Computer simulation evaluation of pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptides in camel blood protein
In recent years, with the improvement of people’s living standards and changes in dietary habits, hyperlipidemia (HLP) has gradually become the “number one killer” that endangers human health. This disease is caused by dysregulation of lipid metabolism in the body. Given the close relationship between cholesterol absorption and lipid metabolism, the cholesterol absorption pathway has become an important intervention target for treating hyperlipidemia, which can effectively prevent hyperlipidemia by reducing the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine. The lipids ingested from the diet are first hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase, broken down into fatty acids and monoglycerides, forming micelles with cholesterol, bile salts, etc., and finally absorbed by cells in the intestine. Therefore, effectively inhibiting pancreatic lipase (PL) activity can reduce the body’s absorption of lipids, alleviate the condition from the source, and prevent diseases. Some drugs on the market have certain side effects that can cause discomfort in patients. Therefore, it is urgent to develop naturally occurring bioactive substances to assist in the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
Bioactive peptides have become a research hotspot in recent years due to their wide sources and high safety factor. Camel blood has a high protein content, with a total protein content of 6.80g/dL and a hemoglobin content of 141.11g/L, which is higher than other livestock. It also has a rich variety of amino acids, meeting the recommended values of WHO/FAO/UNU, and is a potential source of high-quality bioactive peptides. And research has shown that camel blood protease hydrolysates have anti fatigue, antioxidant, and blood pressure lowering effects. Therefore, the preparation of pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptides from camel blood protein has certain research value.
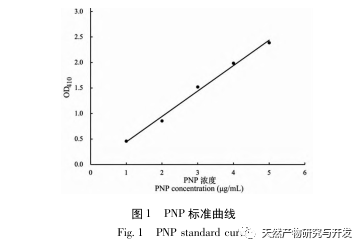
In this study, neutral protease was used to hydrolyze camel blood protein, and pancreatic lipase inhibition rate was used as the evaluation index to optimize the enzymatic hydrolysis process. Matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) was used to determine the molecular weight distribution of camel blood peptides, and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to identify and analyze camel blood peptides. PepSite2 was used to model and predict binding sites, and molecular dynamics simulation was used to evaluate the binding sites and modes of action of the screened peptides, providing a basis for the identification and analysis of camel blood peptides in the future. The study of lipase inhibiting peptides provides reference and new ideas for the development and utilization of camel blood.
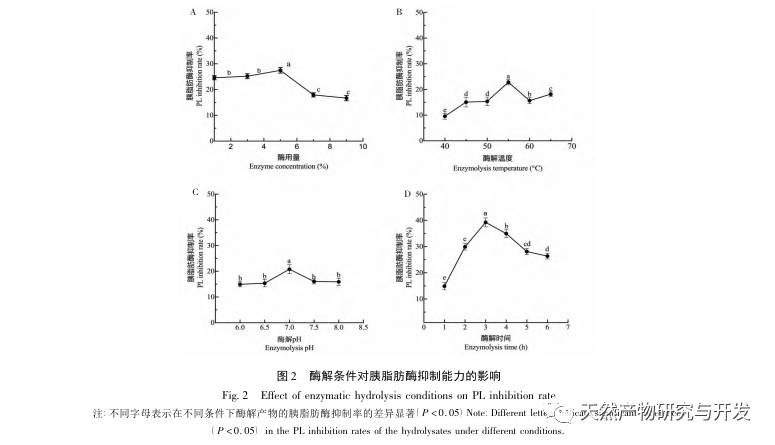
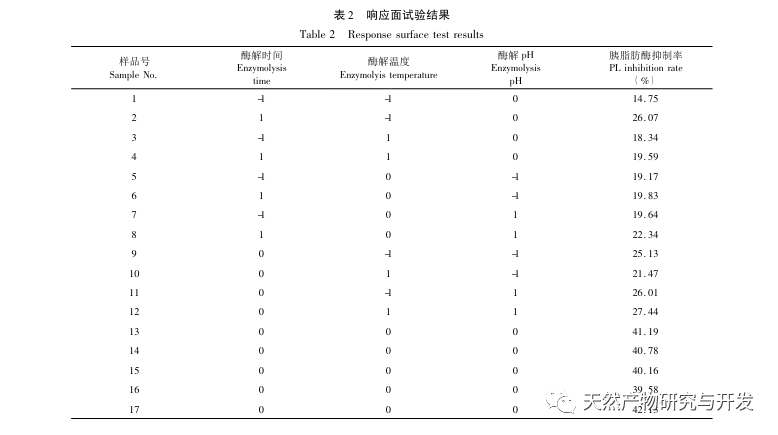
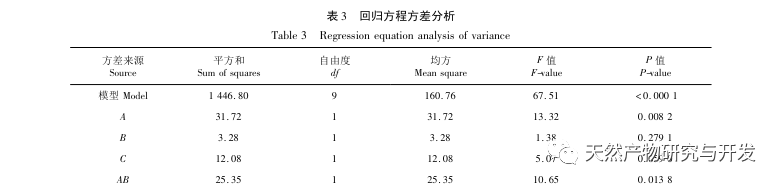
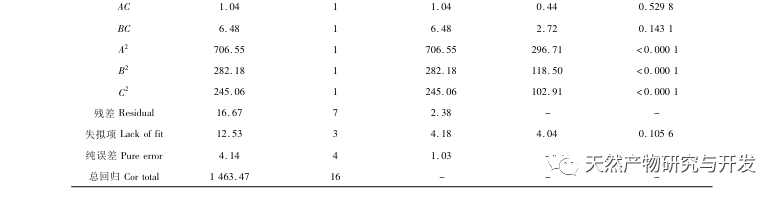
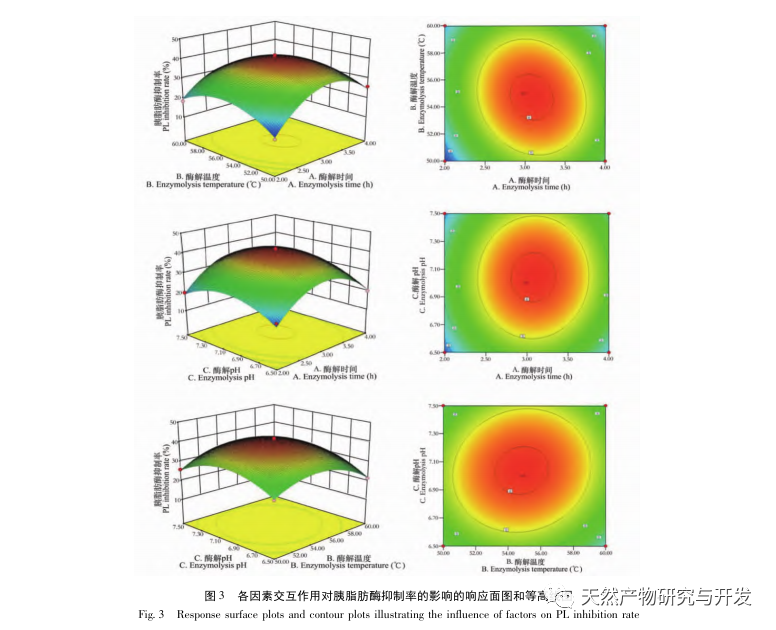
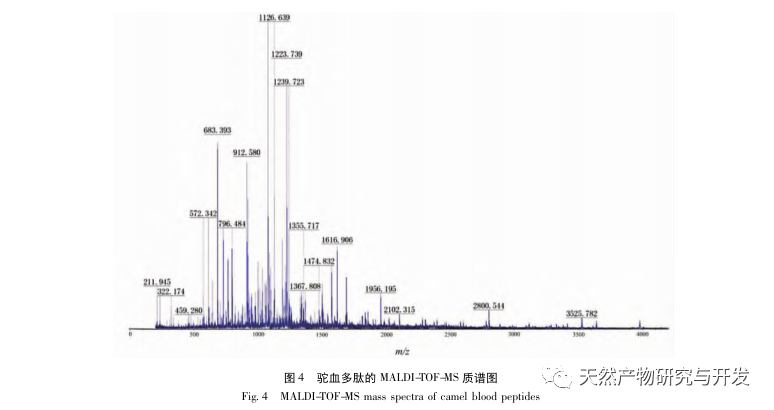
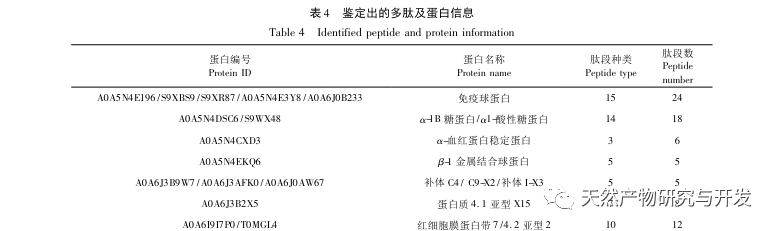

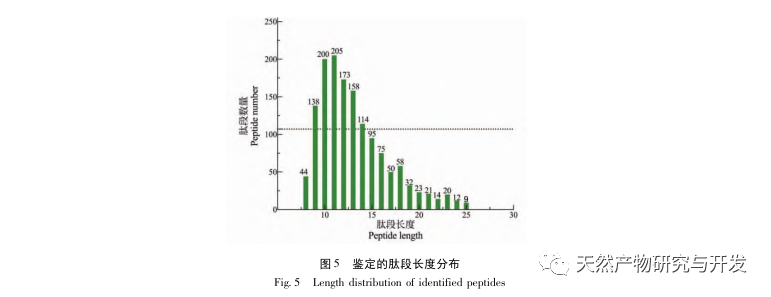
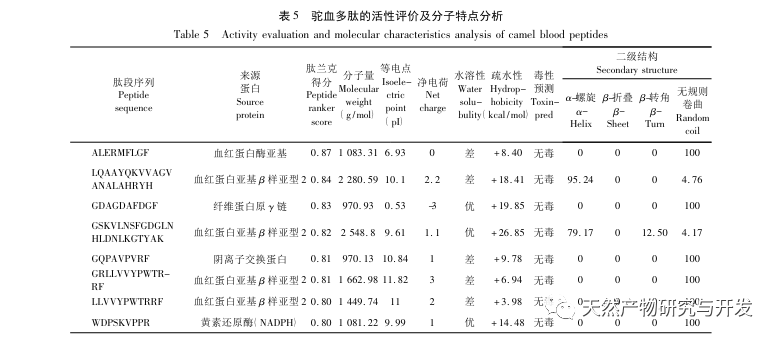
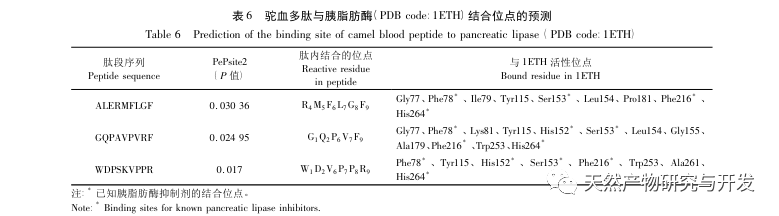
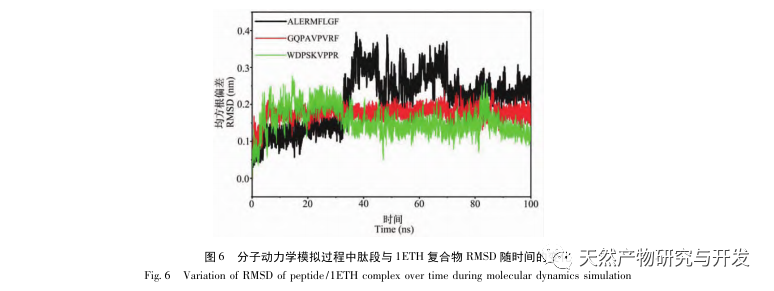
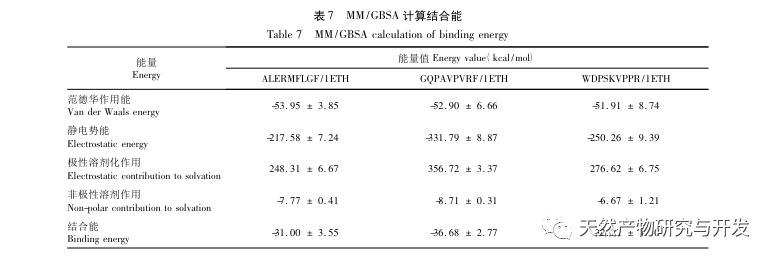
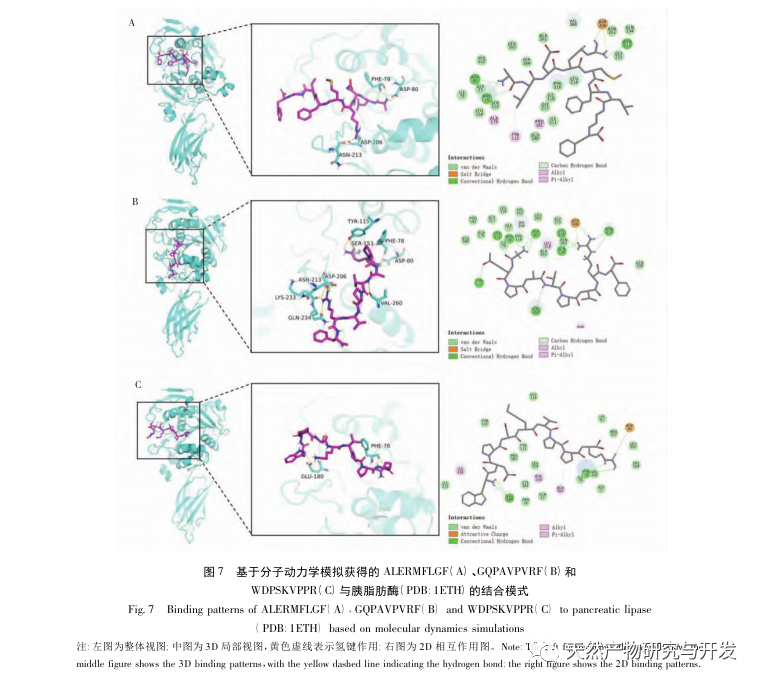
Inhibition of pancreatic lipase is considered one of the important therapeutic interventions for hyperlipidemia and obesity. This study optimized the process of preparing camel blood pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptides by neutral protease hydrolysis based on pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity through single factor and response surface experiments. Under optimal conditions, the pancreatic lipase inhibition rate of camel blood peptide was 42.13%. By analyzing the enzymatic hydrolysis products using MALDI-TOF-MS, LC-MS, and bioinformatics technology, three peptide segments, ALERMFLGF, GQPAVPVRF, and WDPSKVPPR, were identified as significantly binding to pancreatic lipase. Through molecular dynamics simulations, it was found that the three peptide segments mainly bind to the amino acid residues of the PL active site through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, disrupting the function of the pancreatic lipase N-terminal domain valve and inhibiting its activity. Among them, GQPAVPVRF has a high binding free energy and a large number of hydrogen bonds within 100ns, which means it can bind tightly to 1ETH and is expected to become a component of pancreatic lipase inhibitors. The research results indicate that camel blood protein can serve as a source of pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptides. However, there are certain limitations to the results of virtual screening, and in the future, it is necessary to optimize the water solubility and digestive stability of peptide segments. After artificial synthesis, the anti hyperlipidemia effect should be verified through in vitro and in vivo experiments.
