Study on the correlation between the chemical forms of soil inorganic elements and the main effective components of Dianzhong Lou
Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis is a perennial herbaceous medicinal plant in the lily family. It is mainly used as medicine with dry roots and stems, and has a cold and bitter taste. It has the effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, cooling the liver and calming the nerves, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory. In recent years, due to the rapid development of the pharmaceutical industry, the market demand for Dianzhong grandiflorus has doubled. However, the medicinal parts of Dianzhong grandiflorus grow slowly and have low reproduction rates, leading to the depletion of wild Dianzhong grandiflorus resources. Therefore, it is urgent to develop cultivated crops to solve the problem of insufficient supply of wild resources.
Elemental forms are divided into physical and chemical forms, with chemical forms referring to the molecular or ionic forms that elements actually exist in the environment, closely related to their enrichment, mobility, and bioavailability. They mainly include water-soluble states, exchangeable states (weakly acidic extracted states), iron manganese oxidized states (reducible extracted states), organic states (oxidizable extracted states), residual states, etc. At present, research on soil elements mainly focuses on the exploration of their total elemental content. Although total elements can reflect the total content of soil elements to a certain extent, they cannot intuitively reflect the true content of elements that can be absorbed and utilized by plants. Therefore, analyzing the content of various elemental forms in soil will have a more comprehensive significance for understanding the distribution of elements in a certain region. In addition, a large number of scholars have explored the forms and contents of various heavy metal elements in the rhizosphere soil of Chinese herbal medicine, but there is little analysis of other inorganic element forms. Among them, Shen studied the absorption and migration laws of inorganic elements in Danshen and found that the content of inorganic elements in Danshen is greatly influenced by the distribution of rhizosphere element forms, mainly by the interaction of exchangeable, residual, organic, and iron manganese oxidation state contents in the rhizosphere soil. This provides a good demonstration and reference for research on the quality, rhizosphere soil, and element form migration of Dianzhong buildings.
This study used BCR sequential extraction method to extract the chemical forms of each element, and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used for content determination. The distribution and content of 16 inorganic elements in the rhizosphere soil of wild and cultivated Dianzhong Lou were explored, and correlation analysis was conducted with effective components, in order to provide reference for rational fertilization and standardized planting of Dianzhong Lou.

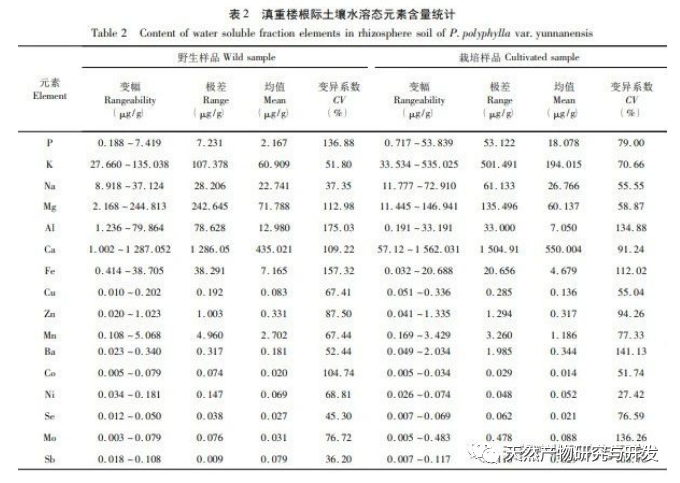

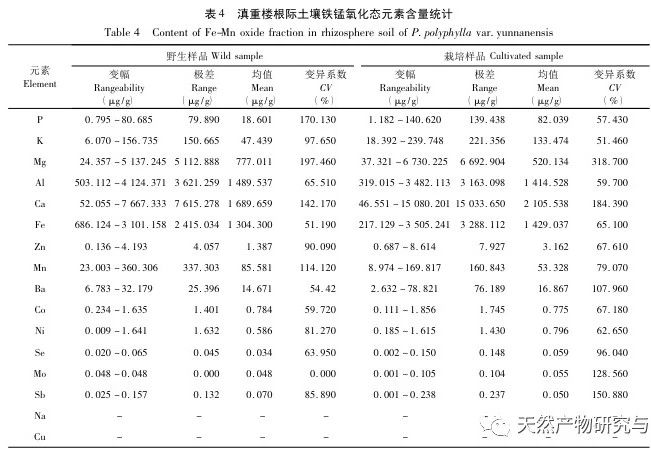
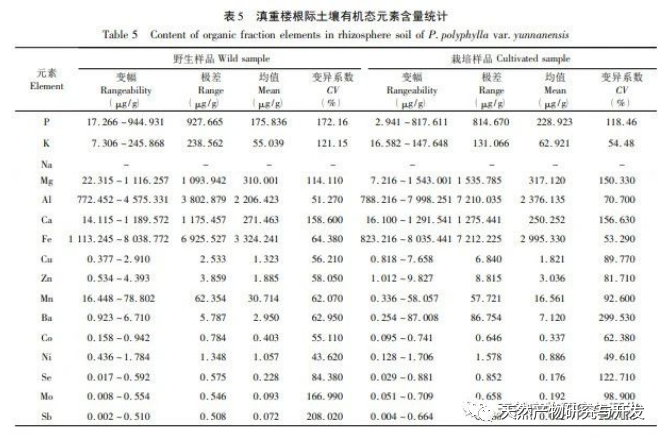


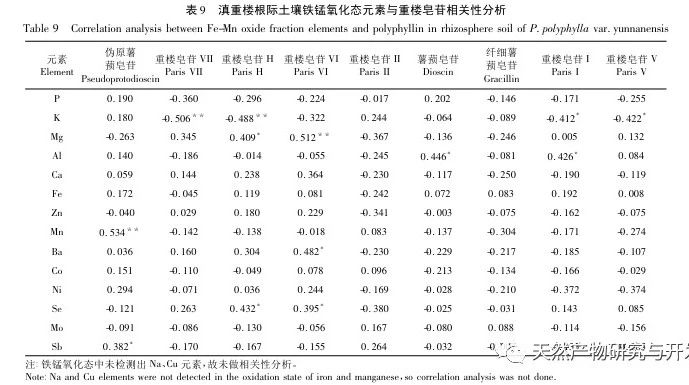

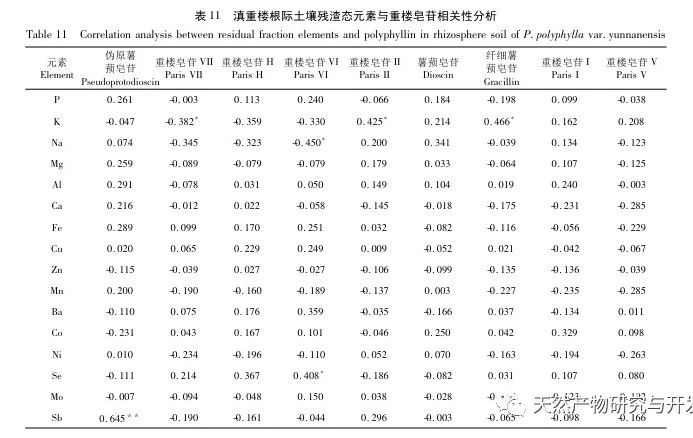
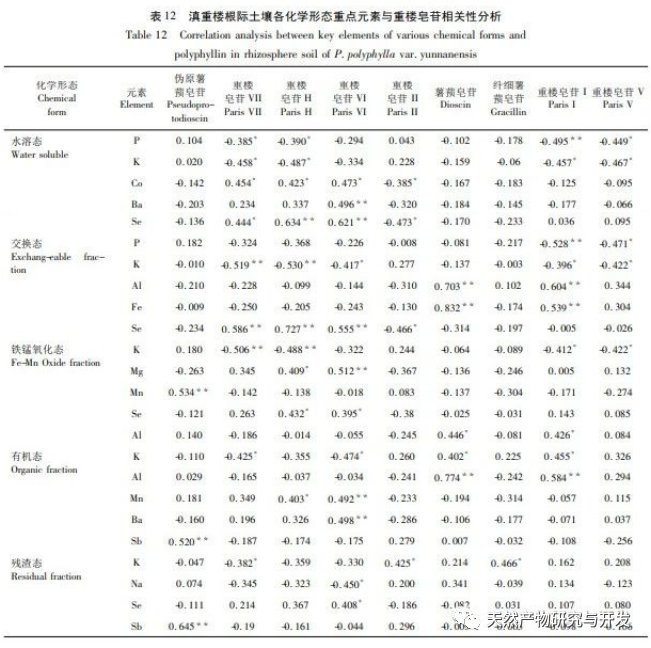
The form of elements is one of the important contents of ecological geochemical investigation and evaluation, and it is an important foundation for studying the cyclic laws of element migration and transformation. Research has shown that water-soluble and exchangeable states have high bioavailability and are easily migrated and transformed in environmental systems for absorption and utilization by plants. Based on the results of this study, the content of K element in water-soluble state is relatively high. As one of the important nutrients for plants, it can promote photosynthesis in Dianzhong, regulate cell osmotic pressure in plants, and enhance their adaptability to adverse environments. Compared with wild Dianzhong Lou, the K element content in cultivated products is significantly higher, indicating better soil fertility in the cultivated plots, which may be closely related to the artificial fertilization of Dianzhong Lou cultivation. However, another important nutrient element P has a low content in the exchangeable and water-soluble states, and a high content in the organic and residual states. In terms of artificial treatment of cultivation plots, phosphorus fertilizer can be appropriately applied to improve soil fertility. Fertilization measures should also be taken to compensate for some elements that play an important role but have low or undetected content. Mo element was not detected in the exchange state, but it has a positive promoting effect on photosynthesis, plant height, and root and stem yield of Dianzhong Lou plants. The oxidation state of iron manganese is a part of the formation of nodules between elements and hydrated Fe2O3 and Mn2O3, and its stability is poor. Studies have shown that this form of heavy metal is easily released through reduction reactions, posing a potential threat to the environment. Organic states have strong chemical bonds and can only decompose under strong oxidation conditions, making them relatively stable. In these two chemical forms, the content of elements such as Ca, Mg, Al, Fe is relatively high, indicating that they have not bound to the above-mentioned ion groups or their complexes are unstable, and Na element has not been detected, indicating that Na+in the free state has been extracted during the exchange state extraction process. Residual state is a form in which an element is encapsulated in a mineral lattice, which is highly stable and not easily released or utilized by plants. It is an inert form. In this study, most elements exist in the form of residues, which indirectly reflects the low content of elements that can actually be utilized. The richness of various chemical forms of elements varies from place to place, and the content of the same element is also inconsistent, with some even showing significant differences. This is related to factors such as the geographical environment, agricultural production methods, cultivation, and later fertilization management of the place of origin. The study on the chemical forms of various elements in the rhizosphere soil of wild and cultivated Dianzhonglou plants intuitively reflects the effective content of soil elements.
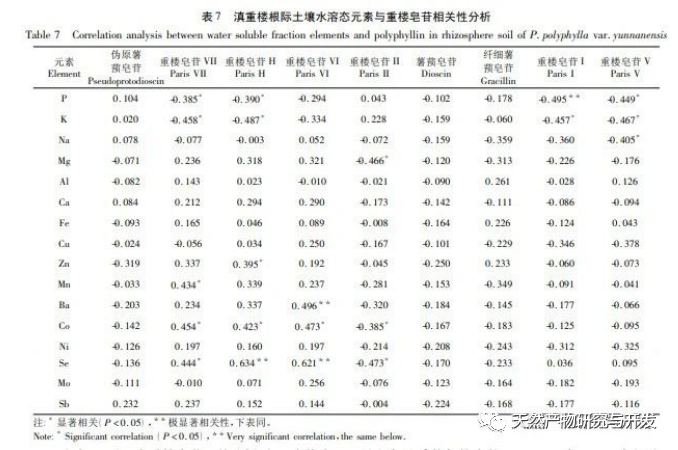
Correlation analysis shows that the quality of Dianzhong Lou medicinal herb is closely related to its rhizosphere soil elements. The effect of nutrients on active ingredients is not necessarily positive, just like the P and K elements in water-soluble, iron manganese oxidized, and exchangeable states, which promote the healthy growth of Dianzhong Lou plants while also inhibiting the accumulation of their active ingredients to a certain extent. The same element in the same chemical form may not have a single effect on the formation of active ingredients, just as organic K and Se elements have both antagonistic and promoting effects on the formation of active ingredients. The trend of the effects of different elements in different chemical forms on the active ingredients may be consistent. Just as elements such as Al, Ba, Fe, Se in different chemical forms show a significant positive correlation with saponins in Paris polyphylla, with Se contributing particularly prominently. Its exchangeable, water-soluble, and organic states all have a great promoting effect on saponins VI, VII, and H. Meanwhile, Se element is also an essential trace nutrient for the human body, and in recent years, Se rich products have been widely sought after. Therefore, applying appropriate Se fertilizer during the artificial cultivation process of Dianzhong Tower can enhance its medicinal and economic value. Residual elements, due to their inherent characteristics, are not easily absorbed and utilized by plants, and their correlation with various active ingredients is much lower than other chemical forms of elements. Therefore, when conducting soil element research, while studying the total amount of elements, attention should also be paid to the analysis of element forms in order to understand the effectiveness of soil elements.
The rhizosphere soil of medicinal plants is a direct medium for material exchange between plants and the external environment, and is the material basis that affects the quality and yield of medicinal plants. The inorganic elements in rhizosphere soil play an important role in the selection, standardized planting, quality formation, and evaluation of suitable planting areas for traditional Chinese medicine. Therefore, it is particularly important to explore the specific element content under various chemical forms and the relationship between each element and the effective ingredients of medicinal materials. This study preliminarily explored the relationship between specific elements in the rhizosphere soil of Dianzhong grandiflorus and its saponins, in order to provide reference for the selection of suitable growth areas, standardized planting, quality formation and evaluation of Dianzhong grandiflorus. Further exploration is needed on the migration and transformation of various inorganic elements in the rhizosphere soil of Dianzhong Lou from different origins.
