Exploring the key components of total flavonoids from Angelica sinensis in anti rheumatoid arthritis based on spectral effect relationship and component knockout
Lamiophlomis Herba (LH), a traditional Chinese medicine, is the dried aboveground part of Lamiophlomis rotata (Benth.) Kudo, a plant in the family Lamiaceae. It is a medicinal herb commonly used by Tibetans and is also commonly used as a traditional Chinese medicine. The 2020 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China states that it has the effects of promoting blood circulation, stopping bleeding, dispelling wind, and relieving pain. It can be used to treat injuries caused by falls, rheumatism, and yellow water disease. Its Tibetan medicine names are “Daba” and “Dabuba”, which have been recorded in Tibetan medical works such as “Yue Wang Yao Jian”, “Four Medical Classics”, “Jing Zhu Ben Cao”, etc. It has a history of 1200 years of application so far; The “Jingzhu Bencao” records that “Du Yi Wei solidifies the essence and diverts yellow water”, indicating that Du Yi Wei can be used for the treatment of “yellow water disease”. According to clinical manifestations, the “yellow water disease” recorded in Tibetan medicine can be classified as “bi syndrome” in traditional Chinese medicine. The “bone bi” and “li jie disease” developed from “bi syndrome” are more closely related to the clinical characteristics of “rheumatoid arthritis (RA)” in modern medicine. Therefore, Du Yi Wei has the potential to treat RA, and existing research has also shown that Du Yi Wei has anti RA effects.
RA is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic and multiple joint inflammations. Its pathological features include tumor like proliferation of synovial cells and formation of vascular opacities, with fibroblast like synoviocytes (FLS) being its main effector cells. At present, the pathogenesis of RA is still unclear. Its incidence rate and disability rate are high, and it is usually latent. The late stage of the disease may lead to different degrees of irreversible disability, which is a modern refractory disease specified by the World Health Organization. The commonly used chemical drugs for treating RA in clinical practice include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids, and biologics. The first three chemical drugs have significant adverse reactions, while the expensive price of biologics limits their long-term application. Therefore, it is particularly necessary to develop new clinical anti RA drugs with low side effects and stable therapeutic effects.
The research group used network pharmacology for the first time to explore the pharmacological substance basis and mechanism of action of Du Yi Wei in the treatment of RA. It was found that the therapeutic effect of Du Yi Wei on RA is related to its 23 components, among which flavonoids account for nearly 40%, indicating that flavonoids play an important role in the anti RA process of Du Yi Wei, especially luteolin; And it is proposed that the main mechanism of Du Yi Wei’s anti RA effect may be inducing apoptosis of synovial cells by inhibiting the PI3K Akt signaling pathway. Meanwhile, the anti RA effect and pharmacological substance basis of Du Yi Wei were studied through a rat adjuvant arthritis model, and the results showed that the total flavonoids of Du Yi Wei have good anti RA effects. The total flavonoids of Du Yi Wei may be one of the main pharmacological substances for its anti RA effect, but the key anti RA components in Du Yi Wei total flavonoids are still unclear and require further research. Therefore, this study aims to explore the key anti RA components in the total flavonoids of Angelica sinensis through spectral effect relationships and component knockout techniques, with the aim of providing theoretical basis and reference for the clinical application of Angelica sinensis in the treatment of RA.



Discussion and Conclusion
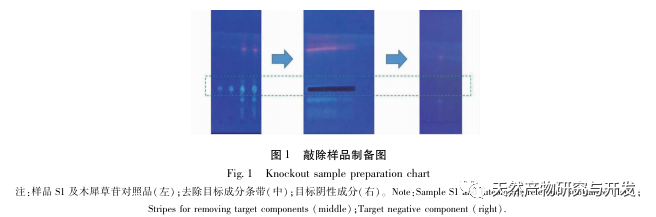
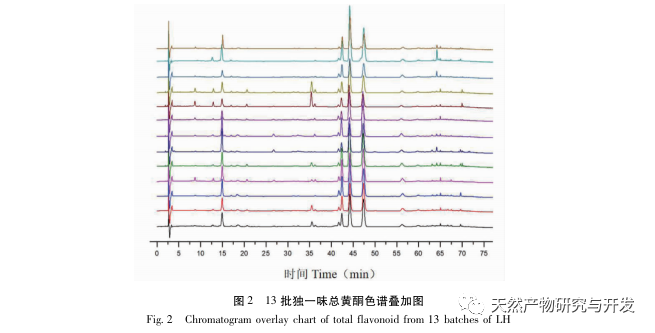
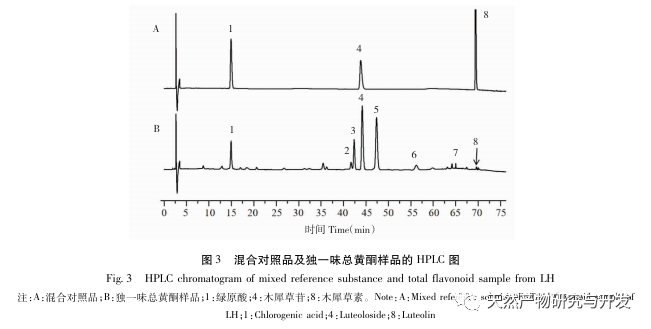
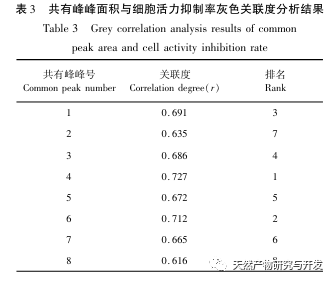
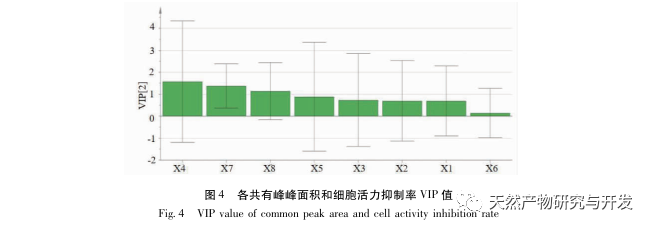
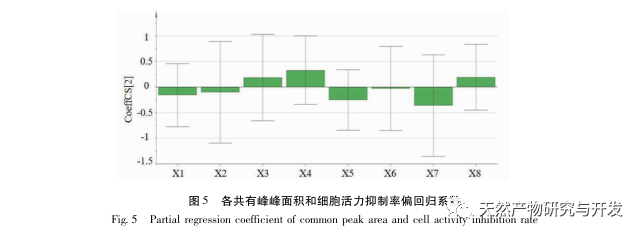
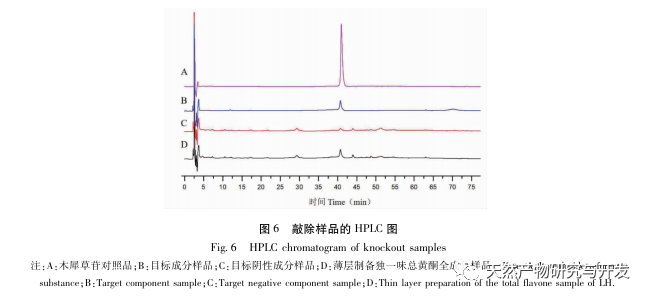
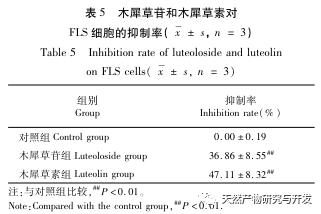
A preliminary study on the fingerprint of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis was conducted using high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector (HPLC-DAD). The similarity between the fingerprint spectra of each batch of Angelica sinensis total flavonoid samples and the established control fingerprint spectra was greater than 0.9, indicating that the chemical components contained in different batches of Angelica sinensis total flavonoid samples were consistent. The research group investigated the effects of different concentrations and administration times of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis on FLS cell viability in the early stage. Based on this, the CCK-8 method was used to treat FLS cells at a concentration of 64 μ g/mL for 48 hours to investigate the effects of different batches of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis on FLS cell viability. The results showed that all 13 batches of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis could significantly inhibit FLS cell viability. Based on the fingerprint spectrum of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis and the results of cell efficacy experiments, grey relational analysis and partial least squares (PLS) regression analysis were used to establish the spectrum effect relationship of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis against RA. The results showed that the components of verbascoside and verbascoside in total flavonoids of Angelica sinensis played a major role in its anti RA efficacy. Based on thin-layer chromatography, the high content of verbascoside in total flavonoids of Angelica sinensis was effectively knocked out, and the effect of each sample on FLS cell viability was determined by CCK-8 method. The results showed that the whole component and target component samples could significantly inhibit FLS cell viability, while the target negative component sample had no significant inhibitory effect on FLS cell viability. At the same time, the effects of equimolar amounts of verbascoside and verbascoside on the viability of RA-FLS cells were compared. The results showed that both verbascoside and verbascoside could significantly inhibit the viability of FLS cells, but there was no significant difference between the verbascoside group and the verbascoside group.
In summary, the results of this study indicate that the components of verbascoside and verbascoside play a major role in the anti RA efficacy of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis. Combined with the fingerprint analysis of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis, the content of verbascoside is significantly higher than that of verbascoside, indicating that verbascoside (C21H20O11) is the key component of total flavonoids in Angelica sinensis for anti RA. It can provide a scientific basis for the clinical application of total flavonoids from Du Yi Wei in the treatment of RA. Osmanthus glycosides are widely present in various medicinal plants, and have significant effects in anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and hypoglycemic aspects, with minimal toxic side effects. Although the components of verbascoside are relatively common, there is currently a lack of literature on the anti RA effects of verbascoside. In this study, the CCK-8 method was used to investigate the effect of verbascoside on RA-FLS cell viability, and it was clearly demonstrated that verbascoside has an inhibitory effect on FLS cell viability. Subsequently, a rat arthritis model can be established for in vivo efficacy verification, and its pathway of action can be explained, providing more references and basis for the clinical use of total flavonoids of Angelica sinensis in the treatment of RA.
