What are the foreign nicotinamide mononucleotide raw material regulations?
Beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is the current “Netflix” raw material. The State Administration of Market Supervision and Regulation (SAMSAR), in its “Reply to Recommendation No. 1067 of the Fourth Session of the 13th National People’s Congress”, supports basic research on NMN and related products, and guides the standardized development of NMN and related products.
Currently NMN products circulating in China are mainly sold in the mode of cross-border e-commerce, and with the development of the market, there are more and more directions of scientific research involved. In the following, we will introduce the market scale, raw material composition, foreign regulations, efficacy claims, safety, etc., and also hope to let consumers understand more clearly the development of NMN abroad.
1. Market size of the U.S. market research firm (GlobeNewswire) data show that the global NMN raw material market sales in 2022 is estimated at 280 million U.S. dollars, and it is predicted that by 2028, NMN raw material sales will reach 496 million U.S. dollars, a compound annual growth rate of 10.0% [1]. Major suppliers include GeneHarbor, Herbalmax, Japan’s Shinkowa and EffePharm. The combined share of raw materials from the four reached a market share of 83%.

China as the largest consumer market of NMN, according to the data of AiMedia Data Center, the market size of food containing NMN ingredients reached 5.106 billion yuan in 2020, a year-on-year growth of 34.87%, and it is expected to climb to 27.013 billion yuan in 2023 with a growth rate of nearly 70.25%, with a relatively fast growth rate of the industry [2]. The market size and growth rate are shown in the figure below.

The above data shows that the current raw material suppliers are basically from Chinese companies, which fully demonstrates that Chinese raw materials in the global scope of the existence of a great competitive advantage. With the continuous deepening of our basic research, it may become a core variety of dietary supplement raw materials exported from China, and also become a concrete embodiment of China’s health food “going overseas” strategy. In addition, China’s market size is also the world’s largest, which fully demonstrates that if NMN is used as a new food ingredient or health food ingredient in the future, it can better meet the needs of consumers.
2.Raw material ingredient β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide.NMN is the precursor substance of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
Studies have shown that mammals cannot directly ingest NAD+, and in order to maintain NAD+ homeostasis in the body, NAD+ biosynthesis in mammals mainly relies on the nicotinamide remediation pathway involving precursors such as NAM and nicotinamide ribonucleic acid (NRNA) [3].
Currently, the precursors of nicotinamide ribonucleic acid mainly include the following two compounds: β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide riboside (NR), and their corresponding structural formulas are shown below.

From the above structural formula, it can be seen that NMN only has one more phosphate group than NR, and the other structures are more or less the same. It has been shown that NR is converted to NMN by nicotinamide nucleoside kinases (NRKs) after entering the cell.
In mammals, NMN is generated from Nicotinamide (Nam) catalyzed by Nampt and subsequently NMN is catalyzed by Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenosine transferase (Nmnat) to generate NAD+.
Extracellular NMN needs to be dephosphorylated to nicotinamide riboside (NR) to enter the intracellular hepatocyte. After entering the intracellular, NR is phosphorylated by Nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK1) to generate NMN, which is subsequently combined with ATP to generate NAD+.
NMN is converted to NAD+ in the human body in order to perform its physiological functions, such as activation of the NAD+ substrate-dependent enzyme Sirt1 (histone deacetylase, also known as silencing regulator protein), regulation of cell survival and death, and maintenance of the redox state, etc. [4].
The current methods for the preparation of NMN can be divided into two main categories: chemical synthesis and biological methods. The chemical synthesis method has been studied earlier and is mainly synthesized by different synthetic steps using nicotinamide, tetraacetyl ribose, etc. as raw materials. Compared with the chemical synthesis method, the preparation of NMN by biological method has the advantages of simple technical route, convenient operation, green environmental protection and low production cost.
At present, the enzymatic synthesis of NMN is mainly based on the generation of NMN by nicotinamide phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) and nicotinamide as substrates catalyzed by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt or Namprt). The yield of NMN can be increased by constructing the mutation of NAMPT by artificial means or utilizing the genetically engineered bacteria containing NAMPT to realize the efficient transformation of synthesis [5].
3. Foreign regulations β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide mononucleoside (NR) are precursor substances of NAD+. As food ingredients or dietary supplement ingredients, their requirements in foreign regulations are summarized in the following table.

As can be seen, NR is basically approved as a food ingredient in the EU, USA, and Japan, and it is equivalent to a source of vitamin B3 (niacin).NMN is regulated as a food ingredient in Japan and the USA.NMN/NR is regulated as a natural health product in Canada.
There are also many Chinese companies that are currently applying for New Dietary Ingredient (NDI) from the FDA, which can be seen on the FDA’s website, as shown below [6].

As can be seen, both applications numbered 1234 and 1240 are NMN applications, and the FDA has responded to this application accordingly.
We also see that there are a number of NMN products marketed in the U.S. This can be seen in the FDA application documents on structure/function claims as shown below [7].

This information seems to contradict the NDI application, which is a feature of the U.S. regulations governing dietary supplements. According to the FDA’s regulations on NDI filings, ingredients that have been marketed in the U.S. before October 15, 1994, can be marketed directly without filing an NDI. If you can’t confirm, you can apply for an NDI filing. Therefore, many companies may think that this ingredient has been sold in the U.S. market before October 15, 1994, so do not need to apply for NDI filing.
4. Functional Claims In recent years, there has been an increasing number of studies on the biological functions of NMN [8,9-18], such as: improvement of age-related pathophysiology and disease conditions, significant reduction of age-related physiological decline, improvement of cellular energy status, the nervous system, and brain cognition (Alzheimer’s), etc., and has shown good results in the improvement of heart disease, diabetes, and many other disease conditions. Organized as shown in the table below.

We downloaded a structure/function application for Swanson Health Products, NMN in the US FDA [19], a screenshot of which is shown below:

The translation claims the following: (1) NMN is a precursor of NAD+ and is essential for cellular health. (2) Energy metabolism. (3) May support healthy blood sugar levels and metabolic function. However, most of the related functional claims come from animal experiments, so it can only be tentatively stated that NMN has some relevant efficacy, which still needs to be confirmed by subsequent full validation, including human validation and other extensive work.
5. Safety and Clinical Research As mentioned above, safety is an important indicator of food, and NR has been approved as a food ingredient in major countries and regions all over the world, so its safety has been proved, and NMN, as a new ingredient, has been approved as a food ingredient in Japan, and can be used as an ingredient of dietary supplements in other countries and regions, which means that its safety has been verified. NMN as a new ingredient has been approved as a food ingredient in Japan, and can be used as a dietary supplement ingredient in other major countries and regions, indicating that its safety has been verified to some extent.
However, there is still a lack of safety data on human beings, and many clinical trials on NMN around the world involve safety and other related functional evaluations. We have compiled a list of clinical studies involving NMN worldwide, and the results are shown in the table below.
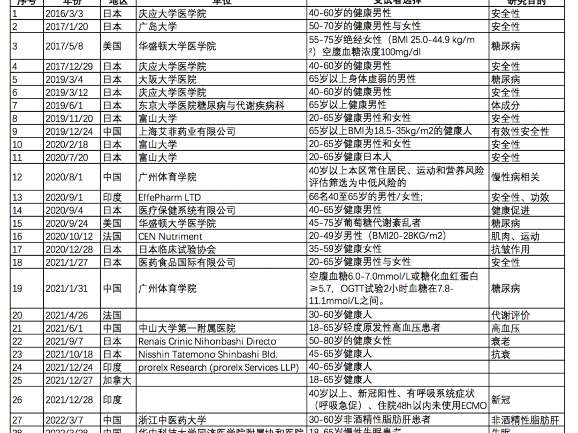
As can be seen from the 28 clinical studies mentioned above, 10 clinical studies dealt with safety. It is believed that the safety data of NMN will also be presented in the near future.
In summary, β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide mononucleoside (NR), as precursor substances of NAD+, have been sold only as scientific research materials for research organizations and expensive in the past few years.
In recent years, the absorption and activity of NMN in the human body have been enhanced by certain biotechnologies, and its production cost has been reduced. Animal experiments have preliminarily verified its wide range of efficacy, and it has gradually begun to emerge in the field of dietary supplements in foreign countries, but the lack of experimental data on human beings has not yet provided comprehensive support for its basic research data.
It is believed that with the continuous development of global clinical research experiments, it will gradually be recognized by the government departments of the United States, the European Union and other countries. As a major country in the production of NMN raw materials, in addition to the accumulation of basic research data, it will gradually become a reality for NMN to become a new food ingredient and health food ingredient, so that it can better serve the Chinese consumers and satisfy the people’s pursuit of a healthy and beautiful life. References: 1. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/07/14/2479548/0/en/Nicotinamide-Mononucleotide-NMN-Size-Share-Growth-2022- 2028-Latest-Developments-Revenue-Gross-Margin-Key-Players-Market-Drivers-Challenges-Trends-Distributors-Customers-and-Forecast. html.2. https://www.iimedia.cn/c1020/77260.html.3.RAJMAN L, CHWALEK K, SINCLAIR D A. Therapeutic potential of NAD-boosting molecules: the in vivo evidence [J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27(3): 529-47.4. ZHAO Juan, ZHANG Jian, YU Zhijian et al. Progress in the study and application of nicotinamide mononucleotide [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(4): 257-262.5. Yu Hanxiao, Zhu Mengjia, Shi Sweetie et al. Research progress on synthesis and application of nicotinamide mononucleotide [J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(8):104-106.6. https://www.fda.gov/food/new-dietary-ingredients-ndi-notification-process/submitted-75-day-premarket- notifications-new-dietary-ingredients.7.https://www.regulations.gov/search?filter=Nicotinamide%20Mononucleotide.8.Mills K F, Yoshida S , Stein L R, et al. Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age – associated physiological decline in mice [J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 24(6): 795-806.9. Li J, Bonkowski M S, Moniot S, et al. A conserved NAD+ binding pocket that regulates protein – protein in-teractions during aging [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6331):1312-1317.10. Kiss T, Nyúl-Tóth Á, Balasubramanian P, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes neurovascular rejuvenation in aged mice: transcriptional footprint of SIRT1 activation, mitochondrial protection, anti -inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects [J]. GeroScience, 2020, 42(2): 527-546.11. Lu L, Tang L, Wei W, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide improves energy activity and survival rate in an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Exp TherMed, 2014, 8(3): 943-950.12. Park J H, Long A, Owens K, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits post – ischemic NAD+ degradation and dramatically ameliorates brain damage following global cerebral ischemia [J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2016, 95: 102-110.13. Yamamoto T, Byun J, Zhai P, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide, an intermediate of NAD+synthesis, protects the heart from ischemia. protects the heart from ischemia and reperfusion [J]. Plos One, 2014, 9(6): e98972.14. Revollo J R, Körner A, Mills K F, et al. Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme [J]. Cell Metab, 2007, 6(5): 363-375.15. Uddin G M, Youngson N A, Doyle B M, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation ameliorates the impact of maternal obesity in mice: comparison with exercise [J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 15063.16. Song J, Li J, Yang F, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide promotes osteogenesis and reduces adipogenesis by regulating mesenchymal stromal cells via the SIRT1 pathway in aged bone marrow [J]. Cell Death Dis,2019, 10(5): 336-347.17.Lin J B, Kubota S, Ban N, et al. NAMPT – mediated NAD+ biosynthesis is essential for vision in mice [J]. Cell Rep, 2016, 17(1): 69-85.18. Guan Y, Wang S R, Huang X Z, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide, an NAD+ precursor, rescues age -associated susceptibility to AKI in a sirtuin 1-dependent manner [J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28(8): 2337-2352.19. https://www.regulations.gov/document/FDA-2021-S-0024-0665.
