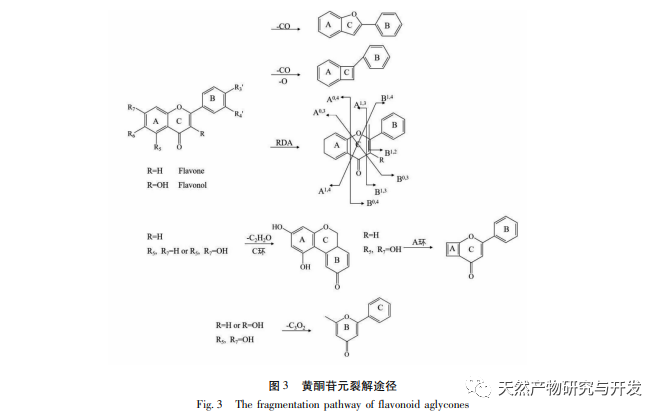
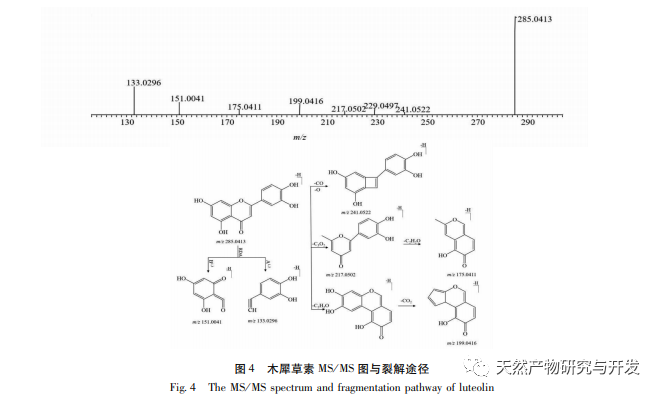
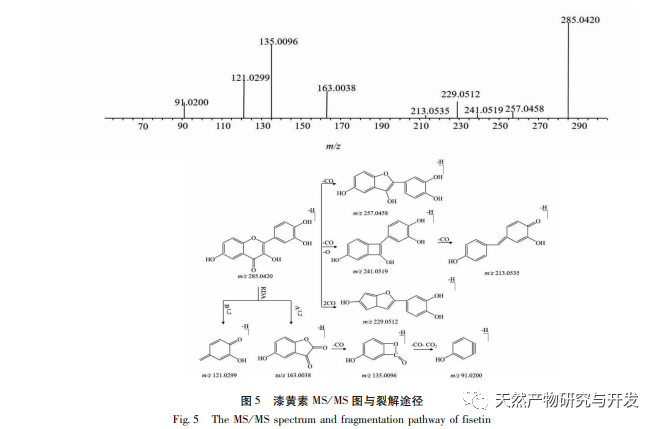
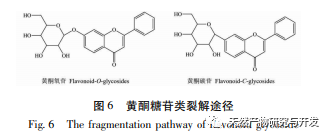
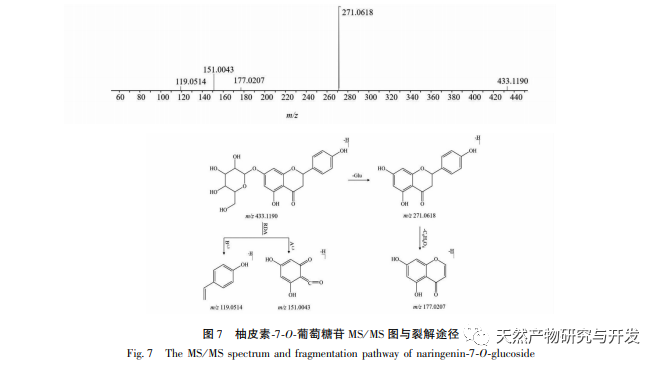
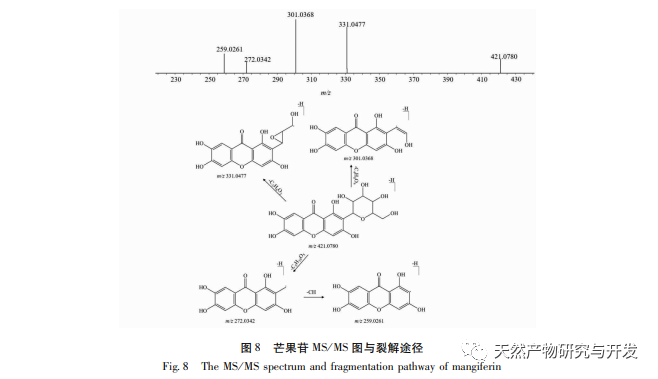
In order to better explore the potential medicinal substances in mango kernels, this study conducted in-depth analysis of the chemical components in mango kernels by changing the mobile phase and optimizing mass spectrometry parameters based on the identification of polyphenolic substances by previous researchers. Regarding the organic phases of methanol and acetonitrile, and the aqueous phases of water, 0.1% formic acid water, and 0.2% formic acid water, the mobile phases were investigated and ultimately determined to be acetonitrile and 0.1% formic acid water. Based on the known compounds gallic acid, 1,2,3,6-tetragalloylglucose, luteolin, quercetin, and mangiferin in mango kernels, parameter optimization was carried out to obtain the optimal fragment ions with corresponding structures. By combining retention time, precise molecular weight, fragment ions from secondary mass spectrometry, and relevant literature, a total of 135 bioactive substances were identified from mango kernels, including 47 gallic acid tannins, 47 flavonoids, 30 organic acids, 3 coumarins, and 8 iridoid glycosides. Among them, coumarins and iridoid glycosides were identified for the first time from mango kernels. At present, research mainly focuses on the polyphenolic substances in mango kernels, and the study of the bioactive substances in mango kernels is not clear enough. Therefore, this experiment uses UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS to systematically and comprehensively analyze the chemical components of mango kernels, providing reference and basis for revealing the mechanism of action of complex components in mango kernels and further development.
