What are the applications and precautions for carrageenan in food?
Edible gum is a widely used food additive in the world, especially in the relatively developed countries of food industry, almost all the food used in edible gum, carrageenan as an important kind of edible gum, has many excellent properties, and plays an increasingly important role in food processing.
The nature and role of carrageenan
1.1 The nature of carrageenan 1.1.1 Physical and chemical properties of carrageenan (Carrageenan), also known as carrageenan gum, antler alga gum, is a high molecular hydrophilic polysaccharide extracted from red algae. Its chemical structure is a linear polysaccharide compound composed of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-D-galactose residues.
Food grade carrageenan is white to light yellowish brown, wrinkled surface, slightly glossy, translucent flakes or powder, odorless or slightly odorless, tasteless, sticky and slippery texture, swells in cold water, can be dissolved in hot water above 60 ℃ to form a viscous transparent or slightly milky white easy-to-flow solution, but is insoluble in organic solvents, in less than or equal to their isoelectric point, they are easy to soluble in alcohols, glycerol, propylene glycol, but with the Detergents, low molecular weight amines and proteins are insoluble.
Due to the unbranched structure of carrageenan macromolecules and their strong anionic character, they can form highly viscous solutions, the viscosity of which depends on the concentration, temperature, type of carrageenan, and the presence or absence of other dissolved substances.
In addition, carrageenan can form many different gels in water or milk-based food systems at low temperatures.
Carrageenan is highly stable and dry powder is not easily degraded by long-term placement. It is also stable in neutral and alkaline solutions and does not hydrolyze even when heated, but in acidic solutions (especially pH ≤ 4.0), carrageenan is susceptible to acid hydrolysis and a decrease in gel strength and viscosity. It is worth proposing that under neutral conditions, if carrageenan is heated at high temperatures for long periods of time, it will also be hydrolyzed, resulting in a decrease in gel strength.
All types of carrageenan can be dissolved in hot water, in hot milk. Dissolving in hot water creates a viscous, clear or slightly milky, easy-flowing solution. Carrageenan can only absorb water and swell in cold water but not dissolve].
1.1.2 The rheological properties of carrageenan based on carrageenan has the nature of the food industry, carrageenan is usually used as a thickener, gelling agent, suspending agent, emulsifier and stabilizer. The production of these carrageenan applications and the rheological properties of carrageenan have a greater relationship, and therefore accurately grasp the rheological properties of carrageenan and its change rule in various conditions of production is of great significance.
Solution viscosity increases exponentially with increasing concentration and decreases exponentially with increasing temperature. In the steady state viscosity and temperature relationship has reversibility, but warming and cooling process “viscosity – temperature” curve slope is different, warming curve slope is smaller, which is caused by hysteresis phenomenon.
When the temperature was lowered to 30℃, the viscosity increased sharply, which was the reason that the carrageenan molecules started to entangle into a reticulated structure gradually. The viscosity of κ-carrageenan and ι-carrageenan increases abruptly when they reach their gel point at reduced temperature; this is not the case for λ-carrageenan.
Constant temperature heating time also has an effect on the viscosity of carrageenan solution. 75 ℃, with the prolongation of constant temperature time, the viscosity of carrageenan solution decreases, because the colloidal molecules dissociate with the heating of the solution, the molecular entanglement is reduced, so the viscosity decreases. When 100 ℃, viscosity with the growth of time and decline, and viscosity decline has a sharp and slow, the reason is that at the beginning, by the high heat caused by the dismantling of the intermolecular entanglement so that the viscosity decreases, after a period of smoother stage, then a few unstable macromolecules began to degrade, the viscosity declined again.
The viscosity of the carrageenan solution increases with increasing pH, then stabilizes as it approaches neutrality, and then decreases again. Acidity is enhanced by an increase in H+, which promotes the dissociation of carrageenan molecules and neutralizes their electrical properties, weakening the electrostatic attraction between the semi-esterified sulfates. Alkaline enhancement, OH and negatively charged carrageenan repel and reduce the entanglement of molecular drop, so the viscosity of the solution decreases under both strong acidic and alkaline conditions.
Solution viscosity decreases when certain cations are present in the solution. This is because the cation can reduce the electrostatic attraction between the semi-esterified sulfate.
1.2 The role of carrageenan in the food industry The role of carrageenan in the food industry is mainly manifested in the three aspects of gelation, thickening and protein reactivity.
1.2.1 Carrageenan and protein reaction in solution protein aggregation to form protein micelles, carrageenan free in solution, and protein micelles of bare amino acid fragments to produce ionic reactions, according to the concentration and pH of the different, respectively, cohesion precipitation, suspension and gelling;
In the solid state of meat products, after salt extraction (curing, tumbling) and heat treatment, proteins react with each other to form a protein mesh structure, which is strengthened by the interaction between carrageenan and proteins.
Carrageenan can strengthen this structure through interaction with proteins. Therefore, carrageenan can stabilize protein solutions by adsorbing protein molecules in the protein solution. Practical application is the stabilizer of dairy drinks and ice cream emulsification stabilizer, stabilizing and thickening milk protein solution.
1.2.2 Gelation of carrageenan 1.2.2.1 Factors affecting the gel strength of carrageenan Gel strength increases linearly with increasing concentration of κ-carrageenan within a certain range. This is because the concentration increases, the number of κ-carrageenan molecules increases and intermolecular cross-linking is enhanced.
The gel strength of κ-carrageenan solution decreases when the temperature increases, but the change curve is different during the temperature rise and fall because the κ-carrageenan molecules in the gel further form a double helix and then a three-dimensional mesh structure when the temperature is lowered, which is exothermic during this gelation process;
And when warming up, the process of gel solubilization absorbs heat. Both heat absorption and exotherm on the change of gel strength produce hysteresis phenomenon, and the slopes of cooling and warming curves are different. For example, taking 20℃ as the base, then the gel strength of κ-carrageenan boutique changes about 2%~3% per 1℃.
The experimental results confirmed that the gel strength of κ-carrageenan starting with 0.2% KCL added was 4.6 times higher than that without KCL. In the short time of gel formation, the gel strength increased rapidly and proportionally with time, then relatively stabilized, and then began to decline after more than 10 hours.
At the early stage of solidification, κ-carrageenan network structure was formed, the gel strength increased rapidly and stabilized, and then free water was released, dehydration and contraction, and the strength decreased. At the later stage, the gel strength decreased faster with the addition of KCL ground up, which was related to the exacerbation of the dewatering contraction by the electrolyte.
When pH<5.0, the gel strength of carrageenan increases with pH; when pH5.0~8.5, it tends to equilibrate; when pH8.0~9.5, the strength decreases; and when pH>9.5, the strength rises again. This is due to the presence of cross-chain kinks in the molecular residues of carrageenan, which significantly decreased the gel strength.
Appropriate concentration of OH can introduce 3,6-anhydroxylated oxygen bridge structure in the macromolecule, which helps to eliminate the kinks, straighten the molecular chain, and form a double helix structure, which leads to the enhancement of gel strength. That is, μ-carrageenan was converted into κ-carrageenan.
According to A.S. M icheel et al. the increase in electrolyte concentration increased the gel strength. Cationic species also play an important role in gel strength.Ca2+, K+, NH4+, Rb+, Cs+ form hard gels whereas Na+, Li+ form weak gels. The latter two cannot gel effectively.
1.2.3 Thickening of carrageenan Relative to the protein reactivity and gelation described earlier, the thickening of carrageenan is relatively weak, and is confused with protein reactivity in practical applications, and is therefore the property that involves the least practical application.
In practice, weakly gelatinous carrageenan thickening is generally used in ice cream and milk beverages, where the combination of the weakly gelatinous network structure produced by the carrageenan-protein system, together with the action of calcium salts, etc., can give the material a certain consistency.
In ice cream, carrageenan plus mannan, with milk protein, the formation of a weak gel network, giving ice cream shape retention, resistance to heat change, to prevent the separation of the pulp, inhibit the growth of ice crystals, to improve the expansion rate of ice cream and melting rate.
Cocoa milk is the most carrageenan used milk beverage, it needs carrageenan-protein system to form a weak gel to provide “support” the consistency of cocoa powder, while carrageenan formed by the weak gel will not destroy the taste produced by other substances. Other milk beverages use less or no carrageenan.
Application of carrageenan in jelly production
2.1 The role of carrageenan in the production of jelly carrageenan as a good coagulant, can replace the usual agar, gelatin and pectin. Jelly made of agar is not flexible enough, the price is higher; gelatin to do the disadvantage of jelly is solidification and melting point is low, the preparation and storage have to be low temperature refrigeration; pectin is the disadvantage of the need to add high solubility of sugar and the appropriate pH in order to solidify.
Carrageenan does not have these shortcomings, carrageenan jelly made of elasticity and no water separation, carrageenan because of its unique gel properties and become the jelly commonly used gelling agent.
2.2 Carrageenan in the amount of jelly jelly according to taste and other classifications, carrageenan in different kinds of jelly in the amount of Table 1.
Table 1 The amount of carrageenan in different kinds of jellies
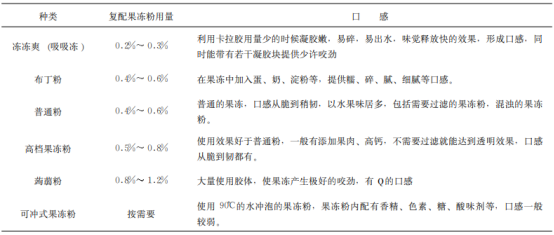
2.3 carrageenan in the application of jellies in the notes 2.3.1 Due to carrageenan – konjac gum system, the latter’s solubility is relatively bad, so it is necessary to carry out heat preservation, heat preservation time is not enough, the konjac gum dissolution is not complete, the jelly made of the texture is not right, and serious will cause the jelly is very tender and not shaped;
But at the same time if the heat preservation time is too long, carrageenan and alkaline or add a buffer such as sodium citrate, konjac gum is prone to deacetylation denaturation, resulting in the phenomenon of “egg drop soup”, jelly may still not be shaped. Therefore, it is recommended that after boiling in summer without insulation, after boiling in winter insulation 10 min, spring and fall between the two.
2.3.2 Add acid, due to the carrageenan is not acid-resistant, add acid temperature is recommended the lower the better, generally in 70 ~ 80 ℃ jelly filling before or according to the actual conditions of the process, or the higher the temperature the carrageenan is more likely to be destroyed, affecting the taste, and at the same time recommended that the citric acid is dissolved in water to add, to avoid causing local over-acid;
Adjustment of pH is generally not less than 4, the need for a more acidic taste, it is recommended that the use of other colloids to assist; at the same time, pasteurization will also affect the taste, need to be adjusted according to the actual situation.
2.3.3 Filtration refers to the use of a sieve to filter the material after boiling, the purpose of which is to remove the konjac gum particles that can not be dissolved, to obtain a relatively very transparent jelly, which can be done to obtain the effect of certain high-grade jelly transparent. Carrageenan in the production of soft candy applications
3.1 The role of carrageenan in soft candy with carrageenan to do transparent fruit soft candy in our country as early as the production, it is fruit flavor, moderate sweetness, crisp and not sticky teeth, and its transparency is better than agar, the price is lower than agar, added to the general hard and soft sugar in the product can make the taste smooth, more elastic, viscous small, high stability.
3.2 The amount of carrageenan in fudge carrageenan fudge according to taste, appearance classification, the amount of carrageenan in different types of fudge in Table 2.
Table 2 The amount of carrageenan in different kinds of soft candy
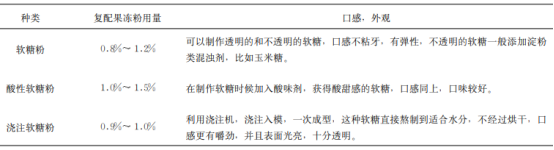
Other colloids used in fondant are gelatin, agar, pectin, modified starch, etc., which have different tastes and characteristics.
3.3 Precautions 3.3.1 Carrageenan-based fondant powder is not easy to dissolve in high sugar concentration, so it is recommended to dissolve it in water first, otherwise it is easy to produce trachoma, a small grain of gelatin.
3.3.2 Pay attention to the reducing sugar content, too low, long storage time is easy to return to the sand; too high, in the boiling sugar is easy to inject the mold is not shaped, pulling.
3.3.3 You can add fancy materials after the end of boiling glue, such as carrot sauce and so on, but to calculate the proportion of soft sugar powder. Carrageenan in the production of meat products
4.1 carrageenan in meat production carrageenan used in poultry products can improve and can be given to maintain moisture, flavor, texture, cutting, freezing and melting and stability to bring benefits. Such as carrageenan for ham and ham sausage can play the role of gel, emulsification, water retention, enhance the role of elasticity, especially to provide appropriate water retention, even when the manufacture of high yield products, it can also have a good water retention, and because it can be complexed with proteins, can provide a fairly good organizational structure, so that the product has a delicate, slicing good, good taste, elasticity, tough and brittle moderate, tender and refreshing and so on. Carrageenan is a necessary food additive for ham, which improves product quality and reduces costs.
In addition, because carrageenan is dispersed in cold salt and does not increase the viscosity of brine, so it will not bring inconvenience in the water treatment of poultry meat. κ-type and ι-type carrageenan or κ-carrageenan compounded with locust bean gum will make the broth gel, and the seasoning is suspended in the broth is clearly visible, and can maintain the flavor of the fish in the canned food. κ-carrageenan, locust bean gum and KCL solution on the surface of the frozen fish to form a film, which protects the fish meat from being destroyed, and the fish flesh will not be damaged. protects the fish from destruction and keeps it intact from mechanical damage during processing.
In ham production, κ-carrageenan binds to free water and interacts with proteins to ensure moisture content and soluble protein content.
4.2 Application of carrageenan in meat products The amount of carrageenan in ham is usually 0.75%, and then controlled by injection, tumbling and other processes, good results can be obtained. Application of carrageenan in ice cream production
5.1 The role of carrageenan in the production of ice cream in ice cream and ice cream production, carrageenan can make the fat and other solid components distributed evenly, to prevent the separation of milk components and ice crystals in the manufacture and storage of the increase; so that the ice cream and ice cream organization is delicate, the structure of the slippery, delicious; in the production of ice cream, carrageenan due to the cations in the milk can be interacted with, resulting in a unique gelation characteristics, can increase the ice cream In the production of ice cream, carrageenan can interact with cations in milk to produce unique gelling properties, which can increase the molding and anti-melting properties of ice cream, improve the stability of ice cream in temperature fluctuations, and it is not easy to melt when placed.
Although carrageenan is not suitable for use as a primary stabilizer in ice cream production, it can be used as a good secondary stabilizer to prevent whey separation at very low concentrations. Because although carrageenan will increase the viscosity of the system, but can not contain enough gum to stabilize the system.
Acacia bean gum, guar gum and carboxymethyl cellulose are good primary stabilizers when used alone or in combination, however, they have the same disadvantage: they cause whey separation in ice cream mixtures. So the addition of carrageenan inhibits this phenomenon.
5.2 Carrageenan dosage in ice cream Different types of ice creams require different ice stabilizers, for example, the low fat content of Snowbet can be used without emulsifiers; while premium ice creams contain a large amount of dairy products, which contain a large amount of milk proteins, which can also act as emulsifiers, which need to be adjusted specifically according to the production process formulated product differences. The amount of carrageenan in different ice creams is shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Amount of carrageenan in different kinds of ice creams
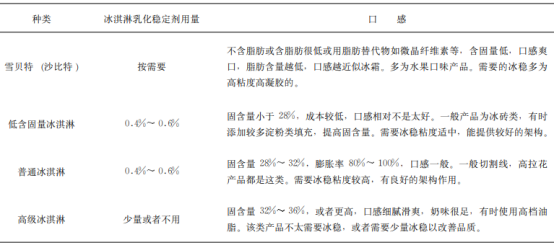
5.3 Precautions for use 5.3.1 A small amount of starch can be added to fill in, a larger amount will have a powdery texture and a poor taste.5.3.2 Carrageenan is used in smaller quantities, and more of it will freeze after aging. Carrageenan in beer production applications
6.1 carrageenan in the role of beer production carrageenan with a strong anionic group — sulfate ester, can be directly or through the metal ions “bridge” and positively charged proteins, esters, dextran combination, due to carrageenan’s long-chain structure of the material properties, the combination and expansion, the formation of flocs, under the action of gravity, very quickly! Precipitate out, so that the wort to achieve the purpose of clarification. Therefore, carrageenan is an effective wort clarifier, it can quickly precipitate protein, so that the wort get a good bright appearance, is conducive to yeast growth, and is favorable to filtration, reduce filtration loss, increase the rate of wort, improve the bio-stability of the beer, and prolong the shelf life of the beer.
6.2 The amount of carrageenan in beer In terms of the amount of use, each manufacturer according to their own raw materials, the proportion of malt and auxiliary materials, the concentration of wort, the characteristics of the process, to find out the reasonable and effective dosage, generally in the range of 15~25mg/kg.
