Research progress on the anti colorectal cancer effects of monomeric active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common malignant tumor of digestive system, which seriously threatens the life and health of countrymen people. According to the Global Cancer Data Statistics 2020, the incidence rate of colorectal cancer accounts for about 10% of all annual diagnosed malignant tumors, causing about 940000 deaths in 2020. In China, the incidence rate and mortality rate of colorectal cancer are 18.63% and 20.09% respectively, ranking first in the world, bringing heavy medical and economic burdens to society. At the same time, due to the insidious onset, the vast majority of colorectal cancer patients are already in the middle to late stages at the time of initial diagnosis, losing valuable opportunities for radical treatments such as surgical resection and local ablation. Therefore, developing and constructing efficient comprehensive treatment strategies has become a hot topic of research for scholars worldwide.
At present, the treatment methods for colorectal cancer mainly include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, which significantly alleviate patients’ symptoms, prolong their survival period, and improve their quality of life. However, in the drug assisted treatment of colorectal cancer, commonly used chemotherapy drugs such as irinotecan hydrochloride, 5-fluorouracil, tigio, oxaliplatin, cetuximab, etc. have caused irreversible damage to normal tissues and organs, accompanied by serious adverse reactions and toxic side effects. For example, 5-fluorouracil may cause serious gastrointestinal reactions during use, which can damage the gastrointestinal mucosa and exacerbate related symptoms. In addition, the issue of resistance to cetuximab has gradually become one of the main problems that clinical doctors have to face. Therefore, developing highly efficient and low toxicity drugs for the treatment of colorectal cancer may be an important measure to enhance the efficacy of colorectal cancer.
In recent years, research has found that the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer involves multiple cascade signaling pathways such as STAT3, TGF – β, PI3K/Akt, and Wnt/β – catenin, as well as abnormal silencing or activation of some targets. Currently, most drugs used for colorectal cancer treatment only target a single target. Although it cannot be ruled out that there are currently a few drugs in clinical practice that can effectively treat colorectal cancer by targeting a single target, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, it is still difficult to achieve effective treatment of colorectal cancer by inhibiting a single signaling pathway or biological target under normal circumstances. The active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine can regulate the cascade reaction of signaling molecules through multiple targets, links, and effects, showing significant advantages in improving symptoms, improving quality of life, and stabilizing lesions in colorectal cancer patients. At the same time, they can effectively prevent and treat the recurrence of colorectal cancer and enhance the efficacy of targeted drugs. For example, traditional Chinese medicine and its related monomers with heat clearing and detoxification effects have been proven to have apoptosis inducing effects mainly related to their regulation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. At the same time, it is not difficult to find that colorectal cancer is often accompanied by the continuous infiltration of various inflammatory factors before carcinogenesis, and the monomer components of traditional Chinese medicine can inhibit the pre cancerous inflammatory response and hinder the process of “inflammatory cancer” transformation. This is also the advantage of traditional Chinese medicine, reflecting the traditional idea of “prevention before disease, prevention before disease”. In addition, patients often take traditional Chinese medicine to prevent recurrence and metastasis after surgery and chemotherapy, in order to prolong their survival time with tumors. In terms of chemical structure, the traditional Chinese medicine monomers currently used for research on colorectal cancer mainly include various structural categories such as alkaloids, flavonoids, polysaccharides, glycosides, phenols, anthraquinones, esters, terpenes, etc. Although these components have made some progress in the field of colorectal cancer treatment, as tumor therapy enters the era of precision treatment, the effective integration of traditional Chinese medicine monomer components in the study of colorectal cancer treatment to maximize their value is also an urgent problem to be solved in the field of basic research. Therefore, starting from the chemical composition of anti colorectal cancer drugs, this article systematically summarizes the research status of traditional Chinese medicine monomer components in the treatment of colorectal cancer, in order to provide reliable reference for clinical research on traditional Chinese medicine anti colorectal cancer.


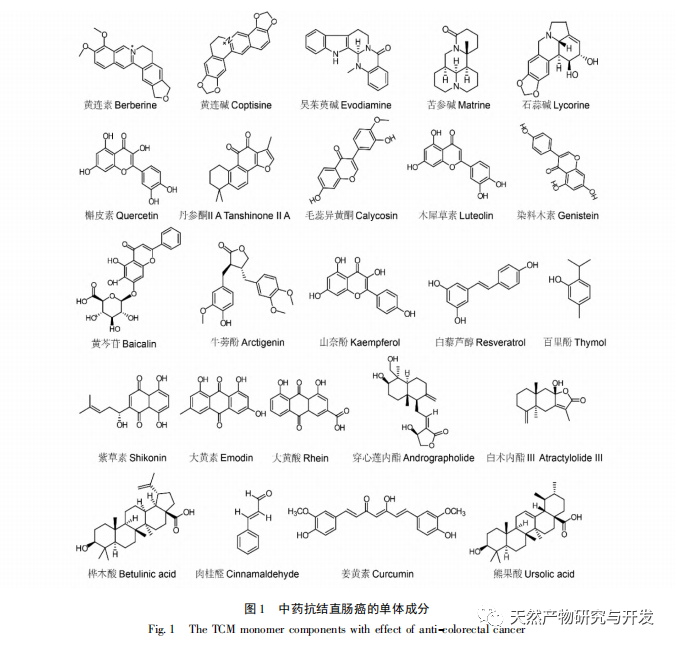

In recent years, the incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer have been increasing year by year due to the combined effects of unhealthy lifestyle habits, changes in dietary structure, and other risk factors. With the proposal of the “Healthy China” strategy, the clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in treating colorectal cancer has gradually been evidenced. Therefore, with the focus on addressing the safety issues of China’s health system, and in the context of deepening the original theory of traditional Chinese medicine, utilizing modern interdisciplinary integration methods to carry out research on the prevention and treatment of major malignant tumors such as colorectal cancer with traditional Chinese medicine may be an important direction for the future. The monomeric components of traditional Chinese medicine have been proven to be an important material basis for exerting anti colorectal cancer biological effects. As an important goal of traditional Chinese medicine research, “explaining clearly and clearly” is often limited by the complexity of the chemical components of traditional Chinese medicine, resulting in increasingly prominent research limitations. Therefore, this article systematically summarizes the anti colorectal cancer effects of natural monomers derived from traditional Chinese medicine from the perspective of chemical structure active substances, and briefly compares and analyzes the differences in anti colorectal cancer effects of each component, in order to provide reference and practical support for clinical research on the treatment of colorectal cancer with traditional Chinese medicine monomers.
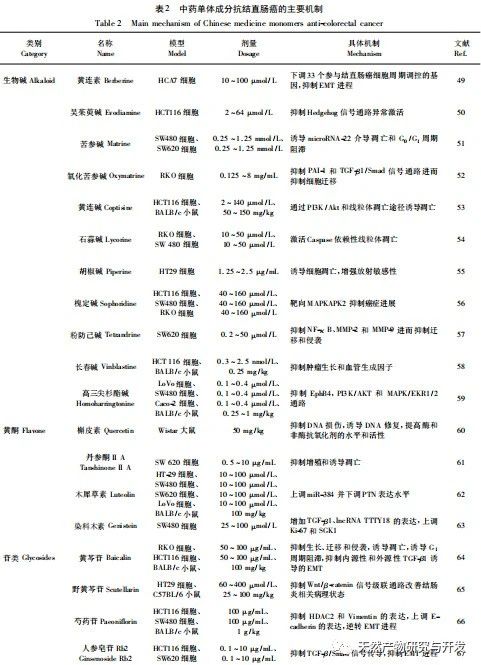
The onset of colorectal cancer is a repeated chronic process with multiple stages and steps, and different structures or characteristics of components can be used for targeted interventions at different stages. The specific chemical structure of drugs is considered the main factor in exerting drug efficacy. Alkaloid active ingredients such as pyridine, tropane, and organic amines mostly contain complex cyclic structures, and the nitrogen atom inside the ring is considered the key to their pharmacological effects. In recent years, tumor immunotherapy has gradually become a focus of research on treatment strategies for colorectal cancer. It mainly stimulates the patient’s own immune system to promote the body to produce anti-tumor immune responses and eliminate tumor cells with the help of the immune system. Research has found that polysaccharides in traditional Chinese medicine, such as Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides and Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides, as well as phenolic compounds such as purpurin and thymol, mainly exert anti colorectal cancer effects by regulating the body’s immune response and oxidative stress, and most of the components have almost no safety issues. Therefore, they may be of great benefit in the prevention, prognosis, and nursing of colorectal cancer. However, although traditional Chinese medicine saponins have significant therapeutic effects in treating colorectal cancer, some of them may cause severe hemolysis and liver and kidney damage when used, such as saponins from Polygonatum sibiricum and Ophiopogon japonicus. In addition, flavonoids, anthraquinones, esters and other components mainly exert their anti colorectal cancer effects by causing multiple biological phenotype changes in colorectal cancer cells, and there is currently no unified or similar chemical structural basis overview. Therefore, conducting more targeted research on the mother nucleus structures with different chemical compositions may be an important direction for interpreting the anti colorectal cancer effects of traditional Chinese medicine monomer components from a chemical structure perspective in the future.
As is well known, the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer is complex. Therefore, the complementary advantages of the disease characteristics of colorectal cancer and the monomeric components of traditional Chinese medicine may further promote the progress of clinical research. In recent years, with the continuous combination of traditional Chinese medicine chemistry and modern technology, there has been an endless stream of Chinese medicine monomers with new skeleton structures. This undoubtedly provides rich chemical structure information for the development of new Chinese medicine drugs, and also constitutes a vast library of natural lead compounds. Developing drug lead compounds with superior properties using active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine as the parent nucleus structure and utilizing strategies such as computer-aided molecular design may be an important direction for future research. Therefore, in the development of traditional Chinese medicine ingredients, the strengths of Chinese ethnic Chinese medicine should be fully integrated, and distinctive new resources of traditional Chinese medicine should be deeply explored in order to promote the development of original new natural medicines.
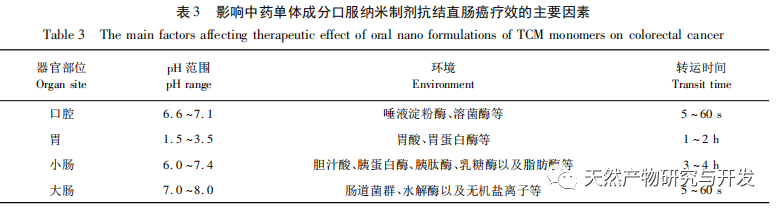
Although the monomeric components of traditional Chinese medicine have shown significant advantages in the treatment of colorectal cancer, most of these chemical structures have a common defect, which is poor water solubility, seriously hindering the clinical translation process. In recent years, new drug delivery strategies based on nanotechnology have continued to empower the active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine, in order to continuously improve the above-mentioned shortcomings. However, it is still necessary to deeply consider various factors that affect the efficacy of drugs, such as the potential impact of pH value, site composition environment, and transport time on oral nano formulations after entering the body (see Table 3). In addition, there is still great uncertainty in the clinical application of nano traditional Chinese medicine that has been proven effective in basic research, which may be attributed to the fact that research conducted at the cellular/animal model level often fails to truly reflect the human pathological and physiological environment and mechanism of action. Overall, discovering the monomeric components of traditional Chinese medicine and exploring their mechanisms of action can help to reveal the scientific connotation of the unique anti-tumor effects of traditional Chinese medicine while further optimizing treatment plans. This has significant value and practical significance for strengthening the research of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of colorectal cancer.
In addition, in the process of exploring new active ingredients in drugs, the important guidance of the scientific connotation of “old drugs for new use” for drug design and development should be emphasized. Taking berberine as an example, the team led by Academician Jiang Jiandong first discovered in 2004 that it has a completely different mechanism in regulating blood lipids from statins, and demonstrated very reliable safety, opening up a prospective research pattern of “old medicine new use” of berberine. Subsequently, Professor Fang Jingyuan’s team of Chinese experts wrote an article in the internationally renowned medical journal The Lancet, stating that their team found in a multicenter randomized double-blind controlled trial based on 891 patients recently diagnosed with adenomas and undergoing total adenoma resection surgery that berberine can effectively prevent the recurrence of rectal adenomas, a precancerous lesion of colorectal cancer. This study greatly enhances the credibility of berberine in the treatment of colorectal cancer and fully confirms the potential of this original natural ingredient as a new candidate drug. Therefore, in future research, adhering to the scientific concept of “old medicine for new use” and the drug development concept guided by clinical needs will greatly promote the secondary development of traditional Chinese medicine products.
Traditional Chinese medicine and its compound formulas are the main forms of medication in clinical practice, and also the specific embodiment of the holistic view and dialectical treatment of traditional Chinese medicine theory. Therefore, a deep analysis of the complex network effect regulation mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine drug efficacy substance clusters is a key link for traditional Chinese medicine to integrate into the international market. However, currently the vast majority of monomeric active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine have shown good anti colorectal cancer effects, but the research focus is usually on the discovery of new signaling pathways or targets. Monomeric ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine are only used as tool drugs, without reflecting traditional Chinese medicine thinking and failing to fully explain the scientific connotation of traditional Chinese medicine. The study of the material basis of traditional Chinese medicine compound efficacy is a key focus of modernization research in traditional Chinese medicine. Therefore, while elucidating the mechanism of a single component, systematic research on the cluster of traditional Chinese medicine components under the theoretical background of traditional Chinese medicine should not be ignored. In addition, when using molecular biology and pharmacology to further explore the anti colorectal cancer effects of traditional Chinese medicine ingredients, attention should be paid to the complexity of the in vivo biological molecular network, focusing only on the changes in upstream and downstream factors, which inevitably has certain limitations in the context of multi-target traditional Chinese medicine ingredients. Therefore, in the future, based on the research of individual components, the material basis of the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine and the relationship between each component can be deeply analyzed from point to surface, achieving a deep integration of basic research and clinical practice, and providing a more solid theoretical basis for ensuring the effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine components in treating colorectal cancer.
