Exploring the mechanism of action of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in treating chronic fatigue syndrome based on network pharmacology and animal model validation
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME), is a complex multi system disease that lasts for more than 6 months. Its clinical manifestations include debilitating fatigue, neurocognitive disorders, headaches, sleep disturbances, and a series of autonomic symptoms, which seriously affect the patient’s work and life. In traditional Chinese medicine, CFS is believed to involve the five organs and is commonly referred to as “fatigue”, “laxity”, “weakness”, “heaviness”, “body weight”, “limb not lifting” in the Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon. It belongs to the category of diseases such as “deficiency fatigue”. With the acceleration of people’s work pace, the pressure of life gradually increases, and the incidence rate continues to rise and shows a trend of younger age, which has become the focus of clinical hot debate. The pathogenesis of this disease is not yet clear, and there are many pathogenic factors. There is also no specific drug for clinical treatment.
Traditional Chinese medicine has multiple components, multiple targets, and overall effects of modulation and leveling. Basic experiments have shown that traditional Chinese medicine has significant effects and advantages in preventing and treating chronic fatigue syndrome. Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Maki no is the whole plant of the gourd family. Modern pharmacological research has found that Gynostemma pentaphyllum has various pharmacological activities, such as lowering blood lipids and blood sugar, anti-tumor, immune regulation, antioxidant and other effects, commonly known as “southern ginseng”. According to literature reports, polysaccharides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum can enhance exercise time and promote skeletal muscle differentiation in mice. At the same time, oral administration of Gynostemma pentaphyllum can have positive effects on patients’ mental fatigue and cognition, and can enhance their immunity. However, its active ingredients and mechanism of action are not yet clear, and the pathogenesis of CFS is complex, so it is very suitable to use network pharmacology methods for research. Network pharmacology is based on computer technology and network database retrieval, combining pharmacology with bioinformatics to study the relationship between drugs and diseases from a systematic perspective. Therefore, this article intends to explore the relevant targets, pathways, and mechanisms of action of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in treating CFS through network pharmacology, molecular docking technology, and animal experiments, providing some reference for its clinical application.
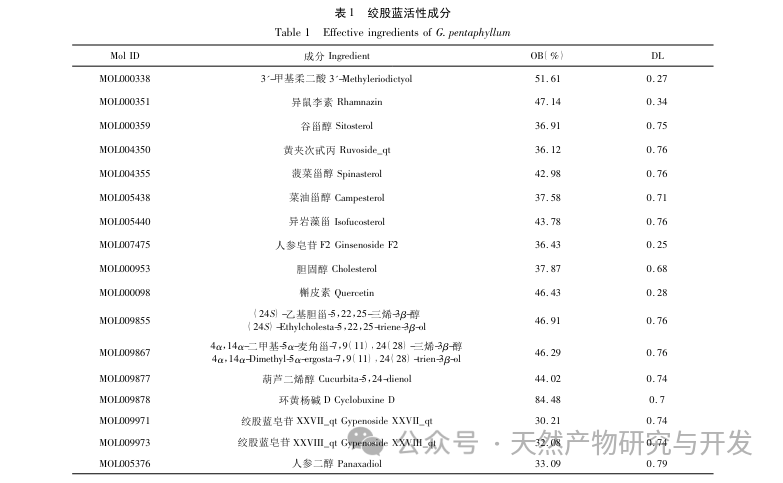

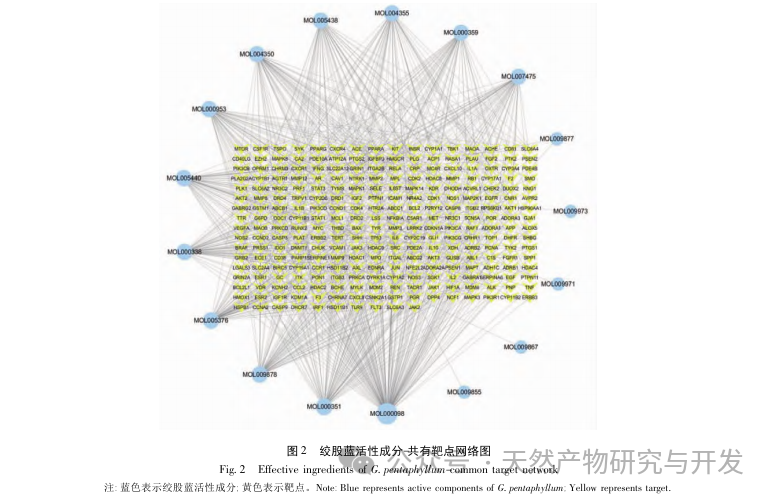
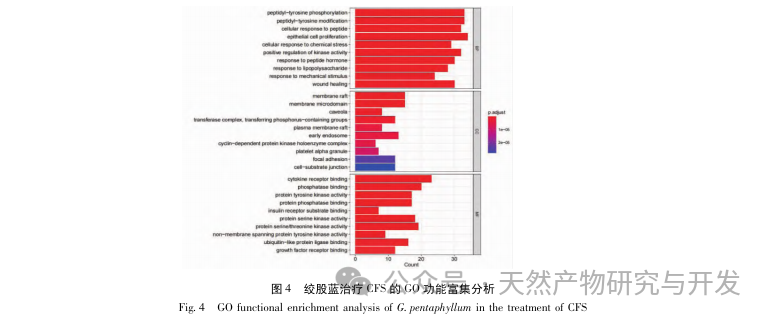

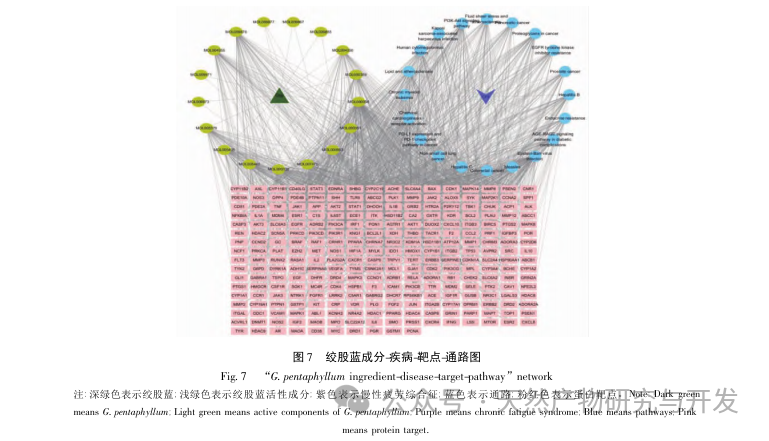

Traditional Chinese medicine plays a key role in the treatment of CFS, mainly through the use of tonifying drugs. Gynostemma pentaphyllum, as a type of tonifying drug, has been reported to have active ingredients that have anti-inflammatory, anti fatigue, oxidative stress improving, and immune enhancing effects. This article analyzes the active ingredients of Gynostemma pentaphyllum through network pharmacology. Through the “Gynostemma pentaphyllum active ingredients target action” network diagram, it was found that components such as quercetin, isorhamnetin, and panaxadiol ranked high in degree values. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that quercetin can significantly increase the activity of catalase (CAT) and total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) in weight-bearing swimming mice, while affecting gluconeogenesis and glucose metabolism, playing a role in delaying or eliminating fatigue. Gong et al. found that isorhamnetin can serve as a potential antioxidant, and its mechanism of action may exert antioxidant effects by regulating the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways, increasing intracellular glutathione (GSH) expression and demonstrating excellent antioxidant and anti fatigue effects. Wang et al. found that panaxadiol can increase the storage of glycogen in the liver muscle of fatigued mice, reduce the content of lactate (LD) in serum, increase LDH activity, and have significant anti fatigue effects. Predict that these components may be key core components for the treatment of CFS with Gynostemma pentaphyllum.
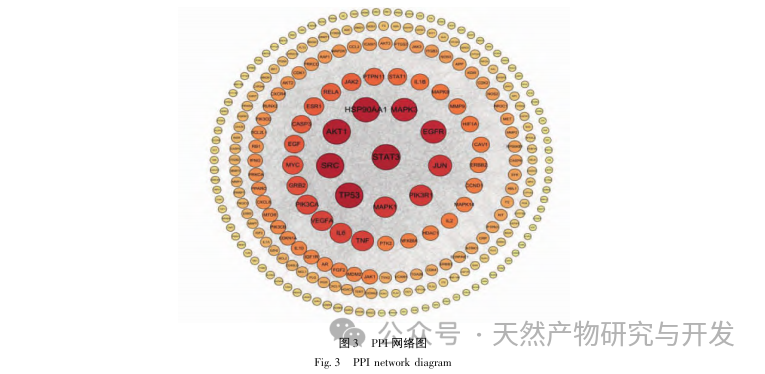
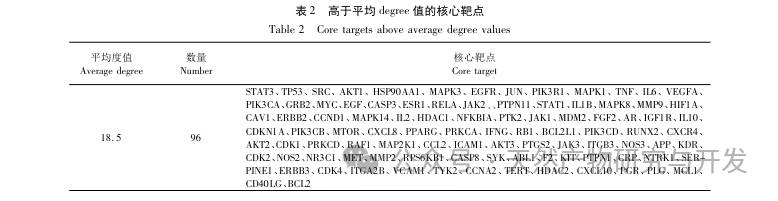
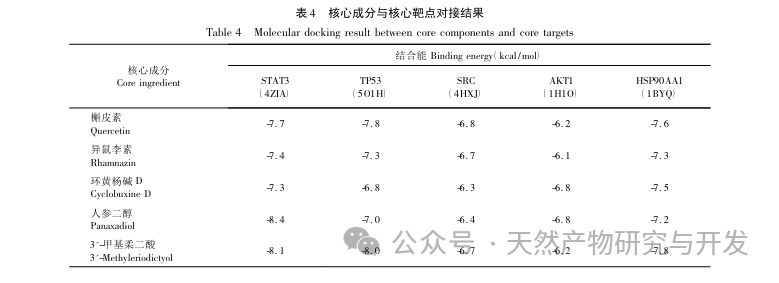
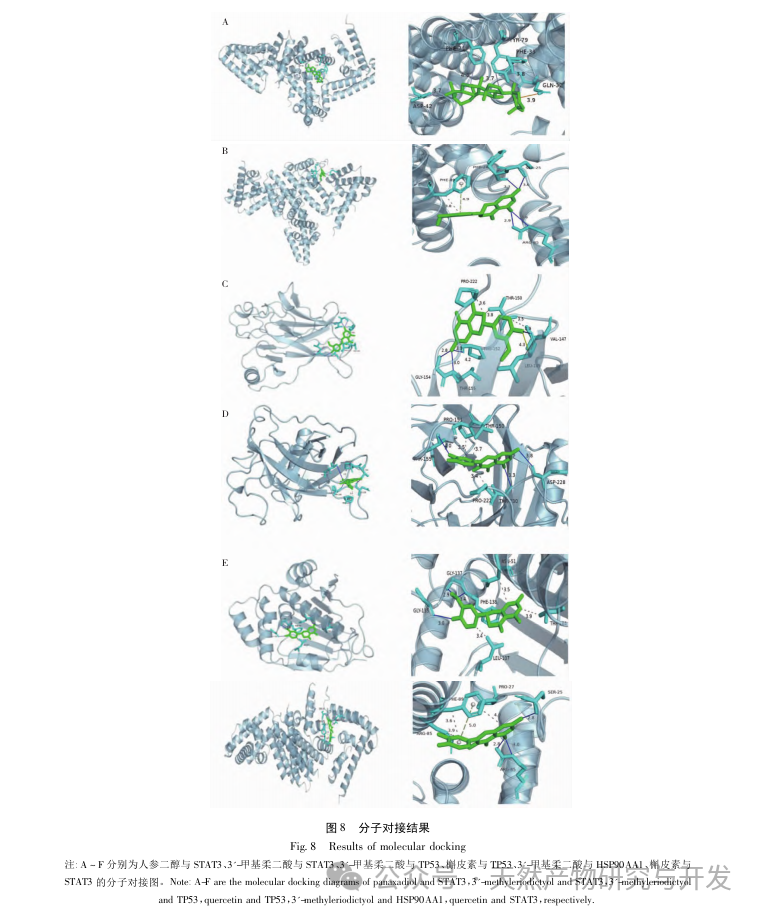
By constructing PPI networks on key targets, it was found that proteins such as STAT3, TP53, SRC, and AKT1 have higher degree values. STAT3, as a signaling and transcriptional activator, can regulate the activity of ATP synthase and interleukin levels, affecting energy metabolism and inflammatory status in the body. Gilad et al. found that SRC can exert immune enhancing effects, and its mechanism of action is to regulate the NF – κ B pathway and immune cells, thereby affecting inflammation and oxidative stress. Fang et al. found that TP53 can reduce cell apoptosis and regulate muscle fatigue by inhibiting the expression of P53 protein in skeletal muscle of fatigue rats. Other studies have also shown that it has a balancing effect on oxidative stress. AKT1 promotes mitochondrial biosynthesis and affects tissue energy metabolism by regulating MAPK phosphorylation and activating PPAR α/PGC-1 α. Studies have shown that it affects fatigue status by regulating energy metabolism. This indicates that STAT3, TP53, SRC, and AKT1 can act on CFS by regulating energy metabolism, oxidative stress, cell apoptosis, and may be key targets for the treatment of CFS with Gynostemma pentaphyllum. This article further conducts molecular docking between key targets and core components, and the results show that both have high binding activity, among which STAT3 protein has the best binding ability to core components.
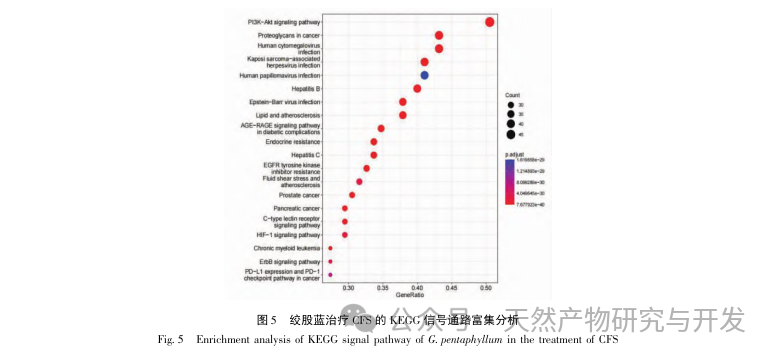
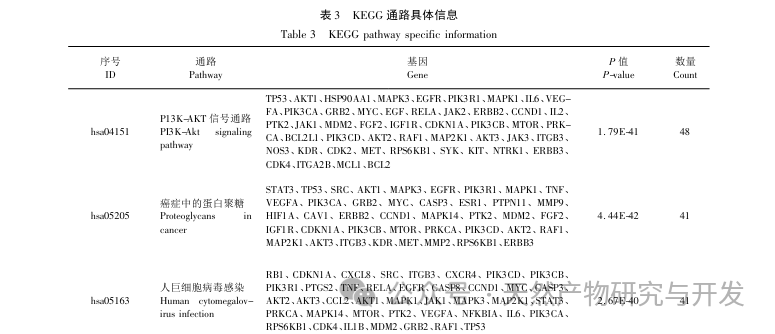
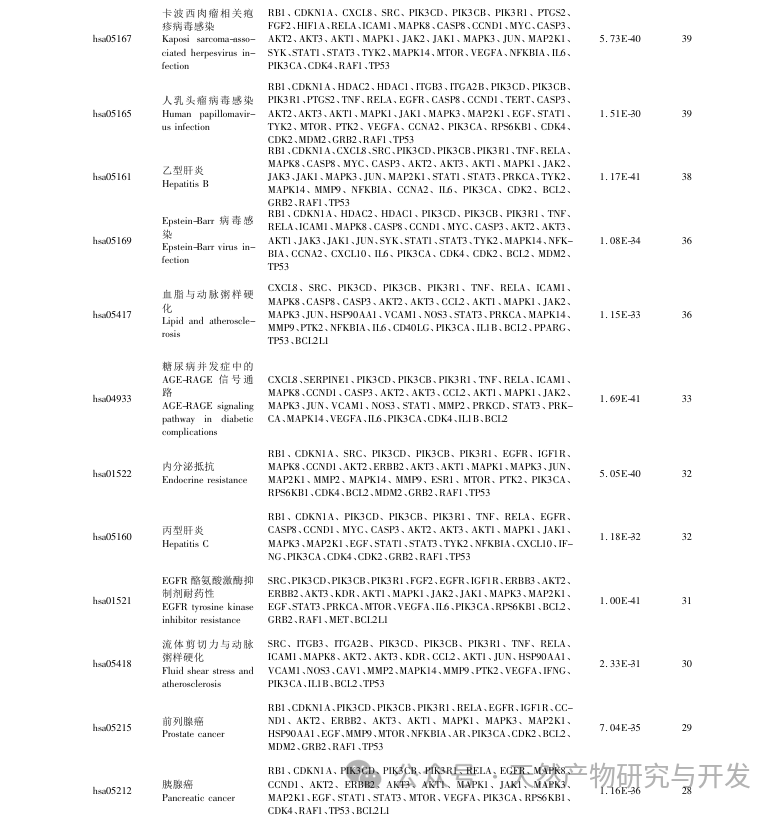
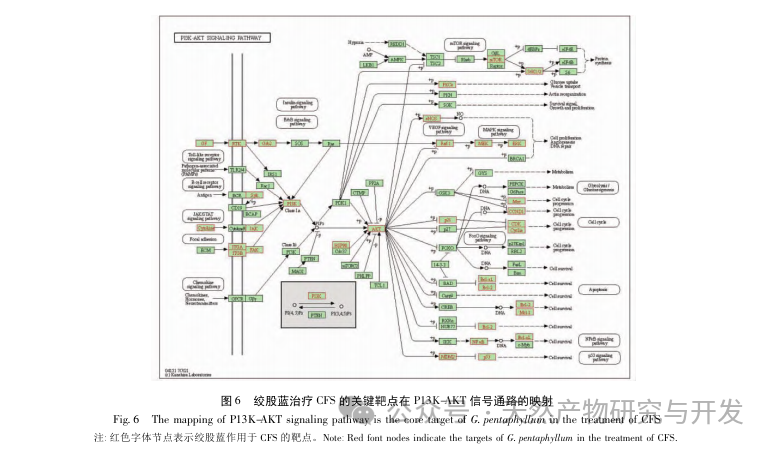
The enrichment analysis of GO and KEGG, key targets, showed that the treatment of CFS with Gynostemma pentaphyllum involves P13K/AKT, fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, HIF-1 signal transduction pathway, AGE-RAGE and other signal pathways, of which P13K/AKT signal pathway has the largest number of enriched genes. CFS is accompanied by inflammation in the brain, affecting neuronal proliferation and apoptosis. The P13K/AKT signaling pathway is closely related to various enzyme biological effects and glucose metabolism, and can affect the HPA axis in the brain to improve neuroinflammation and alleviate central fatigue. P13K can activate the expression level of AKT protein and participate in cellular metabolism, proliferation and differentiation, anti apoptosis and other aspects by phosphorylating P13K and AKT protein. Previous studies have shown that total saponins of Gynostemma pentaphyllum can activate the P13K/AKT signaling pathway, inhibit the release of downstream pro apoptotic proteins, reduce oxidative stress, and improve brain damage, indicating the importance of the P13K AKT signaling pathway in the treatment of CFS with Gynostemma pentaphyllum. By mapping the P13K-AKT signaling pathway again using KEGG Mapper, it was found that most key targets were mapped onto this signaling pathway. The P13K/AKT pathway is a potential pathway for the treatment of CFS with Gynostemma pentaphyllum.
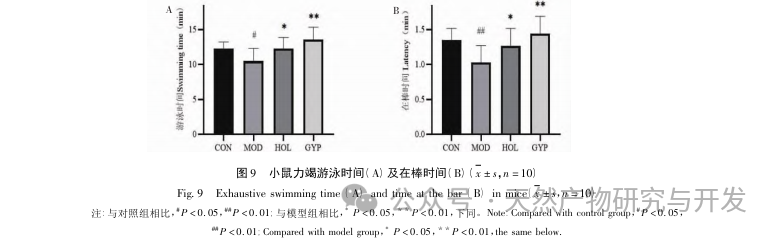
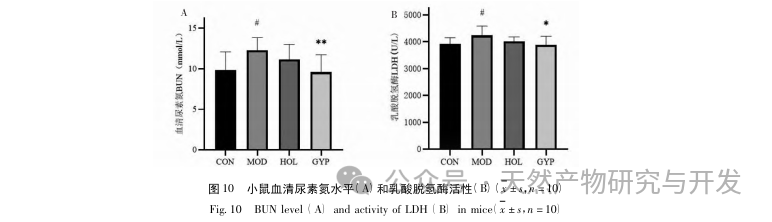
To further investigate the mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in treating CFS, a CFS mouse model was established through food restriction and forced swimming. Through exhaustion swimming and stick spinning experiments, it was found that Gynostemma pentaphyllum can significantly prolong the exhaustion swimming time and stick time of mice. The improvement of exercise endurance is the most objective indicator for evaluating drug anti fatigue, indicating that Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins have significant anti fatigue effects, can reduce the accumulation of fatigue metabolites, and enhance exercise time. When exercising vigorously, the body is in a relatively anaerobic state, relying on muscle glycolysis for energy supply, which leads to an increase in LDH and BUN, causing a series of functional disorders such as nerve conduction and muscle contraction, affecting the production, release, and storage of energy, and further leading to physical fatigue. This study found that Gynostemma pentaphyllum can significantly reduce the levels of BUN and LDH activity in the serum of CFS mice, indicating that Gynostemma pentaphyllum can reduce the accumulation of metabolic products in the body. Western blot results showed that Gynostemma pentaphyllum can increase the expression levels of PI3K and Akt, while reducing the expression levels of P-PI3K, P-AKT, and STAT3, thereby regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. This suggests that the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway may be a key pathway for Gynostemma pentaphyllum in the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome.
In summary, the core active ingredients of Gynostemma pentaphyllum, such as quercetin and isorhamnetin, may act on multiple targets such as STAT3, TP53, SRC, AKT1, HSP90AA1 by regulating oxidative stress and energy metabolism, and regulate multiple pathways such as the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. They have the potential to treat CFS with multiple components, targets, and pathways. This study can provide reference for the in-depth research and clinical application of Gynostemma pentaphyllum.
