The effect of Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang on the expression of related tumor suppressor genes in the “inflammation cancer transformation” of spleen deficiency damp heat ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an inflammatory disease that occurs in the colon, mainly damaging the colonic mucosa and gradually affecting the entire colon from the proximal end. If inflammation continues to stimulate, it can easily lead to the occurrence of colitis related cancers. Ulcerative colitis associated carcinogenesis (UCAC) is one of the serious complications of ulcerative colitis, which undergoes an evolutionary process of “inflammation atypical hyperplasia cancer”. The process of inflammation leading to tumor development is a step-by-step process that involves complex biological processes. For the pathogenesis of inflammation cancer transformation, some studies suggest that it is related to the excessive activation of oncogenes and the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. The imbalance in expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes is the essential cause of tumor development.
Traditional Chinese Medicine categorizes cancer associated with UC as a diagnosis of “chronic diarrhea”. The main pathogenesis of inflammatory colorectal cancer is spleen deficiency and damp heat. Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang is a formula that combines the principles of promoting water infiltration, dispersing dampness and heat in wine, regulating qi and awakening the spleen, and strengthening the spleen and qi. Therefore, this study established a spleen deficiency damp heat UC-UCAC mouse model and intervened with Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang for treatment. By observing the changes in the ultrastructure of the mouse colon mucosa and the effects of Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang on the expression of related oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in the colon tissue of spleen deficiency damp heat UC-UCAC mice, the possible mechanism of delaying the transformation of spleen deficiency damp heat UC-UCAC was explored, in order to lay a theoretical foundation for preventing the occurrence of UC-UCAC.

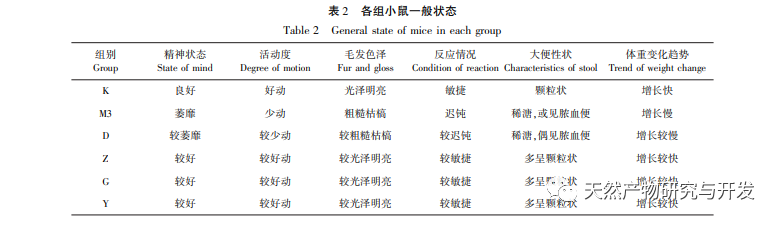
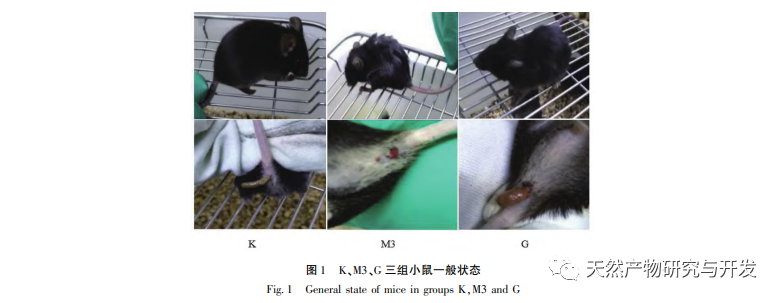
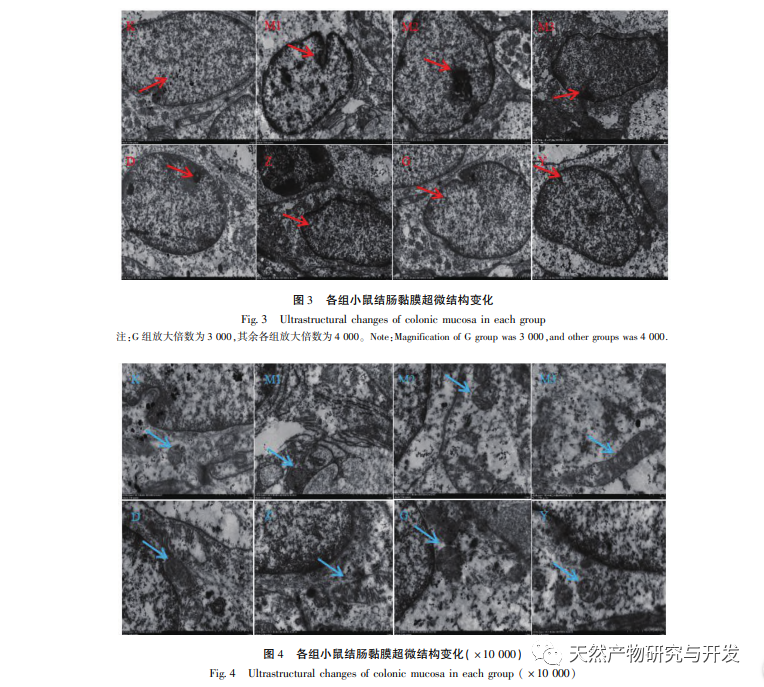
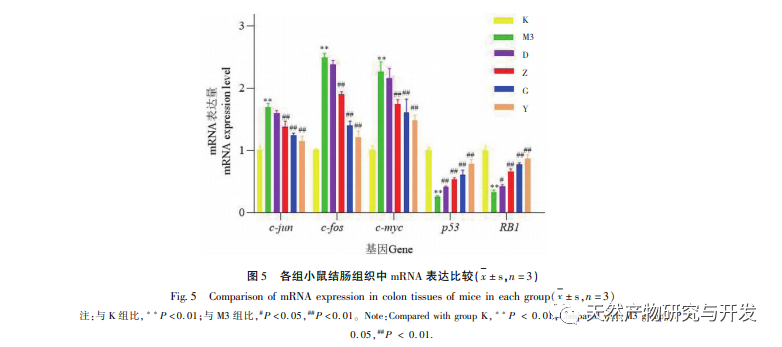
 UCAC is gradually formed under continuous and repeated stimulation of UC. The process of inflammation progressing into tumors involves complex biological processes, and researchers believe that the overactivation of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in the body are the essential causes of tumor formation. The process of carcinogenesis involves changes in cellular oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Proto oncogenes are cellular oncogenes that exist in animal genomes and are closely related to cell proliferation. If proto oncogenes are overexpressed, cells can form tumors due to excessive proliferation; Tumor suppressor genes, also known as anti-cancer genes, are negative regulatory factors in the biological process of cell proliferation. Studies have shown that typical representatives of oncogenes associated with colorectal cancer include c-jun, c-fos, and c-myc, while typical representatives of tumor suppressor genes associated with colorectal cancer include p53 and Rb genes. C-jun, c-fos, and myc belong to the myc gene family, which can promote cell proliferation and play an important role in tumor formation. Both c-fos and c-jun are early established genes, and activated c-fos and c-jun form AP-1 in the form of c-jun/c-fos dimer or c-jun homodimer. AP-1 induces the expression of corresponding oncogenes and promotes malignant transformation of cells. The p53 gene is a tumor suppressor gene that regulates cell proliferation and differentiation by negatively regulating the cell cycle. When it is deleted or mutated, it can promote unrestricted cell growth, leading to the development of tumors. Studies have shown that mutations in the p53 gene are the most critical factor in UC carcinogenesis. Retinoblastoma gene 1 (RB1) is the first cloned tumor suppressor gene isolated from humans. Previous studies have shown that the RB1 gene is involved in biological processes such as cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, and pRB induced apoptosis is achieved through activation of the tumor suppressor gene p53. During the process of cell apoptosis, pRB has a bidirectional regulatory effect. On the one hand, if cells undergo carcinogenesis, pRB initiates the apoptotic program through the p53 pathway, causing malignant cells to undergo apoptosis; On the other hand, if certain factors are overexpressed or pro apoptotic proteins are expressed, pRB interacts with these proteins to promote normal cell proliferation.
UCAC is gradually formed under continuous and repeated stimulation of UC. The process of inflammation progressing into tumors involves complex biological processes, and researchers believe that the overactivation of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in the body are the essential causes of tumor formation. The process of carcinogenesis involves changes in cellular oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Proto oncogenes are cellular oncogenes that exist in animal genomes and are closely related to cell proliferation. If proto oncogenes are overexpressed, cells can form tumors due to excessive proliferation; Tumor suppressor genes, also known as anti-cancer genes, are negative regulatory factors in the biological process of cell proliferation. Studies have shown that typical representatives of oncogenes associated with colorectal cancer include c-jun, c-fos, and c-myc, while typical representatives of tumor suppressor genes associated with colorectal cancer include p53 and Rb genes. C-jun, c-fos, and myc belong to the myc gene family, which can promote cell proliferation and play an important role in tumor formation. Both c-fos and c-jun are early established genes, and activated c-fos and c-jun form AP-1 in the form of c-jun/c-fos dimer or c-jun homodimer. AP-1 induces the expression of corresponding oncogenes and promotes malignant transformation of cells. The p53 gene is a tumor suppressor gene that regulates cell proliferation and differentiation by negatively regulating the cell cycle. When it is deleted or mutated, it can promote unrestricted cell growth, leading to the development of tumors. Studies have shown that mutations in the p53 gene are the most critical factor in UC carcinogenesis. Retinoblastoma gene 1 (RB1) is the first cloned tumor suppressor gene isolated from humans. Previous studies have shown that the RB1 gene is involved in biological processes such as cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, and pRB induced apoptosis is achieved through activation of the tumor suppressor gene p53. During the process of cell apoptosis, pRB has a bidirectional regulatory effect. On the one hand, if cells undergo carcinogenesis, pRB initiates the apoptotic program through the p53 pathway, causing malignant cells to undergo apoptosis; On the other hand, if certain factors are overexpressed or pro apoptotic proteins are expressed, pRB interacts with these proteins to promote normal cell proliferation.
In the entire process of colitis cancer transformation, its pathogenesis can be attributed to spleen deficiency and unhealthy, damp heat accumulation in the intestines. Many researchers believe that the pathogenesis of colitis cancer transformation is mainly spleen deficiency and damp heat. Li et al. believe that spleen deficiency and damp heat are the main pathogenesis of inflammatory colorectal cancer. Fan et al. believe that spleen and stomach weakness is the root cause of precancerous lesions in colon cancer. Yan et al. believe that damp heat blocking the intestines is the hallmark of its pathogenesis. Wang et al. believe that damp heat accumulation syndrome is the main syndrome type of colorectal cancer. Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang, also known as “Ge Hua Jie Jiu Tang” or “Jie Cheng Tang”, comes from Li Dongyuan’s “On the Spleen and Stomach” during the Jin and Yuan dynasties, and is known for “excessive drinking and injury”. The composition, dosage, and indications of Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang were described in the book “Spleen and Stomach Theory”. As the saying goes, “Green skin is three parts, wood fragrance is five parts, orange peel, ginseng, Poria cocos, and Poria cocos are one and a half cents each, Shenqu fried yellow, Alisma, dried ginger, and Atractylodes macrocephala are two cents each, and white bean curd kernels, Ge Hua, and Sha Ren are five cents each… But if you sweat a little, you will get rid of the alcohol disease.” Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang is a representative formula for treating alcohol injuries. Some researchers believe that the pathogenesis of the disease of damaging “alcohol” can be summarized as spleen and stomach weakness, and damp heat stagnation. The sweet, cold, and fragrant Ge flower in the formula is a good product for relieving drunkenness and invigorating the spleen. It is also clear and light, and can promote the release of wine dampness from the surface, making it a medicinal herb. The record of Ge Hua in the Han Dynasty’s “Collection of Medical Formulas and Explanations” states: “This hand and foot Yangming medicine is also used. Excessive drinking leads to the accumulation of dampness and heat toxins in the stomach and intestines. Ge Hua enters Yangming alone, causing dampness and heat to be released from the muscles.” Shenqu eliminates the accumulation of greasiness; Bai Kou and Sha Ren are dry and damp, affecting the stomach; Poria cocos, Atractylodes macrocephala, Zexie, and Poria cocos strengthen the spleen and eliminate dampness, allowing dampness and heat to pass through urine; Green skin, orange red, and wood fragrance promote the circulation of qi and stomach, and promote the stagnation of alcohol and food. When qi flows, it promotes the circulation of saliva, and when saliva flows, it humidifies to achieve the purpose of dehumidification and relieving stagnation; Dried ginger is warm and beneficial for water transport; Ginseng tonifies qi, prevents toxins, and disperses too much. In short, Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang has the functions of dispersing water, promoting water flow, regulating qi in the middle to invigorate the spleen, and strengthening the spleen to promote digestion. It is a formula that combines the methods of promoting water infiltration, dispersing dampness and heat in wine, regulating qi to invigorate the spleen, and strengthening the spleen and qi. Through the rigorous combination of traditional Chinese medicine from Ge Hua group, regulating qi group, strengthening spleen group, promoting water group, and warming the middle group, it has the power to warm the spleen and stomach, eliminate wine accumulation, and clear heat and dampness. In short, the pathogenesis theory of Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang includes the combination of deficiency in the root and excess in the target, mixed cold and heat, and imbalance of qi movement. It is a formula that combines both digestion and supplementation, warming and clearing, and nourishing qi and promoting qi circulation. Therefore, this study selected Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang to intervene in spleen deficiency damp heat type UCAC mice, in order to explore the mechanism of Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang in the process of colitis cancer transformation.
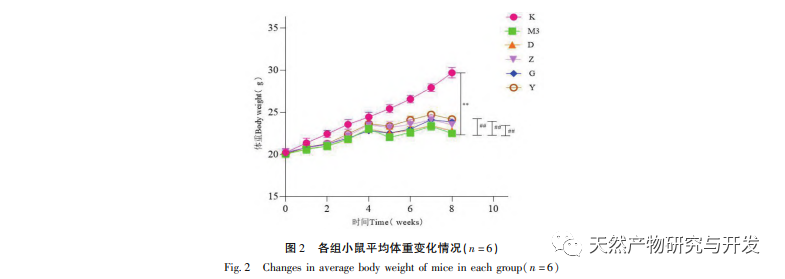
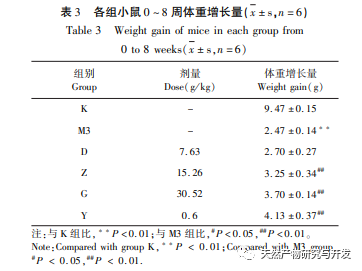
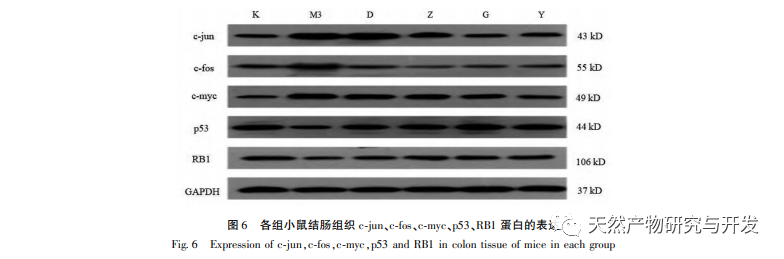
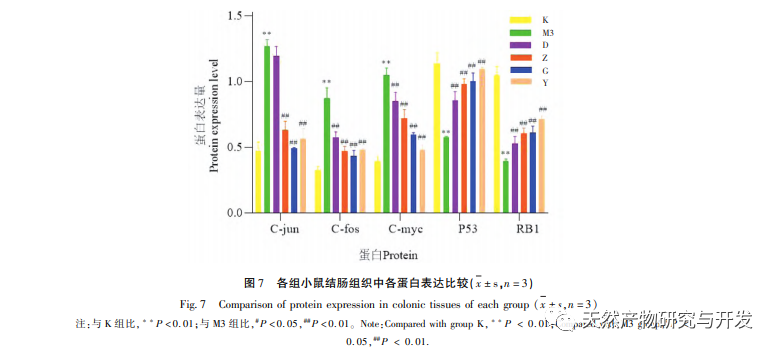
The results of this study showed that the expression levels of c-jun, c-fos, and c-myc proteins in the colon tissue of the model group mice were significantly increased compared to the blank group, while the expression levels of p53 and RB1 proteins were significantly decreased compared to the blank group; The expression levels of c-jun, c-fos, and c-myc mRNA were significantly increased, while the expression levels of p53 and RB1 mRNA were significantly decreased compared to the blank group; After treatment with various drug groups, the expression levels of c-jun, c-fos, and c-myc proteins in mouse colon tissue were significantly reduced, while the expression levels of p53 and RB1 proteins were significantly increased; The expression of c-jun, c-fos, and c-myc mRNA was significantly reduced, while the expression of p53 and RB1 mRNA was significantly increased, especially in the high and medium dose groups of Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang and the mesalazine group. Ge Hua Jie Cheng Tang can not only improve the general conditions of model mice such as mental state, diet, body weight, and activity, but also improve the colon mucosa of mice. It can also affect the expression levels of related oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis processes.
