With the deepening development of glycobiology in recent years, chitin, chitosan and chitooligosaccharides have been discovered one after another and put into research and development, especially in the field of health care products, these products are selling like hot cakes. So what is the relevance between these three, and what is the difference?
Chitin, Chitosan, Chitooligosaccharides
Chitin (thickener, stabilizer)
Chitin. Chitin was discovered in 1811 by the French scholar Braqueño, and extracted from crustacean shells by Ogier in 1823 and named CHITIN, which translates to Chitin.
Sensory characteristics: gray-white flakes or powder
Chitin was the first product to be used in practice and the first “functional food” to be approved in Japan. However, chitin is insoluble in water, alkali, general acids and organic solvents, and is only partially soluble in concentrated acids, and is partially decomposed by chitinase and lysozyme in the gastrointestinal tract of the human body, so its absorption rate is extremely low, and the dosage is large, and the reaction to taking it is as high as 70% or more. Chitin is chemically processed to remove the acetyl group, and it becomes chitosan.
Chitosan, also known as deacetylated chitin (thickener, coating agent)
Chitosan (chitosan), chemical name for polyglucosamine (1-4)-2-amino-B-D glucose, chitin (chitin) by the deacetylation of the role of the chitosan, in general, N-acetyl removed more than 55% can be called chitosan.
Sensory characteristics: white or yellowish flakes or powder.
Chitosan is already soluble in dilute acid, which is a step forward than chitin. However, chitin and chitosan are both large molecules, with molecular weights ranging from several hundred thousand to several million, and both are insoluble in water.
Chitin is deacetylated to get chitosan, and then after further degradation, it becomes chitosan.
Chitosan (New Food Ingredients)
Utilizing chitosan as raw material and degrading chitosan into small molecules, it is chitosan oligosaccharide. Its molecular weight is around 3000 Da, and the degree of polymerization is 2-20. Therefore, chitosan itself is a kind of mixture, in which there are monosaccharides all the way up to chitodecasaccharides, and each kind of sugar has its certain functionality.
Sensory characteristics: light yellow solid powder
Chitosan can be directly dissolved in water, the water solubility is more than 99%, the absorption rate of human body is 99.88%, the dosage and the reaction after taking are greatly reduced, and the physiological regulation effect directly involved in the human body is more significant than that of chitosan, and it has a lot of functions superior to that of the high molecular weight chitosan.
While chitosan has to be degraded by human biological enzymes to get part of small molecular weight chitooligosaccharides first, in general, the ratio of degradation is 1-5%, and the rest of 95% polysaccharides will be excluded through human intestinal system, so chitooligosaccharides increase the immune function of the body stronger than chitosan.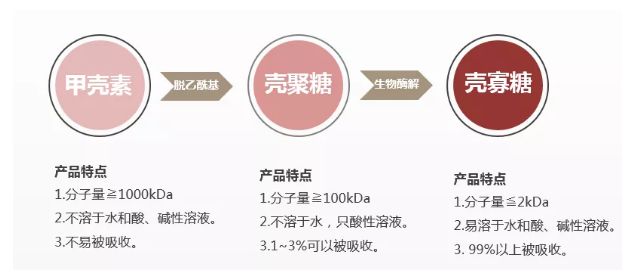
Specific differences between chitosan and chitosan
1. Molecular weight difference: Chitosan is a brand new product obtained from chitosan processed by special biological enzyme technology, with molecular weight below 3000 Da; Chitosan is a product of partial deacetylation of chitin, with molecular weight of 500-1,000,000.
2. Difference in solubility: chitosan has lower molecular weight and can be completely dissolved in water; chitosan can only be dissolved in dilute acid solution. The enhancement of water solubility is an important factor affecting some physiological activities of chitosan, only when it is dissolved in water, it can be absorbed and utilized by living organisms and show biological activities, so chitosan is easier to be absorbed by human body, animals and plants.
3. Functional difference: Chitosan with molecular weight below 2000 shows unique physiological activities and functions: improving the function of macrophages; inhibiting the growth and metastasis of tumor cells; lowering cholesterol and blood lipids; antibacterial, antimicrobial and significant moisture-retaining and moisture-absorbing abilities, and so on.
Chitosan with molecular weight below 5000 has the ability to hinder the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria, promote protein synthesis and activate plant cells, thus promoting rapid plant growth.
The many functions of chitosan show that it is an alternative in the family of oligosaccharides. Chitosan is the only alkaline, positively charged oligosaccharide found in the oligosaccharides, and this characteristic also determines that it is the only oligosaccharide that can be absorbed by intestines and enter into the blood circulation, and it is the basis for it to play many other biological functions when it reaches the whole body through the blood circulation.
The prerequisite for intestinal absorption of chitosan is that it is not digested by digestive enzymes. Chitosan is a polymer made of glucosamine linked by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds, and the digestive enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract of human beings mainly act on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds, so that chitosan can maintain its structural integrity in the gastrointestinal tract.
