Extraction, Purification, and Antioxidant Activity Analysis of Total Flavonoids from Artemisia annua
Artemisia japonica Thunb. is a common species of Artemisia in the Asteraceae family in many parts of China. It is a perennial herb with a fragrant aroma and is a medicinal and edible plant. Its tender stems and leaves are edible and have a great flavor. Artemisia annua has a bitter and slightly sweet taste, with a cool nature, and can be used as a whole herb for medicinal purposes; Has the effects of clearing heat, cooling blood, and detoxifying. Modern pharmacological research has shown that Artemisia annua contains abundant compounds such as flavonoids, polysaccharides, polyphenols, saponins, and volatile oils, which have various health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-aging effects. The terpenes, alkaloids, flavonoids, steroids, phenols, unique amino acids, and polysaccharides contained in Artemisia annua have insecticidal, antibacterial, and bactericidal activities, and can be used to develop plant-based insecticides.
Flavonoids are a class of natural organic products with carbonyl groups, and are named flavonoids because they mostly have color. As an important class of secondary metabolites in plants, flavonoids have significant physiological and pharmacological effects. In nature, dicotyledonous plants such as Asteraceae, Leguminosae, and Lamiaceae generally contain more flavonoids. As a plant of the Artemisia genus in the Asteraceae family, Artemisia annua is particularly rich in flavonoids.
At present, Artemisia annua is widely used as a vegetable for consumption or as a medicinal herb in traditional Chinese medicine clinical formulas. The development of medicinal resources of Artemisia annua in modern medicine and health is still at a low level, and there are few research reports on the total flavonoids of Artemisia annua at home and abroad. Gu et al. analyzed the chemical composition of Artemisia scoparia and identified the main flavonoids as Artemisia scoparia, 8,4 ‘- dihydroxy-3,7,2’ – trimethoxyflavone, 3,5-dihydroxy-6,7,3 ‘, 4’ – tetramethoxyflavone, etc; Zhang et al. studied the extraction method of total flavonoids in Artemisia annua and found that the highest yield of total flavonoids in Artemisia annua was obtained by Soxhlet extraction with 85% methanol solution for 2 hours, while the yield was lower by extraction with 70% ethanol solution for 6 hours, but it was the most suitable for industrial production. There have been no reports on the extraction, purification process optimization, and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from Artemisia annua.
Based on this, this study used the above ground stems and leaves of Artemisia annua as experimental materials, optimized the ethanol extraction process of Artemisia annua total flavonoids using response surface methodology, and explored the purification conditions of Artemisia annua total flavonoids by macroporous resin on this basis. The antioxidant activity of Artemisia annua total flavonoids was analyzed, in order to provide theoretical basis and data reference for the development and application of Artemisia annua in the fields of medicine, health care, and food.
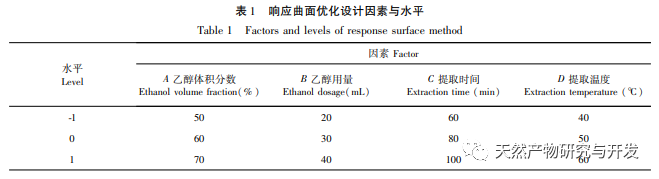
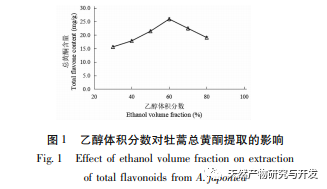
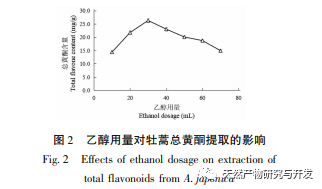
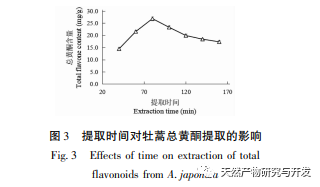
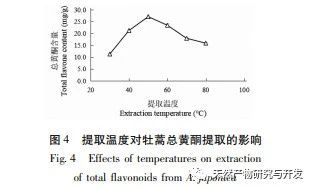
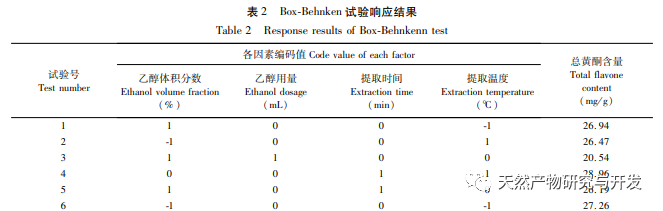

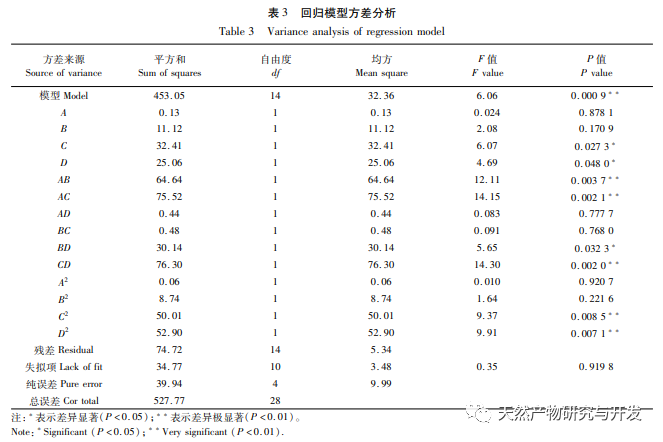
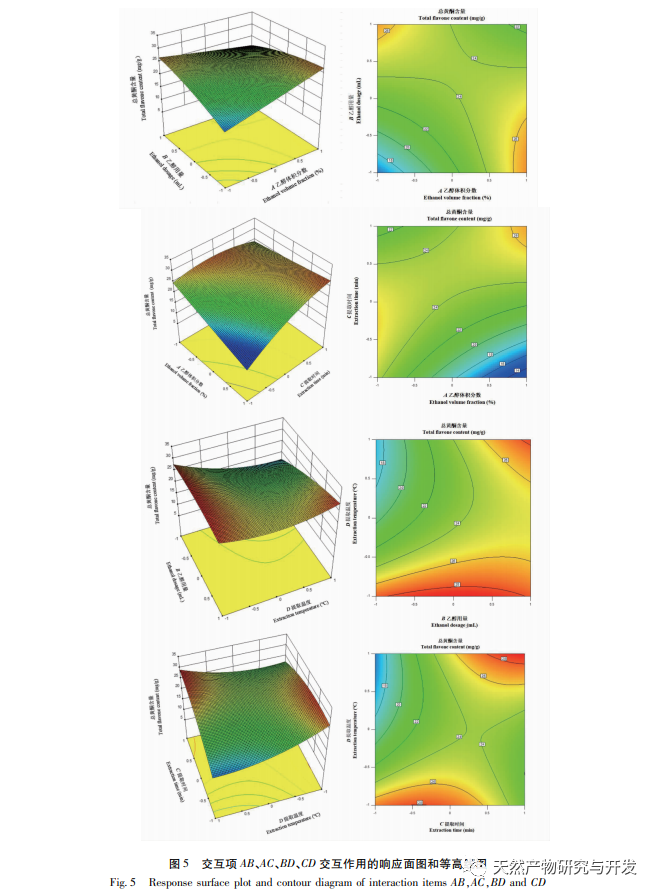
The study used the aboveground parts of Artemisia annua collected from Feixi County, Anhui Province as materials, and analyzed the effects of ethanol volume fraction, extraction temperature, liquid to material ratio, and extraction time on the total flavonoid extraction content of Artemisia annua using response surface methodology. The optimal process conditions for ethanol extraction of Artemisia annua total flavonoids were determined to be ethanol volume fraction of 70%, ethanol dosage of 20mL, extraction time of 85min, and extraction temperature of 40 ℃. Compared with the traditional ethanol extraction method, the optimal extraction process conditions obtained in this experiment have shortened the extraction time to a certain extent, avoided the impact of long-term extraction on the active ingredients, and improved the extraction amount and efficiency of total flavonoids in Artemisia annua.
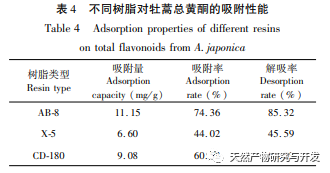
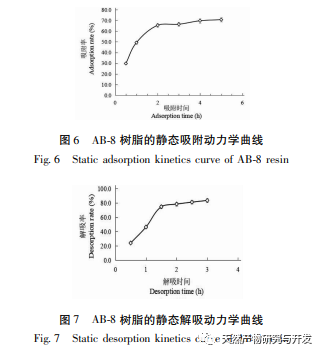
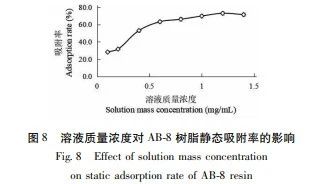
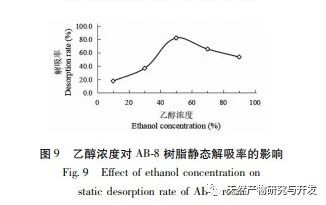
The experiment on the purification effect of macroporous resin on total flavonoids in Artemisia annua found that AB-8 had high adsorption and desorption rates of 74.36% and 85.32%, respectively, making it an ideal macroporous resin for adsorption and separation of total flavonoids in Artemisia annua. During the purification process, it is advisable to control the static adsorption time of AB-8 resin for total flavonoids in Artemisia annua at 2 hours, with a static adsorption rate of 65.47%; The optimal time for static desorption of total flavonoids from Artemisia annua is 1.5 hours, with a static desorption rate of 74.63%; The optimal concentration for the static adsorption of AB-8 resin is 1.2mg/mL for the total flavonoid extract of Artemisia annua; The optimal concentration for static desorption of AB-8 resin is 50% ethanol concentration.
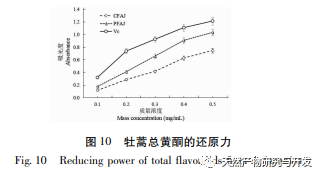
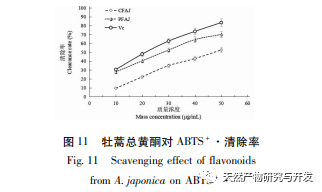
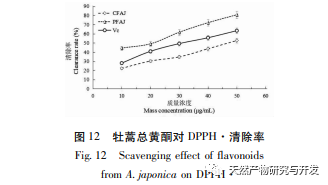
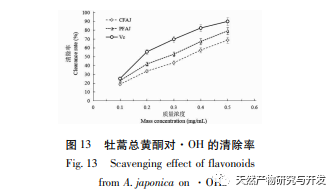
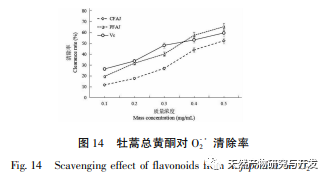
Excessive free radicals seriously affect human health, potentially damaging biofilm lipids, causing tissue damage, and leading to the occurrence of various diseases. Reducing the harm of free radicals to the human body is of great research significance. Flavonoids have the ability to scavenge free radicals. The experiment selected indicators such as reducing power and scavenging ABTS+·, DPPH ·, · OH, O2- · free radicals to analyze the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids in Artemisia annua. The results showed that total flavonoids in Artemisia annua had strong reducing power and exhibited good scavenging ability for ABTS+·, DPPH ·, · OH, and O2- ·, showing a dose effect. After purification, the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids in Artemisia annua was enhanced. The total flavonoids of Artemisia annua have the potential and application value as plant flavonoid resources, and can be used as a natural antioxidant for in-depth research, providing a theoretical basis for further development and application of Artemisia annua total flavonoids.
