A new phenolic glycoside compound in the fungus Aureobasidium pullulans (De Bary) Arnaud is a yeast like fungus that exists in different environments, such as fruit surfaces or woody tissues and leaves from early development to maturity. According to Index Fungorum, this fungus belongs to Ascomycota, Pezizomycotina, Dothideomycetes, Dothideomycetidae, and Dothideales. The biocontrol activity of its fungi against pathogenic bacteria in fruits, vegetables, and field storage has been widely reported, such as Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum on apples, and Aspergillus niger on edible grapes through A Pullulans were significantly controlled. And it can produce various metabolites, such as pullulan polysaccharide, melanin, single-cell protein, mannitol oil, poly (malic acid), 2-propylacrylic acid, 8,9-dihydroxy-2-methyl-4H, 5H-pyranochron-4-one, 2-methylsuccinic acid, hexol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol, etc. It is a natural biological control resource with development and application value. According to literature review, it is currently known that A The research on the chemical composition of pullulans mainly focuses on the extraction of large molecular substances, while there are relatively few reports on secondary metabolites. Therefore, this article aims to further investigate A Pullulans secondary metabolites and their antibacterial activity against A Chemical composition analysis was conducted on the ethyl acetate fraction of pullulans solid fermentation products, and the crude ethyl acetate extract was screened for activity to provide a theoretical basis for subsequent development and utilization.
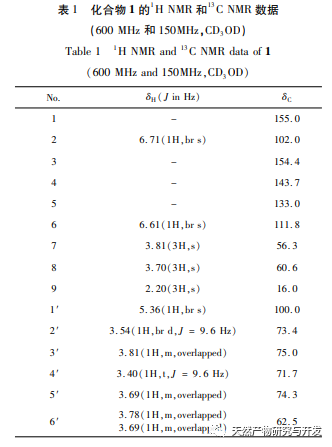
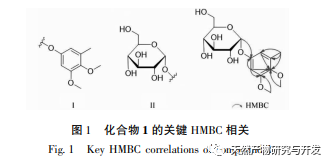
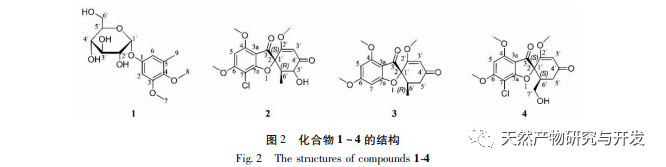

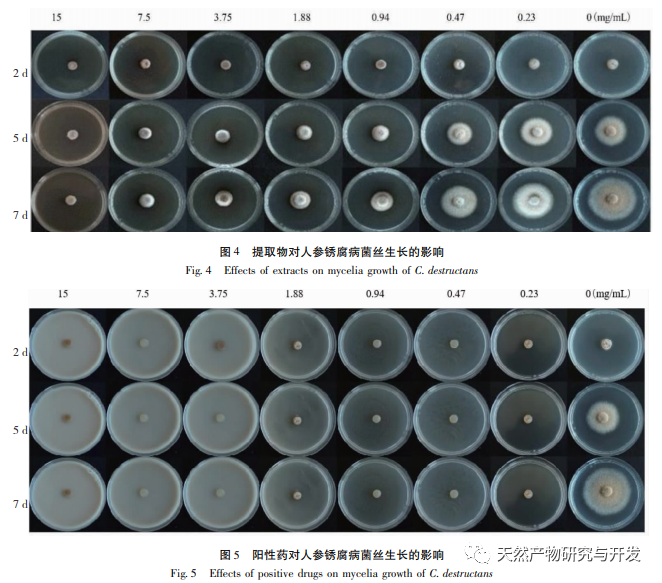
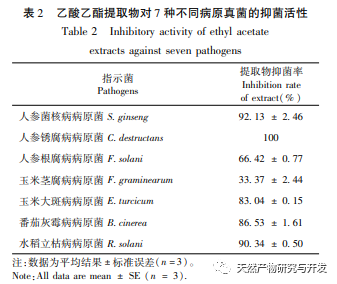 Fungus A Pullulans solid fermented ethyl acetate extract has antibacterial activity against the pathogens of ginseng rot, ginseng rust, ginseng root rot, corn stem rot, corn leaf spot, tomato gray mold, and rice stem rot. Among them, it has the best inhibitory effect on the pathogen of ginseng rust and rot, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 1.88mg/mL. Four compounds were isolated and identified from the extract, including one new phenolic glycoside compound (1) and three gibberellins compounds (2-4). Griseomycin is a neutral compound and an aromatic derivative antibiotic. The mechanism of its antibacterial effect is to competitively interfere with the synthesis of fungal cell DNA, thereby inhibiting its growth. At present, it is mainly used to treat skin diseases and fungal infections in the stratum corneum, and its antibacterial activity has also been studied in agricultural diseases. For example, Su Mingxing et al. and Liu Yun et al. found that oxytetracycline has a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of Fusarium. According to literature reports, compounds 2 and 3 have a certain inhibitory effect on Microsporum gypseum, while compound 4 has weaker antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Therefore, it is speculated that A Pullulans are compounds that exert antibacterial effects in the biocontrol activity of agricultural diseases. In the future, activity screening will be conducted on the isolated monomer compounds in order to provide A Pullulans provide a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of medicinal theory and biological activity.
Fungus A Pullulans solid fermented ethyl acetate extract has antibacterial activity against the pathogens of ginseng rot, ginseng rust, ginseng root rot, corn stem rot, corn leaf spot, tomato gray mold, and rice stem rot. Among them, it has the best inhibitory effect on the pathogen of ginseng rust and rot, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 1.88mg/mL. Four compounds were isolated and identified from the extract, including one new phenolic glycoside compound (1) and three gibberellins compounds (2-4). Griseomycin is a neutral compound and an aromatic derivative antibiotic. The mechanism of its antibacterial effect is to competitively interfere with the synthesis of fungal cell DNA, thereby inhibiting its growth. At present, it is mainly used to treat skin diseases and fungal infections in the stratum corneum, and its antibacterial activity has also been studied in agricultural diseases. For example, Su Mingxing et al. and Liu Yun et al. found that oxytetracycline has a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of Fusarium. According to literature reports, compounds 2 and 3 have a certain inhibitory effect on Microsporum gypseum, while compound 4 has weaker antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Therefore, it is speculated that A Pullulans are compounds that exert antibacterial effects in the biocontrol activity of agricultural diseases. In the future, activity screening will be conducted on the isolated monomer compounds in order to provide A Pullulans provide a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of medicinal theory and biological activity.
