Study on the Chemical Composition of Changguan Hongshan Tea Slices
Camellia longituba Chang is a perennial small tree in the Camellia genus of the Theaceae family. It was first reported by Professor Zhang Hongda of Sun Yat sen University in 1990, and the type specimen was collected from Enshi, Hubei Province. According to Volume 49, Volume 3 of the Flora of China, there are approximately 36 genera and 700 species of plants in the Theaceae family. The Theaceae genus is the largest in the Theaceae family, and there are 238 species of Theaceae plants in China, mainly distributed in the southwest to southeast, with the highest number in Yunnan, Guangxi, Guangdong, and Sichuan. The chemical components in Camellia plants mainly include flavonoids, saponins, polyphenols, plant sterols, fatty acids, and alkaloids. Among them, flavonoids are mainly flavonols, with quercetin, kaempferol, and catechins being the most common; The main saponin components are pentacyclic triterpenoid saponins of the oleanane type. The biological activity is manifested in various aspects such as antibacterial, anti mutation, anti-cancer, anti ulcer, antioxidant, and lipid-lowering.
The urea transporter (UTs) family is a type of channel protein molecule that transports urea (urea). Currently, two families, UT-A (UT-A1, UT-A2, UT-A3, UT-A4, UT-A5, and UT-A6) and UT-B, have been characterized. UTs play an important role in the renal urea cycle, establishing a gradient of urea concentration in renal medullary tissue and participating in the mechanism of urine concentration. The urea concentration and osmotic pressure in the renal marrow tissue of UT-B knockout model mice were reduced, and the decreased urine concentration ability did not affect other renal functions and the clearance rate of other major solutes (Na+, K+, Cl -) in the body. Therefore, the inhibitory effect of UT-B can increase urine output without causing potassium loss or affecting fluid electrolyte balance. This study screened UT-B inhibitors through a red blood cell lysis model.
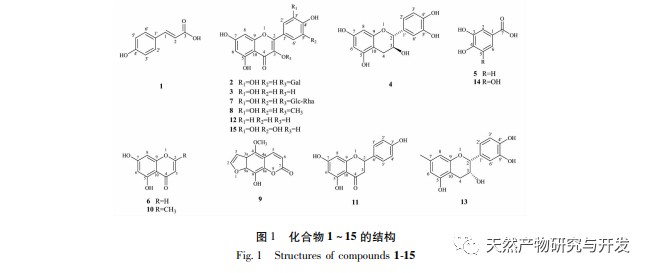
As a new member of the Camellia genus, the chemical composition of Changguan Camellia has been in a blank state before. In order to further explore the basic medicinal substances of Camellia sinensis, this study investigated its chemical composition and obtained 15 monomeric compounds, including 9 flavonoids, 3 phenolic acids, 2 chromogens and their derivatives, and 1 coumarin compound. Their chemical structures were elucidated using techniques such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. All 15 compounds were isolated for the first time from Camellia sinensis plants, and compounds 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 were isolated for the first time from the Camellia genus. From the types of compounds isolated, it can be seen that the main compounds in Camellia sinensis are flavonoids and phenolic acids, which are basically consistent with the types of compounds in the Camellia genus. The UT-B inhibitory activity of compounds was screened, and the results showed that gallic acid (14) and myricetin (15) had significant diuretic activity. Therefore, in subsequent work, in-depth research should be conducted on the mechanism of action of such compounds. This article provides a material basis for the pharmacological research of Changguan Hongshan tea, and also provides a reference for the development and application of Changguan Hongshan tea.
