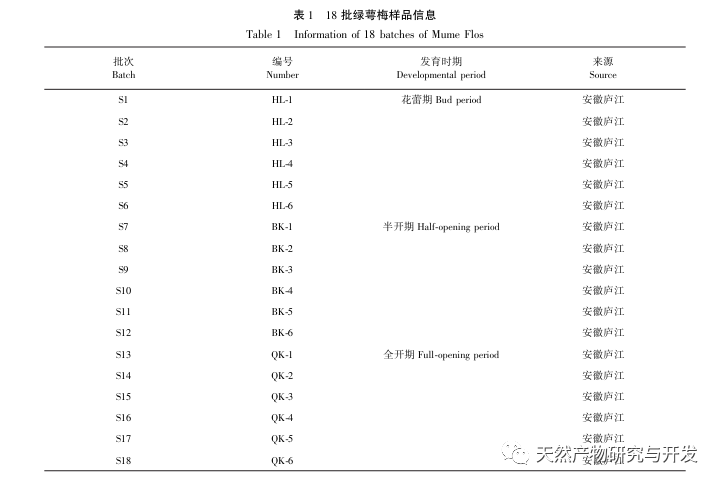
Characterization of Composition Differences and Antioxidant Activity of Green Calyx Plum at Different Development Stages by UPLC-QE-MS Combined with UPLC
Green sepal plum is a dried flower bud of Prunus mume (Sieb.) Sieb. et Zucc., a plant in the Rosaceae family. It is included in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia as a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine. It has the effects of soothing the liver, promoting digestion, resolving phlegm, and dispersing nodules. It is commonly used to treat diseases such as liver and stomach qi pain, depression, and scrofula. Both ancient records and modern research suggest that plum blossoms are excellent for medicinal use with their “green sepals”. Their characteristics include a grayish green sepal and yellow white petals, with a fragrant aroma and good clinical efficacy. As a medicinal and edible herb, green calyx plum can also be used to make tea, pastries and other foods. It blooms in winter, fresh and elegant, and is listed as the top flower with high ornamental value. The comprehensive application of green calyx plum is receiving increasing attention.
Domestic and foreign scholars have conducted extensive research on the chemical composition and pharmacological effects of plum blossoms. The phenylpropanoid and flavonoid components, represented by chlorogenic acid, are the main material basis for the pharmacological activity of plum blossom. Their antioxidant, anti platelet aggregation, anti melanin production, and antidepressant effects have been widely reported. In recent years, flavonoids in plum blossoms have received increasing attention due to their antioxidant and antidepressant properties. Chlorogenic acid, isorhamnetin, quercetin, isoquercitrin, hyperoside, rutin and other flavonoids have been isolated and identified from plum blossoms. However, there are few reports on the overall chemical composition of green calyx plum, which hinders the in-depth research and development of its secondary metabolites.
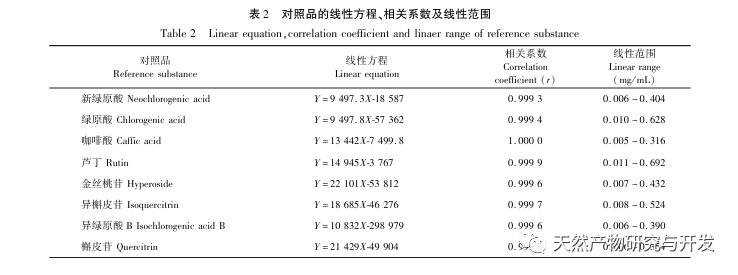
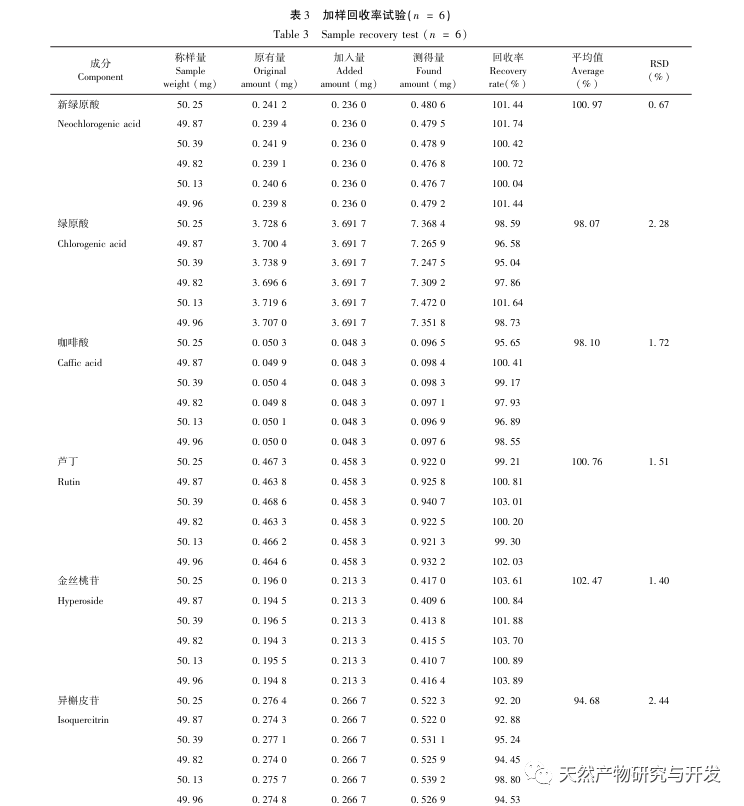
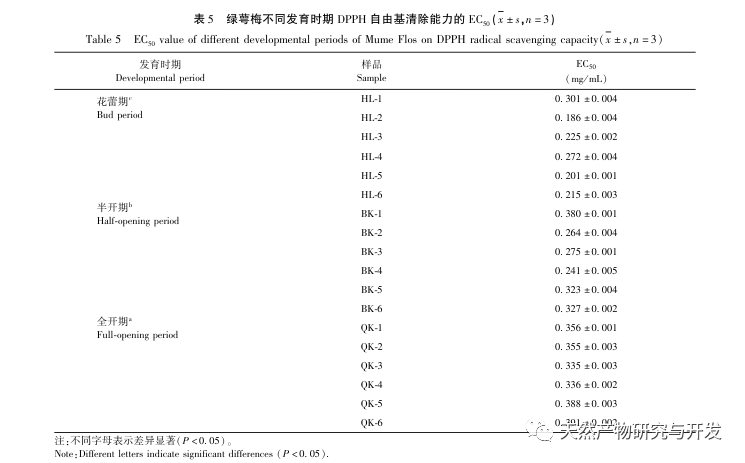
The secondary metabolites of medicinal plants have various biological activities and are an important material basis for medicinal herbs to exert their pharmacological effects. Research has found that different growth and developmental stages of plants are important factors affecting the accumulation of secondary metabolites in plants. Especially for floral medicinal herbs, the harvesting period can significantly affect the accumulation of secondary metabolites. To study the dynamic changes of chemical components and differences in antioxidant activity in organs of green calyx plum at different developmental stages, first, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole electrostatic field orbital trap mass spectrometry (UPLC-QE-MS) was used for qualitative analysis to clarify the chemical composition of green calyx plum; Through UV? Visible spectrophotometry was used to determine the total flavonoid and total phenylpropanoid content of 18 batches of green calyx plum samples at three developmental stages; Further, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) was used to determine the content of eight indicator components (neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rutin, hyperoside, isoquercitrin, isochlorogenic acid B, and quercitrin) in samples of green calyx plum, and the differences in the content of the eight components at different developmental stages were compared; The DPPH method was used to determine antioxidant activity, and the correlation analysis was conducted between the content of total components and indicator components and antioxidant activity. The research results provide a scientific basis for clarifying the differences in chemical composition and activity of green calyx plum at different developmental stages, and determining the optimal harvesting period for green calyx plum medicinal materials.
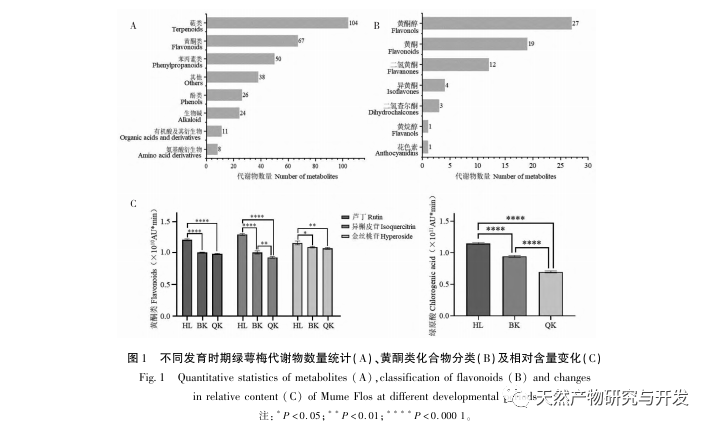
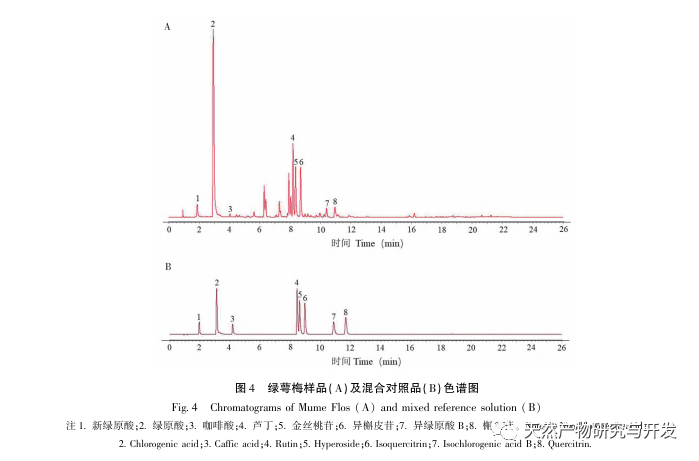
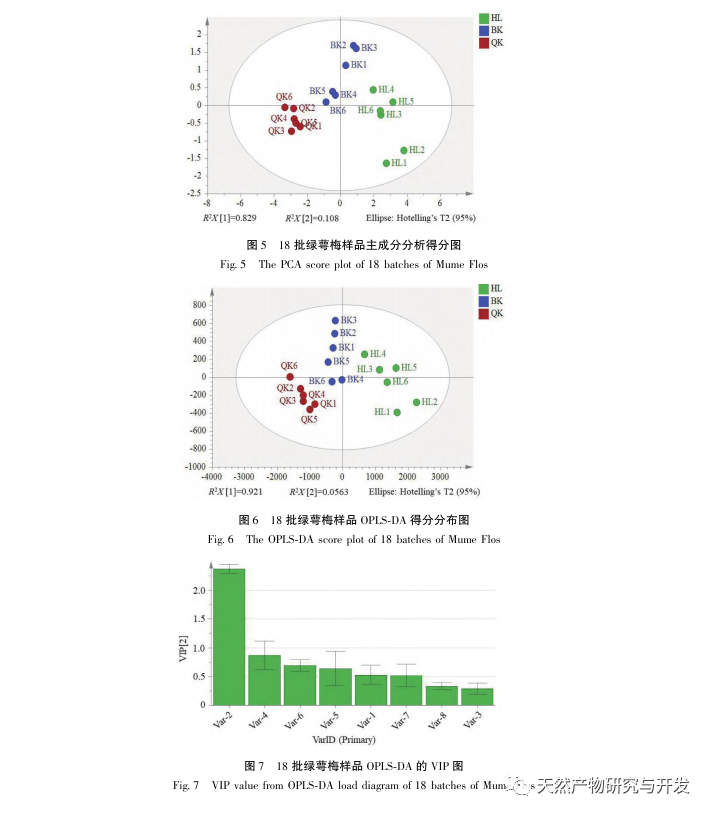

In this experiment, a total of 328 secondary metabolites were detected in green calyx plum using UPLC-QE-MS method. Flavonoids and phenylpropanoids accounted for a high proportion, with 67 and 50 compounds, respectively. Among the flavonoids, flavonols had the highest proportion, and components such as hyperoside and isoquercitrin, which serve as quality standards for plum blossoms, all belong to this class of substances. Studies have found that flavonols play an important regulatory role in flower organ development; Only one component of anthocyanins was detected, which may be related to the white color of the green calyx plum blossom.
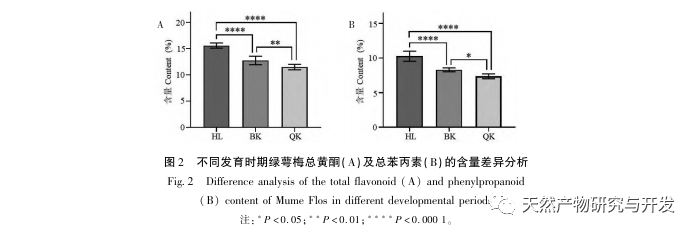
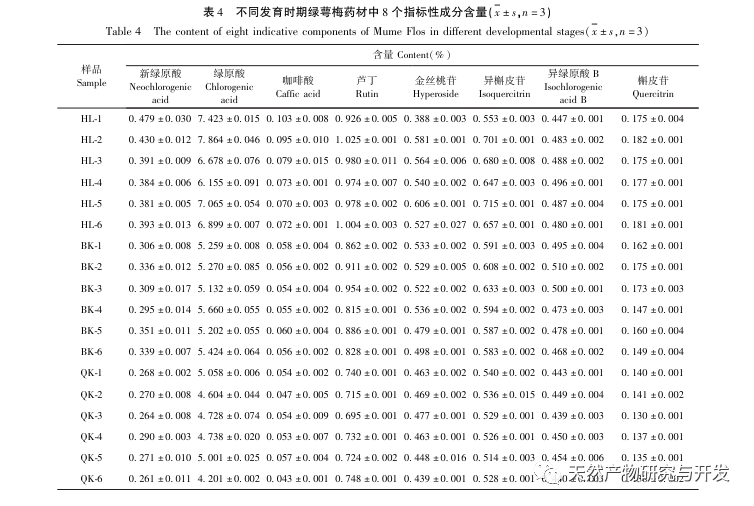
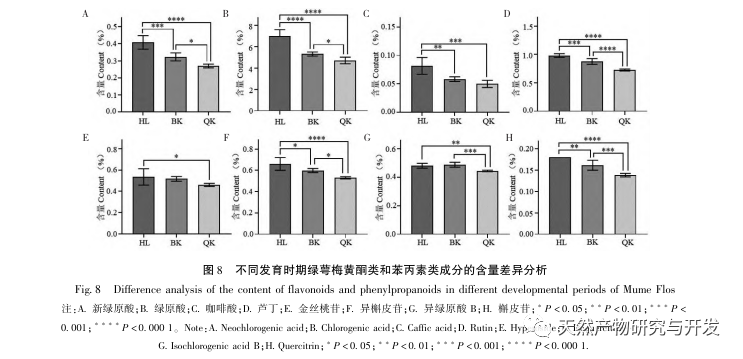
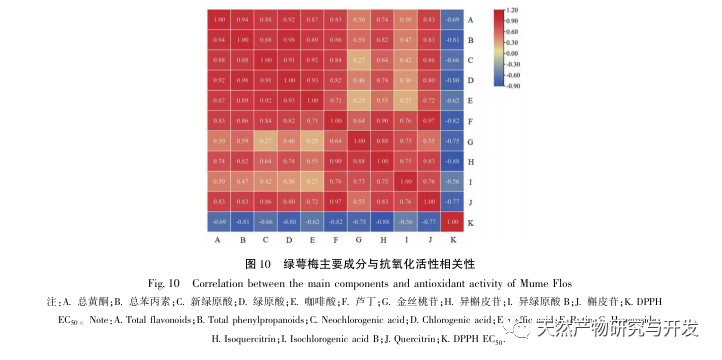
Further comparison of the changes in the composition of green calyx plum at different developmental stages showed that the content of total flavonoids and total phenylpropanoids was highest during the bud stage, and gradually decreased with the degree of flower opening. The content determination results of 8 indicator components (neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rutin, hyperoside, isoquercitrin, isochlorogenic acid B, quercitrin) showed significant differences between the bud stage and the fully open stage, with neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, isoquercitrin, and quercitrin showing extremely significant differences (P<0.0001); Chemical stoichiometry analysis showed that there were certain differences in the chemical composition of green calyx plum in the three periods, and chlorogenic acid could be used as a differential quality marker. Overall, the green calyx plum in the bud stage has advantages in terms of chemical composition and antioxidant activity, with significant differences compared to the semi open and fully open stages. Therefore, the harvesting period of medicinal materials should be controlled as much as possible during the bud stage.
In summary, this experiment used UPLC-QE-MS combined with UPLC method to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the chemical composition and differences of green calyx plum at different developmental stages, and compared its antioxidant activity differences through DPPH method. This provides a scientific basis for the dynamic changes in the chemical composition of green calyx plum and the optimal harvesting period of medicinal materials.
