Research on Rapid Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Quality Based on Big Data and Pattern Recognition Technology
Traditional Chinese medicine is the mainstay of the traditional Chinese medicine health industry, and the quality of traditional Chinese medicine is related to the development of the health industry. At present, there are still problems with the quality of traditional Chinese medicine, such as a wide variety, large differences, long traceability process, cumbersome testing indicators, and lack of scientific evaluation methods. In addition, the massive amount of raw data generated and accumulated in the process of quality supervision of traditional Chinese medicine has not found any patterns from the data, and the effective utilization rate is low, resulting in problems of rich data and poor knowledge. Under the promotion of the Action Plan for Promoting the Development of Big Data issued by the State Council in 2015, the application of modern information technologies such as big data integration, cloud computing, and blockchain in the scientific supervision of the traditional Chinese medicine industry has become an inevitable development trend in the future. The hidden patterns and rules in big data of the traditional Chinese medicine industry often cannot be discovered through experience or intuition. It is necessary to draw on the thinking and methods of big data analysis to transform low-quality and fragmented data such as the growth environment, planting and processing, processing, chemical composition evolution, and traditional quality control of medicinal materials into high-quality and high-value density information. Then, with the help of data mining, machine learning, artificial intelligence and other computing methods, combined with professional knowledge and judgment of traditional Chinese medicine, mathematical models related to application can be established to make entity relationships transparent and provide important basis for scientific supervision of the quality of traditional Chinese medicine.
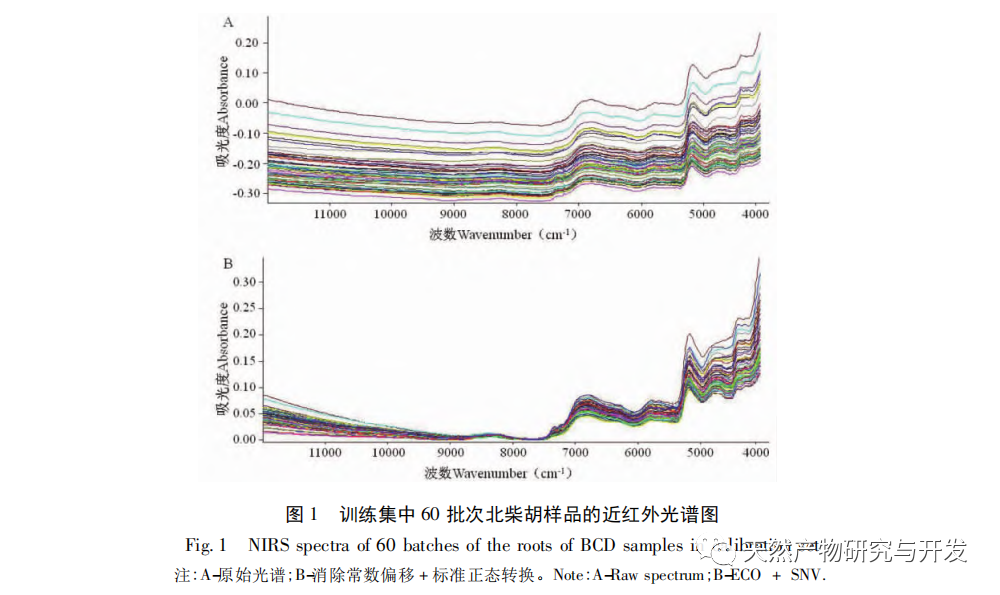
With the rapid development and application of chemometrics, instruments and technologies for food and drug safety testing have been rapidly developed. The detection methods have also evolved from early physical and chemical, microscopic, chromatographic, and mass spectrometry (MS) technologies to non-contact near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), Raman spectroscopy (RS), terahertz (THz), and hyperspectral imaging (HI) technologies. Among them, NIRS has been developed in recent years, which collects the combined frequency and doubling information of the vibration and rotation of hydrogen containing groups X-H (X=C, N, O) in the near-infrared spectrum of the tested substance for qualitative and quantitative analysis. It is widely used in agriculture, petroleum, chemical industry, tobacco and food, and has gradually been applied in the pharmaceutical and drug regulatory industries, with great potential for rapid qualitative and quantitative detection and analysis of drugs.
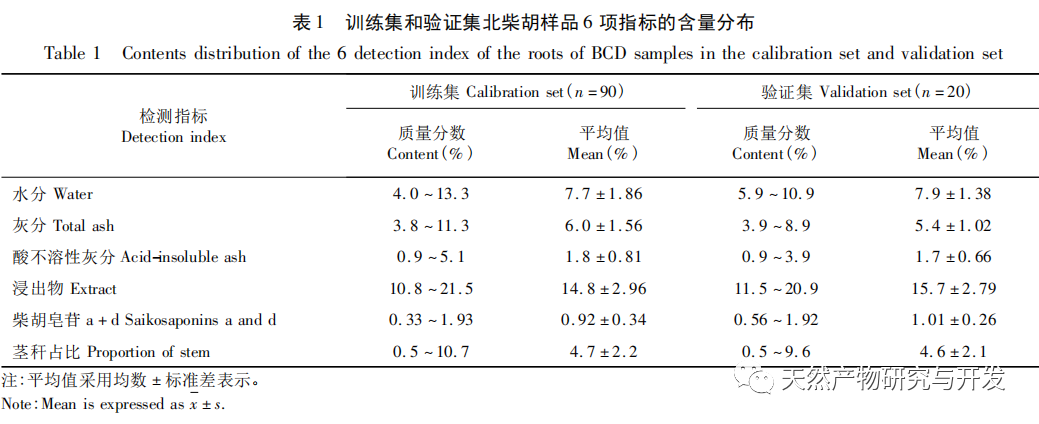
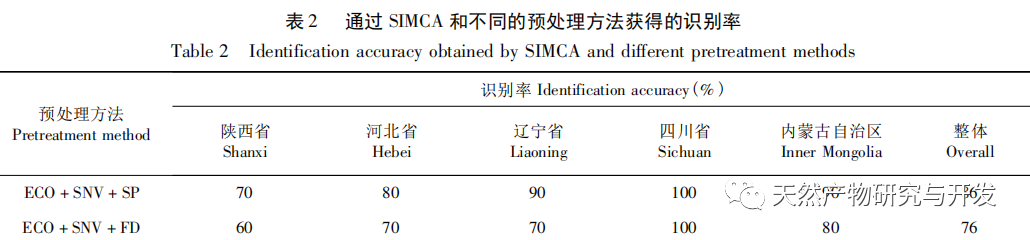
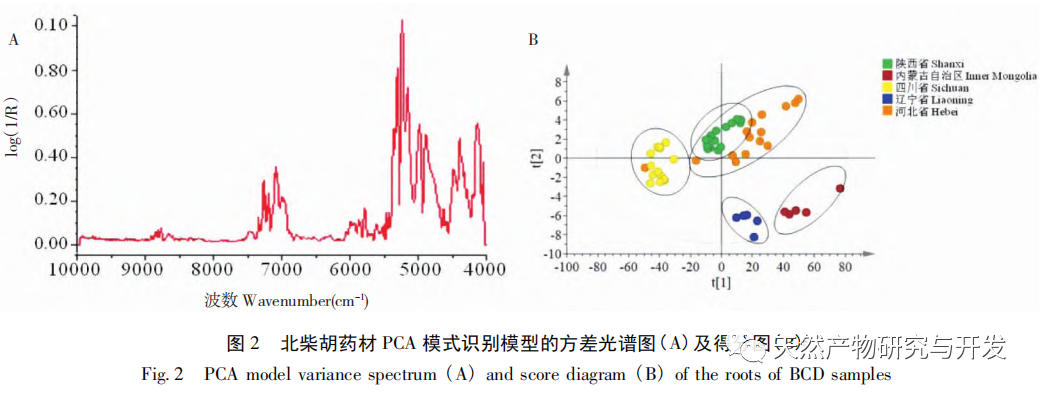
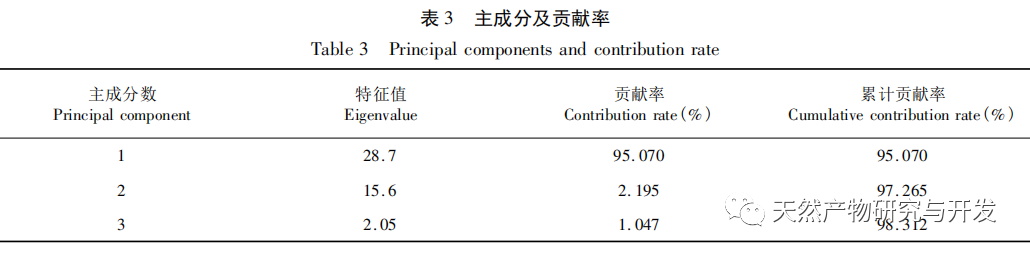
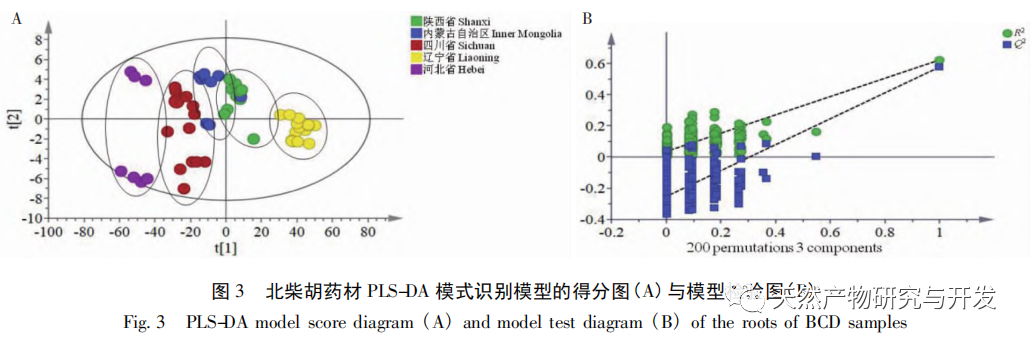
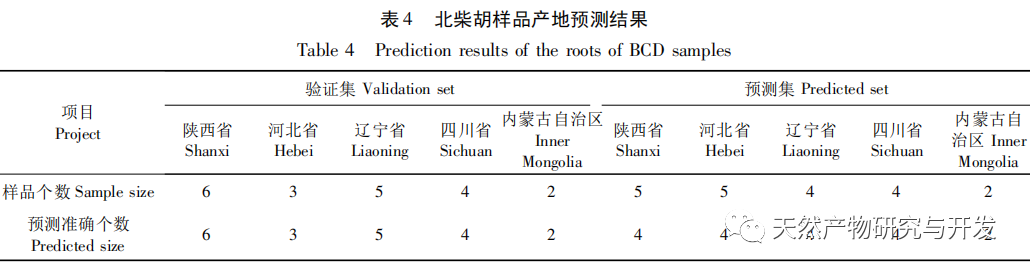
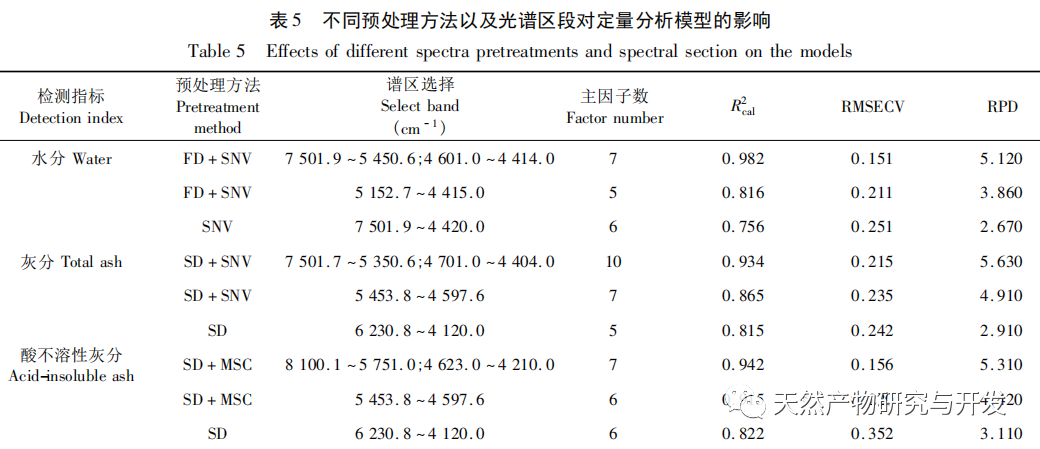
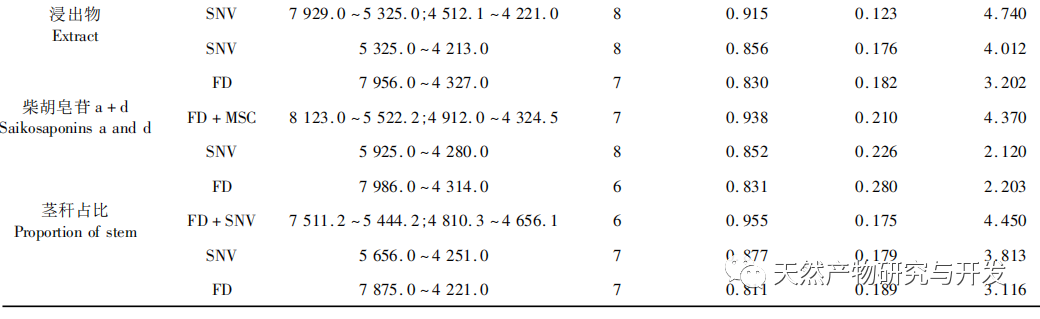
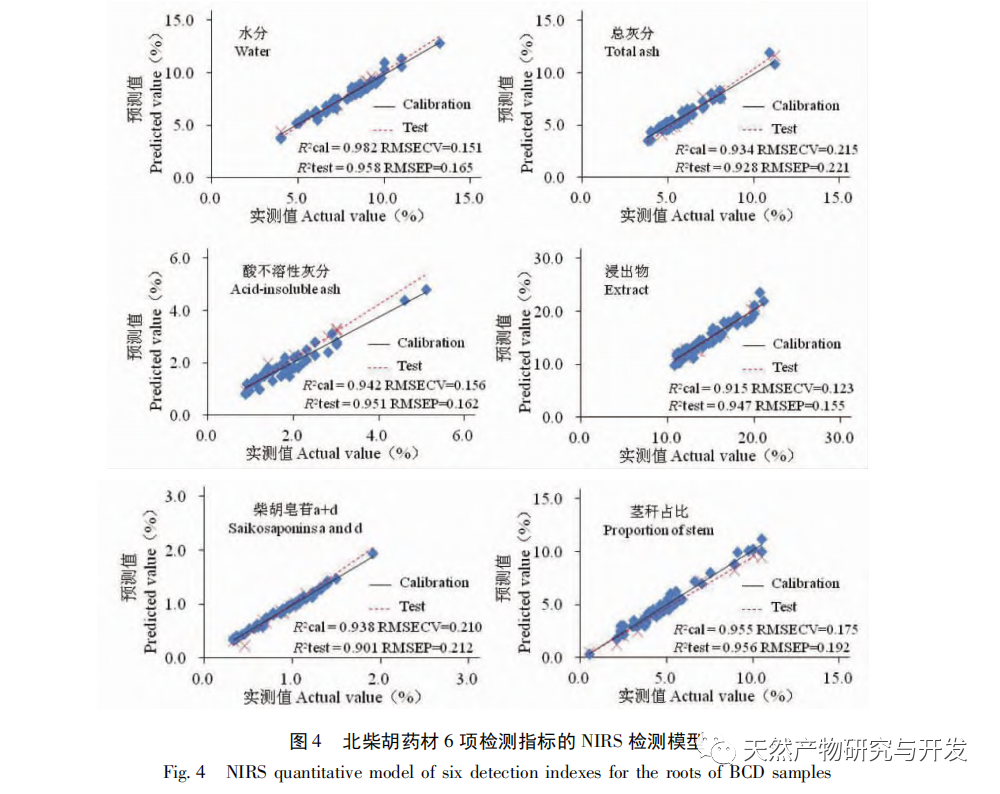
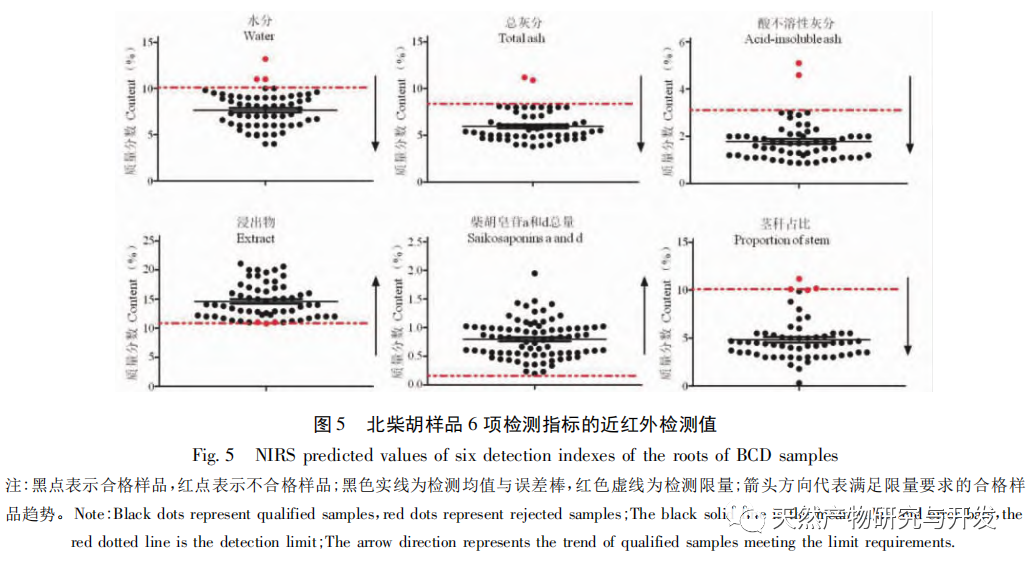
Bupleurum chinense DC, also known as Narrow leaved Bupleurum B., is a plant in the Apiaceae family The dried root of scorzonerifolium Willd. is a commonly used bulk medicinal herb in China. It was first recorded in the “Shennong Bencao Jing” and is classified as a top-grade herb. It has the effects of relieving fever, soothing the liver and relieving depression, and promoting yang qi. The former is commonly known as “Beichaihu”, while the latter is commonly known as “Nanchaihu”. North Chaihu is mainly produced in Hebei Province, Heilongjiang Province, Liaoning Province, etc., while South Chaihu is mainly produced in Liaoning Province, Jilin Province, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, etc. Due to the complexity of the original plant species of Bupleurum chinense, there are about 100 biological species in this genus. There are 36 biological species, 17 varieties, and 7 forms in China. In addition, there are significant differences in the quality of medicinal materials due to changes in growth environment, variety variations, processing, and incomplete removal of non medicinal parts. At present, the 2015 and 2020 editions of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia have limited the content of moisture, ash, acid insoluble ash, extract, saikosaponin a and d in Chaihu, which plays an important role in the quality control of Chaihu. However, Q-marker studies have found that the volatile oil, fatty oil, triterpenoid saponins, and flavonoids in Bupleurum chinense are the main active ingredients for its antipyretic, sedative, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and cough suppressing properties. At present, although multiple indicators coexist in the quality evaluation of Bupleurum chinense, the testing indicators are single and the limit is too low, which cannot meet the needs of quality evaluation and grading. In addition, a large amount of fragmented raw data has been generated and accumulated during the regulatory process, which has not been fully utilized and lacks systematic integration. Therefore, based on the background of big data, this study takes Bupleurum chinense as an example, collects various testing data of 130 batches of Bupleurum chinense medicinal materials tested by our center using the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, and uses NIRS analysis technology, chemical stoichiometry, and mathematical modeling methods to conduct pattern recognition research on various testing data of Bupleurum chinense medicinal materials. We establish a rapid traceability analysis model, content prediction model, comprehensive evaluation and grading database for Bupleurum chinense medicinal materials, systematically evaluate the quality of Bupleurum chinense medicinal materials, and provide new ideas for the scientific supervision of Chinese medicinal material quality.

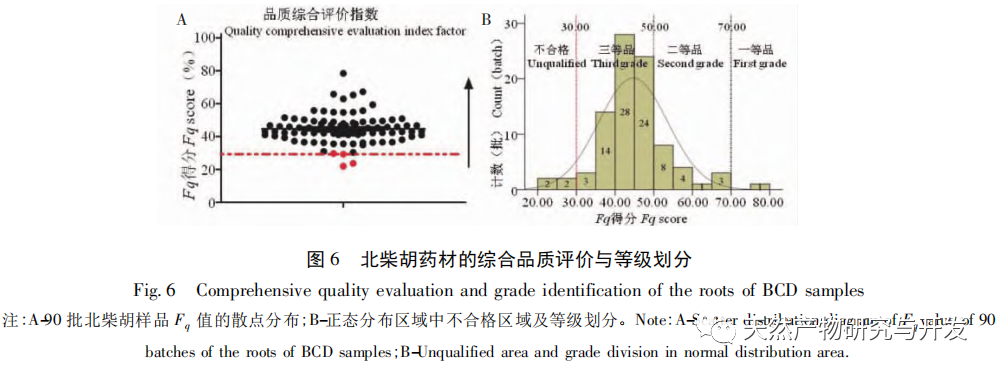
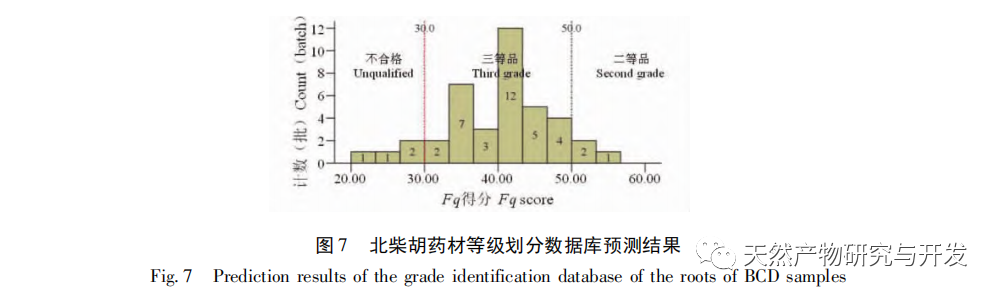
Referring to Germany’s “Industry 4.0”, China’s traditional Chinese medicine industry is currently at the level of Industry 2.0, which is relatively lagging behind. Sigma gap refers to the gap between product performance and consumer expectations. In the Six Sigma management method (6 Sigma is a goal), China’s traditional Chinese medicine industry is currently at the level of 2.0~3.0 Sigma. The reason for the above gap is that products are difficult to trace, too dependent on final product testing, and lack of process understanding. From 2018 to 2020, the failure rate of spot check of Chinese traditional medicine is far higher than that of traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations and chemical medicine. The quality of traditional Chinese medicine decoction pieces is the basis for the clinical safety and effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine, and is related to the development of the traditional Chinese medicine health industry. It is particularly important to carry out research on new methods of traditional Chinese medicine supervision and achieve scientific supervision of traditional Chinese medicine quality. There are many factors that affect the quality of traditional Chinese medicine, such as variety, habitat, harvesting, processing, storage, etc., which have a certain degree of complexity, but there are also inevitable internal connections. To achieve scientific supervision, it is necessary to integrate interdisciplinary technology, information science, and big data science. In recent years, China has done a lot of work on the quality control of traditional Chinese medicine, but it still cannot meet the increasingly high quality control requirements. Regarding this, some studies have proposed the concept of traditional Chinese medicine quality markers (Q-markers), which provide direction for the evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine quality. However, the comprehensive evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine quality involves multiple Q-markers, and the contribution of different Q-markers to the quality of traditional Chinese medicine is also different, lacking a scientific comprehensive evaluation method. This experiment proposes the concept of the comprehensive evaluation index Fq for traditional Chinese medicine, combined with the current evaluation system of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Based on the results of big data analysis, the Rij data of each detection index is dimensionless, and the coefficient of variation method is used to optimize the calculation of the weight coefficient Wi of the traditional Chinese medicine quality evaluation index, avoiding the subjective preference of expert weighting and objectively reflecting the relative importance of each index in traditional Chinese medicine quality evaluation. A rapid and scientific evaluation method suitable for the comprehensive evaluation and grading of traditional Chinese medicine quality has been established, providing a new approach for the scientific supervision of traditional Chinese medicine quality.
Scientific supervision is the guarantee of drug safety, effectiveness, and quality controllability. The scientific supervision of traditional Chinese medicine quality should not only combine traditional experience, current evaluation systems, and advanced technical methods, but also introduce modern information technology and statistical methods. By extracting and analyzing big data, a comprehensive evaluation method and grading standards for traditional Chinese medicine quality should be established. Pattern recognition technology has the characteristics of “integrity” and “fuzziness”, and is a comprehensive and quantifiable means of identification. It is currently in line with the characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine and can well reflect the authenticity of traditional Chinese medicine. FQ is a developing system that will continue to iterate and improve with the continuous accumulation of big data and the introduction of Q-markers, and can be better applied to the scientific supervision of traditional Chinese medicine quality.
