What are the effects of guar gum on the proliferative effect of lactic acid bacteria and yogurt quality?
Guar gum is a water-soluble dietary fiber, the main component of which is galactomannan, which can be used as a thickener in food.
By partially hydrolyzing guar gum and lowering the average relative molecular mass of polysaccharides, the viscosity, solubility and other physicochemical properties of polysaccharides can be altered, which in turn produces a lot of biological activities that were not available before hydrolysis.
In vitro fermentation experiments have shown that the addition of partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG) promotes an increase in the number of viable probiotic flora, such as Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus spp. in feces, and promotes the production of short-chain fatty acids.
The ability of PHGG to regulate intestinal flora was further confirmed by Ohashi et al. through a 2-week human experiment, in which volunteers ingested 6 g of PHGG per day for 2 weeks, and the increase in the number of Bifidobacterium spp. and butyric acid-producing bacteria in the feces indicated that PHGG had the effects of promoting the increase of beneficial flora in the colon, promoting the production of short-chain fatty acids in the intestinal tract, and protecting the health of the intestinal tract.
Effect of PHGG on the growth of fermenter strains
Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus are two types of bacterial agents that are often added to yogurt, and the results in Table 2 show that PHGG has a promoting effect on the growth of both types of bacteria.
As can be seen from Table 2, when Lactobacillus bulgaricus was inoculated alone for fermentation of yogurt, the number of viable bacteria in the PHGG group was significantly increased compared to the blank group, and there was a tendency for the number of viable bacteria to increase with the increase in the amount of PHGG added.
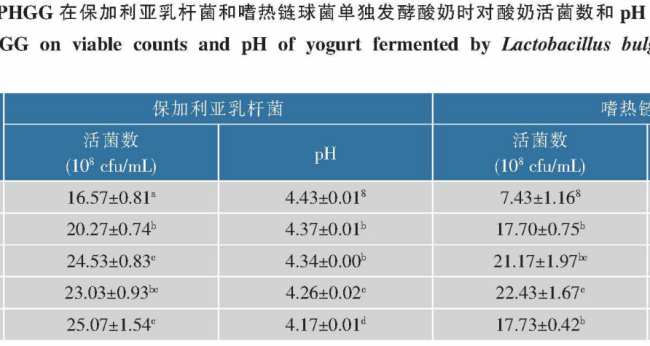
Effect of PHGG on the number of viable bacteria in yogurt
When co-fermenting yogurt using Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, the effect of adding different mass concentrations of PHGG on the number of viable bacteria in yogurt was significant.
The results of the 1st day of refrigeration showed that at the end of fermentation, the number of viable bacteria in the yogurt increased with the addition of PHGG. During the process of refrigeration, the viable bacterial counts of all groups showed a tendency of increasing and then decreasing, and after 21 d of refrigeration, the viable bacterial counts of all groups decreased significantly, but the viable bacterial counts of the PHGG group were always higher than those of the blank group in terms of the whole refrigeration stage (Fig. 1).
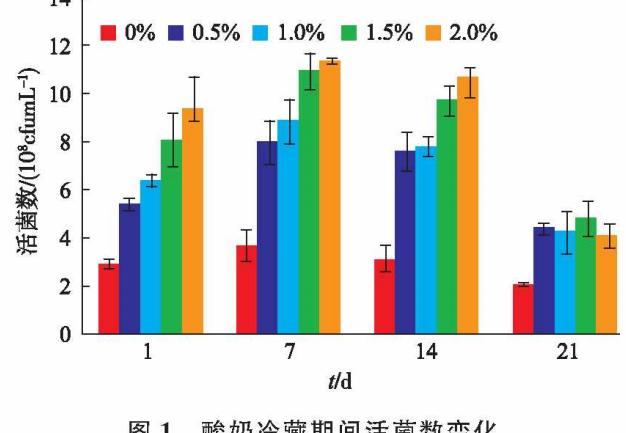
Effect of PHGG on yogurt acidity
PHGG can increase the acidity of yogurt and decrease the pH of yogurt, but it will not cause serious post-acid. The test results show that PHGG can promote the growth of lactic acid bacteria, the number of live bacteria in yogurt after fermentation for the same time is higher, more metabolites accumulated in yogurt, lactic acid metabolites affect the acidity of yogurt, so the yogurt with added PHGG has higher acidity.
Effect of PHGG on the viscosity characteristics of yogurt
With the increase of PHGG addition, the viscosity of yogurt showed an increasing trend, and the increasing trend slowed down after the addition of 15 g/L. The results are shown in Fig. 3.
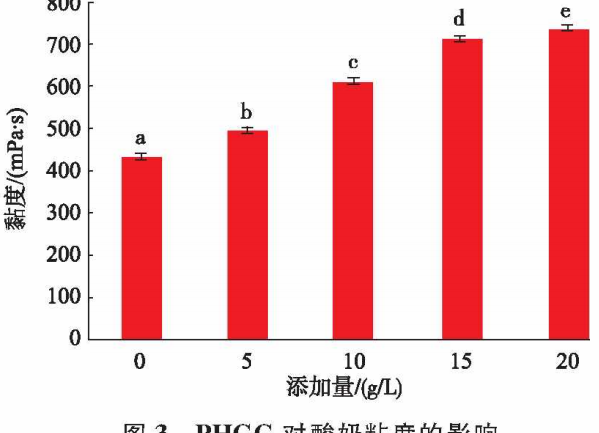
Viscosity is an important indicator of yogurt quality, affecting the organizational structure and sensory quality of yogurt. The composition of raw milk and the use of additives, the choice of leavening agent, homogenization method and other processing conditions will affect the viscosity of yogurt.
Effect of PHGG on water retention of yogurt
With the increase of PHGG addition, the water holding capacity of yogurt increased, and the difference between groups was significant.
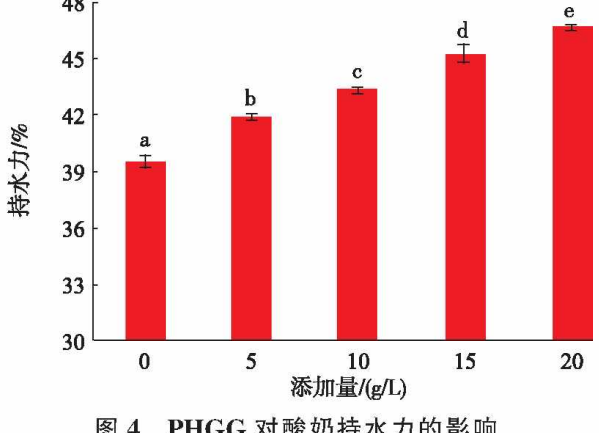
Both water holding capacity and viscosity are important indicators to characterize the textural properties of yogurt. Increased water holding capacity indicates that PHGG can reduce whey precipitation and improve the texture and mouthfeel of yogurt. Increased water holding capacity and viscosity help to improve yogurt gel strength and product stability. For solidified yogurt, it is especially important to increase gel strength to avoid curd breakage and whey precipitation during transportation. To summarize
PHGG can promote the proliferation of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus during yogurt fermentation, increase the number of viable bacteria in yogurt, promote the acid production of lactic acid bacteria, accelerate curdling, significantly increase the viscosity and water-holding capacity of yogurt, and improve the textural qualities of yogurt, and the organoleptic qualities of yogurt reached the optimal level when the amount of PHGG was added at 10-15 g/L. The results indicated that PHGG can be used to enhance the gel strength of yogurt to avoid the breakage of whey during transportation. The results showed that PHGG can be used as an effective yogurt additive.
