Study on Alkaloids in Lotus Leaves and Their Exciting Effects on 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C Receptors
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disorder caused by various factors such as excessive nutrient intake and genetics. It not only affects the quality of life of patients, but also causes many cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and coronary heart disease, seriously threatening human health. Exploring natural active ingredients with lipid-lowering and weight loss functions from medicinal herbs of the same origin as food and medicine, and developing drugs or health products with lipid-lowering and weight loss activities, is an important way to address the public health problem of obesity faced by humans.
Lotus leaf, also known as lotus leaf, is the fresh or dried leaf of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn., a plant in the family Nymphaeaceae. It has the same medicinal and edible properties and has the effects of dispersing blood stasis, stopping bleeding, clearing heat and dispelling dampness. It is mainly used to treat spleen deficiency, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, heat and thirst. This herb has been included in previous generations. The commercially available Tongmai Jiangzhi Tablets, Jiangzhining Granules, Hedan Granules, Hugan Qingzhi Granules, Tangzhiqing and other traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations for regulating fat and reducing weight all contain lotus leaf components. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that lotus leaves are rich in alkaloids and flavonoids, which have various pharmacological activities such as lipid regulation, blood pressure reduction, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral effects. However, despite being commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine for weight loss and health supplements, the specific lipid regulating and weight reducing components in lotus leaf alkaloids are not very clear.
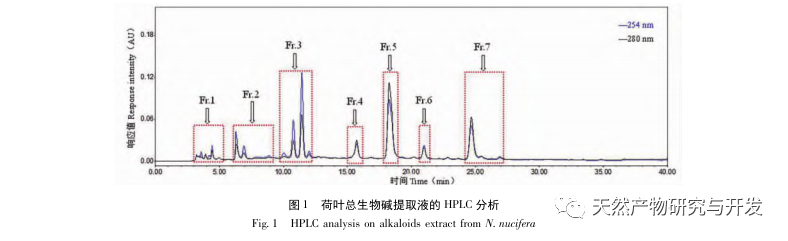
In order to further elucidate the pharmacological substance basis of the lipid-lowering and weight loss activity of lotus leaves, this study systematically isolated alkaloids in lotus leaves using a combination of traditional acid extraction and alkaline precipitation with modern high-performance liquid chromatography preparation under LC-MS tracking guidance. The excitatory effects of the isolated bioactive components on 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors were tested, in order to provide more theoretical basis for the development of innovative drugs and health products based on lotus leaf lipid-lowering and weight loss activity.
Obesity is one of the main inducements of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hypercholesterolemia, and metabolic diseases such as diabetes. Fat regulation and weight loss can help prevent and assist in the treatment of these diseases. 5-hydroxytryptamine is a widely distributed neurotransmitter in mammals, which regulates and controls movement patterns by activating or antagonizing its corresponding receptor functions. It is closely related to many functions in the human body, such as diet, sleep, and emotion regulation. Studies have shown that within a certain range, the higher the activity of receptors such as 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C in the serotonin receptor family, the more likely people are to experience satiety and anorexia, leading to decreased appetite and reduced food intake; Munusamy et al. suggested that the alkaloids in lotus leaves may achieve dieting effects by activating 5-HT2A receptors.
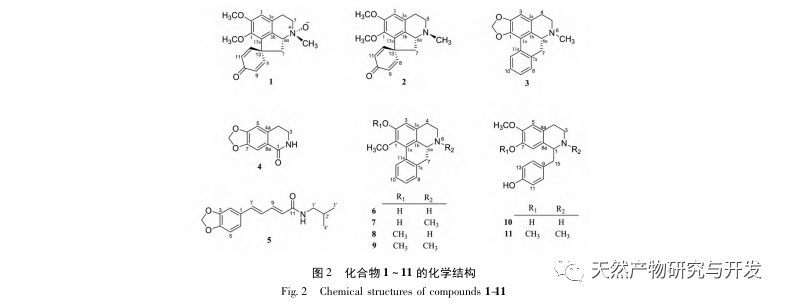
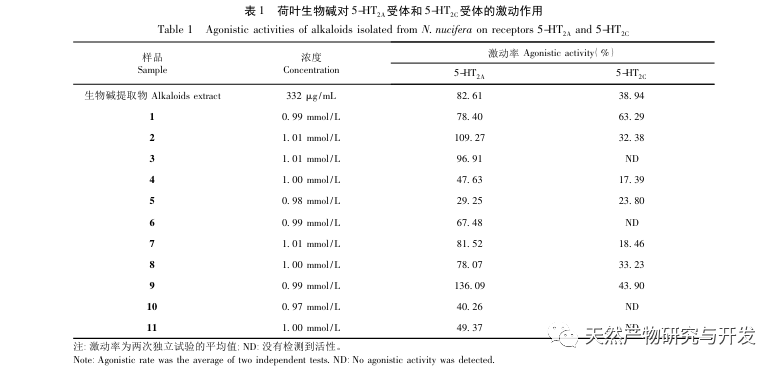
To further elucidate the material basis of the lipid regulating and weight reducing activity of lotus leaves, this study used a combination of traditional acid extraction and alkaline precipitation with modern high-performance liquid chromatography preparation techniques to isolate alkaloids from lotus leaves. A total of 11 alkaloid compounds were obtained, among which compounds 1, 4, and 5 were obtained from lotus leaves for the first time. The activity test results showed that the obtained compounds all have certain excitatory effects on 5-HT2A receptors, which is consistent with the research results of Munusamy et al., further revealing that lotus leaf alkaloids may have the effect of activating 5-HT2A receptors to achieve dieting, lipid regulation, and weight loss. In addition, the original opioid alkaloids (1,2) and opioid alkaloids (3,6-9) have similar excitatory effects on 5-HT2A receptors and stronger activity than other types of alkaloids. The specific structure-activity relationship needs further study.
In summary, this study enriches the chemical information of lotus leaf alkaloids, further revealing the possible pharmacological basis and mechanism of lotus leaf lipid regulation and weight loss, and providing more theoretical basis for the development of innovative drugs and health products based on lotus leaf lipid regulation and weight loss activities.
