Identification of Ficus microcarpa and its related species based on ITS2 sequence and HPLC fingerprint
The Ficus pandurata Hance, also known as the milk tree or milk seed, is a plant in the Ficus genus of the Moraceae family. It is mainly distributed in Guangdong, Guangxi, Jiangxi, Hainan, Fujian, Hunan, Hubei, Jiangxi, Anhui, Zhejiang and other places. According to the “Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine”, “Fujian Medicinal Records”, and “Jiangxi Folk Herbal Formula Testing”, the root and leaf parts of the Ficus microcarpa are used as medicine. It has a mild nature, a sweet and slightly cool taste, and is non-toxic. It has the effects of clearing heat, invigorating the spleen, stimulating appetite, nourishing qi and generating fluids, and dispelling dampness and stagnation. It is used to dispel wind, dampness, detoxify, treat malaria, and promote lactation. For example, the “Jiangxi Folk Herbal Formula Testing” records that moderate amounts of Ficus microcarpa roots and Malan can be used to treat jaundice when taken orally in a clear water decoction; An appropriate amount of banyan root, Brahma root, Stephania tetrandra, Acanthopanax senticosus root and wormwood stem can be used to treat lumbar spine pain with the mixture of Baijiu and water of the same volume. In Guangdong, Ficus microcarpa has a long history of eating and medicine, and a deep mass base, which has become an important part of the local characteristic Tonic Diet and the raw materials of dietetic medicine. Modern research has shown that Ficus microcarpa contains active ingredients such as triterpenoids, flavonoids, coumarins, and phenolic acids. Among them, bergamot lactone has various pharmacological activities such as anti-tumor, blood sugar regulation, insomnia improvement, prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and anti allergic effects; Psoralen has pharmacological effects such as anti osteoporosis, neuroprotection, anti-tumor, estrogen like, anti-inflammatory, etc; Both have anti osteoporosis effects, are abundant and readily available, and are representative active ingredients of Ficus microcarpa.
At present, there are three main types of mixed products of Ficus microcarpa medicinal herbs on the market: Ficus microcarpa var. holophylla, Ficus microcarpa var. angustifolia, and Ficus microcarpa var. hirta. Quanyuan Qinye Ficus and Tiaoye Ficus are variants of Qinye Ficus, with transitional leaf shapes among the three; In addition, both Ficus microcarpa and Ficus microcarpa use their roots as medicine and have a milky aroma. They are often sold in the market under the trade name Milk Tree Roots, resulting in uneven quality of the medicinal materials. At present, modern research on Ficus microcarpa mainly focuses on pharmacognosy, chemical composition, and pharmacological activity, and there are no reports on the quality standards of Ficus microcarpa. DNA barcode identification is a molecular biology identification method that uses a standard, relatively short DNA sequence for species identification. This method is of great significance in promoting the development and utilization of new Chinese medicine resources, alleviating the shortage of Chinese medicine identification talents, managing the circulation of Chinese medicine markets, and addressing the hidden seed problems that morphology is difficult to overcome. HPLC fingerprint is a reliable method for identifying the authenticity, evaluating quality consistency, and stability of traditional Chinese medicine chemical components obtained through chromatographic techniques based on the understanding of the overall action of substance groups. In this experiment, ITS2 sequences were used for molecular identification of Ficus microcarpa and its related species. HPLC fingerprint spectra were established to determine the differences in the content of psoralen and bergamot lactone, and to identify Ficus microcarpa and its related species from different origins. This provides a scientific basis for the quality control and evaluation of Ficus microcarpa medicinal materials.
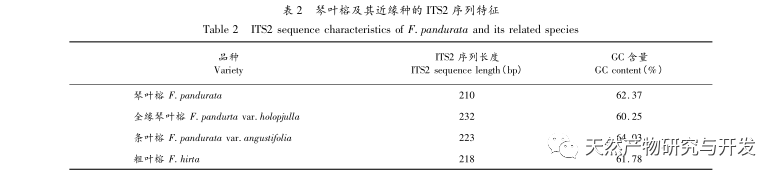
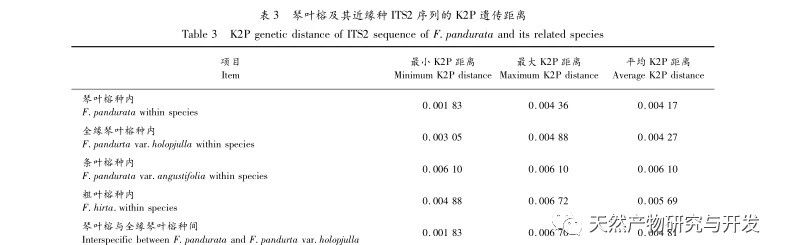

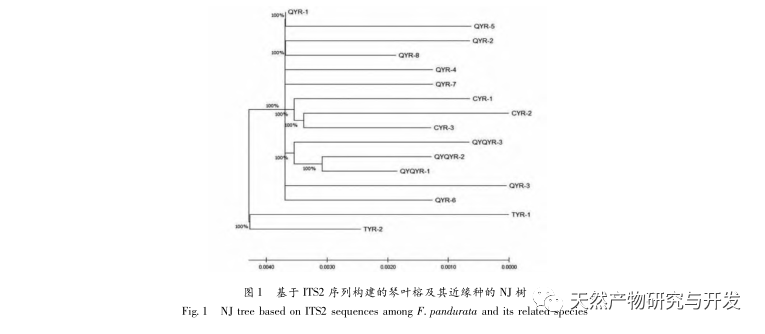
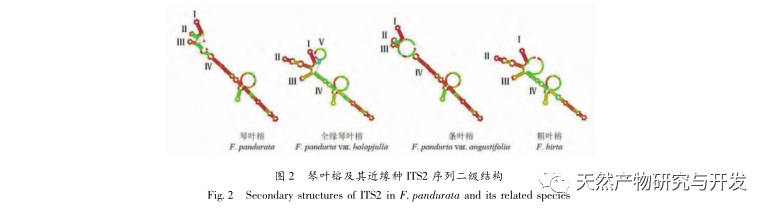
 The experiment analyzed the ITS2 sequence, K2P genetic distance, NJ tree clustering analysis, and secondary structure of Ficus microcarpa and its related species. Both NJ tree clustering analysis and secondary structure can effectively distinguish Ficus microcarpa and its related species. However, the genetic distance within and between K2P species has certain limitations in identifying Ficus microcarpa and its related species, and requires the combination of NJ tree clustering analysis and secondary structure for identification.
The experiment analyzed the ITS2 sequence, K2P genetic distance, NJ tree clustering analysis, and secondary structure of Ficus microcarpa and its related species. Both NJ tree clustering analysis and secondary structure can effectively distinguish Ficus microcarpa and its related species. However, the genetic distance within and between K2P species has certain limitations in identifying Ficus microcarpa and its related species, and requires the combination of NJ tree clustering analysis and secondary structure for identification.
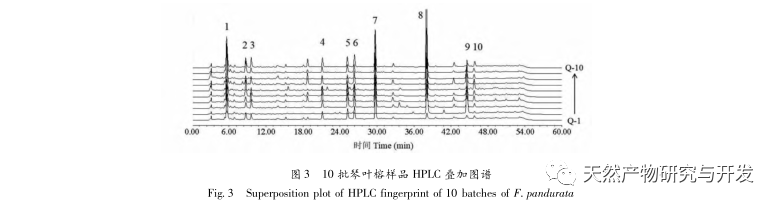
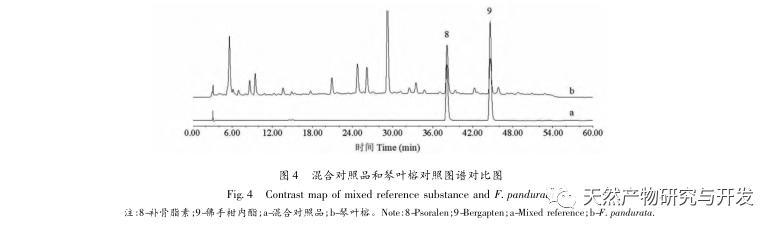
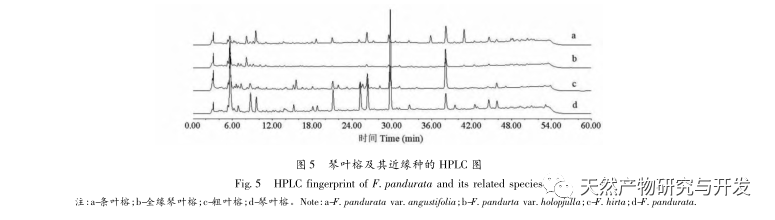
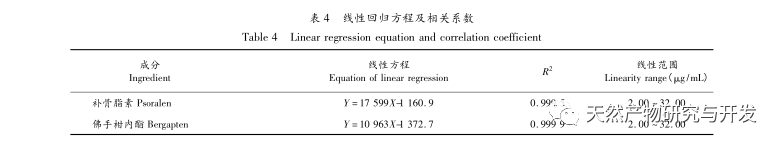
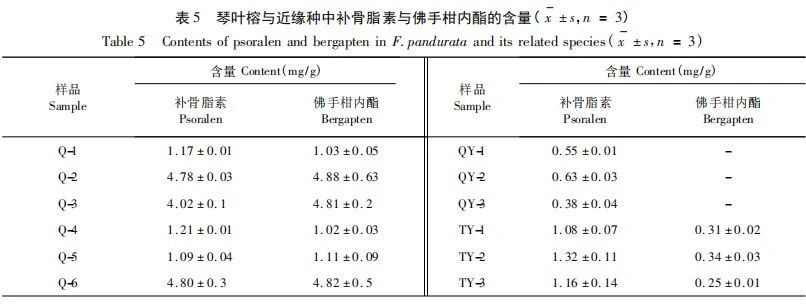
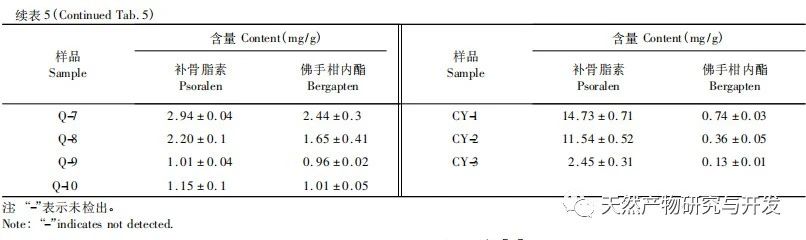
The experiment investigated chromatographic conditions such as different extraction solvents, detection wavelengths, column temperatures, mobile phase systems, and chromatographic columns. The results showed that using 95% ethanol extraction, XBridge Peptide BEH C18 (5 μ m, 4.6mm × 250mm) chromatographic column, detection wavelength 330nm, column temperature 30 ℃, flow rate 1.0mL/min, and mobile phase methanol-pH8 phosphate buffer solution, the peak shapes and separation degree of each color spectrum were good. We have established HPLC fingerprint spectra of Ficus microcarpa and its related species, filling the gap in the study of HPLC characteristic spectra of Ficus microcarpa. The fingerprint spectra of Ficus microcarpa and its related species show significant differences in the number of characteristic peaks and relative retention time, which can intuitively distinguish Ficus microcarpa from its related species and be applied to the quality evaluation of Ficus microcarpa. There are a total of 10 chromatographic peaks in Ficus microcarpa from different origins, most of which were not detected in Ficus microcarpa and Ficus microcarpa. The similarity between closely related species and Ficus microcarpa is less than 0.807; There is a significant difference in the content of psoralen and bergamot lactone between Ficus microcarpa and its related species. The content of Ficus microcarpa and Ficus microcarpa is significantly lower than that of Ficus microcarpa, indicating a difference in quality between Ficus microcarpa and its related species. It has important practical guidance value for using the content of psoralen and bergamot lactone as quality control indicators for Ficus microcarpa. Therefore, fingerprint spectra, similarity, and content determination can objectively and accurately distinguish the authenticity of Ficus microcarpa medicinal materials, which can be effectively used for quality control and authenticity identification of Ficus microcarpa medicinal materials.
In summary, the DNA barcode and HPLC fingerprint of Ficus microcarpa and its related species have been established. The method is simple, reliable, stable, and has good repeatability, which can be used for fingerprint research and authenticity identification of Ficus microcarpa and its related species. At the same time, it provides a scientific basis for further improving the quality of Ficus microcarpa.
In the PPI network, 42 important targets were selected based on degree ranking, which were mainly divided into 5 categories: protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPN1, PTPN2, PTPN6, PTPN11, etc.), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PIK3R1, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, etc.), mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK8, MAPK14, etc.), cyclin dependent kinases (CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, etc.), and other important targets (VEGFA, HSP90AA1, LCK, etc.). These important targets can provide reference for targeted therapy of UC.
