The influence of pH and temperature on the antibacterial and fresh-keeping properties of anthocyanins from blueberry pomace
Blueberries (Vaccinium spp.), evergreen shrubs of the Ericaceae family or evergreen plants of the Vaccinium genus, have deep blue fruits when most varieties mature, soft and juicy flesh, and are rich in various nutrients. They are a functional health fruit that can be used as both medicine and food. According to the International Blueberry Association, China has become the world’s largest blueberry planting base. In 2021, China’s blueberry production was 474100 tons, of which 154000 tons were used for processing, resulting in a large amount of by-product fruit residue during the processing. Research has shown that the anthocyanin content in blueberry pomace exceeds the minimum level of anthocyanin content in blueberry fruit, indicating good resource reuse value. At present, the comprehensive utilization of by-products from blueberry pomace mainly involves direct use as animal feed, food additives, and processing into slow-release products. Blueberry anthocyanins, as natural colorants, have rich functional activity and specific acid-base coloring properties compared to artificial pigments. Therefore, extracting anthocyanins from blueberry pomace not only greatly turns waste into treasure, but also effectively solves the problem of energy conservation and emission reduction in the blueberry industry, fully utilizes its application properties to develop high-value terminal products, and extends the industrial chain of blueberry resources.
This study used blueberry pomace as the test material to evaluate the effects of different pH and temperature on the color and properties of anthocyanins in blueberry pomace during food processing and storage. The antioxidant and antibacterial activities were evaluated and analyzed, and the mechanism of antibacterial inhibition was studied. The aim is to lay a theoretical foundation for the practical application of developing new colored food preservation films with antioxidant and antibacterial activities in the future.
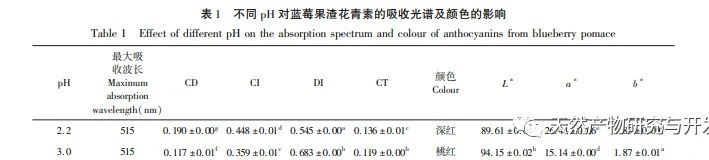
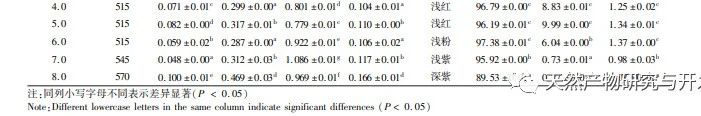
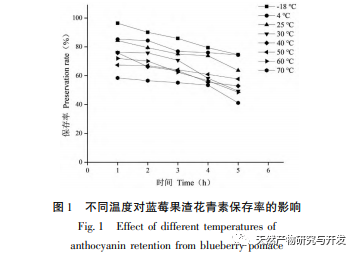
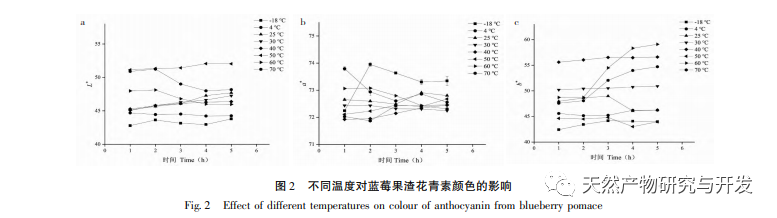
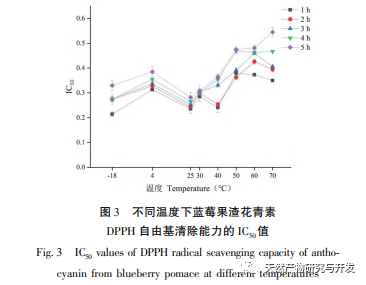
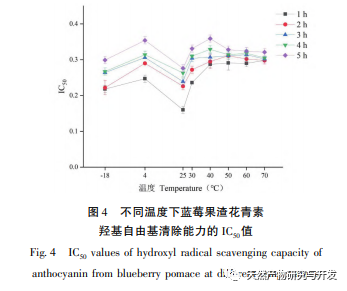
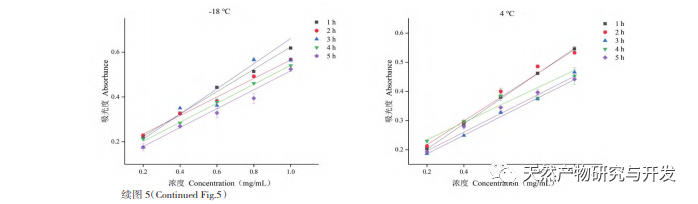
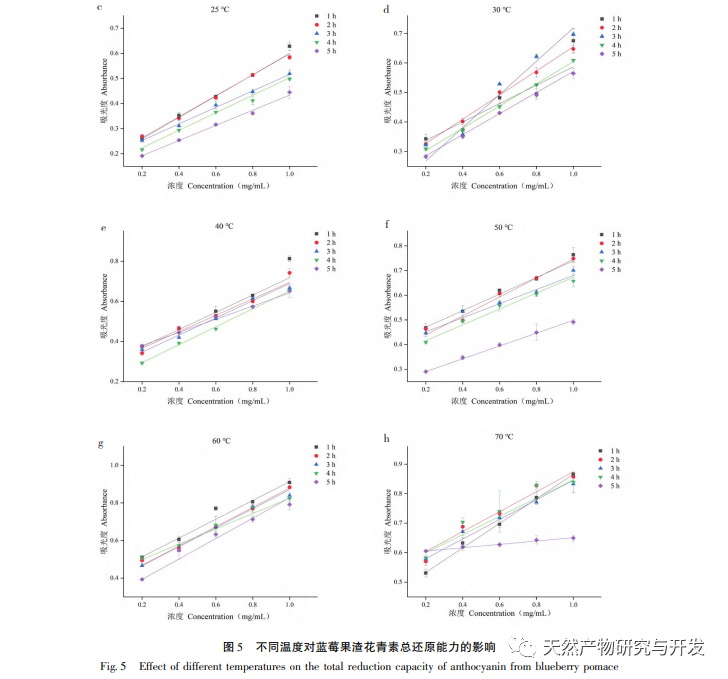
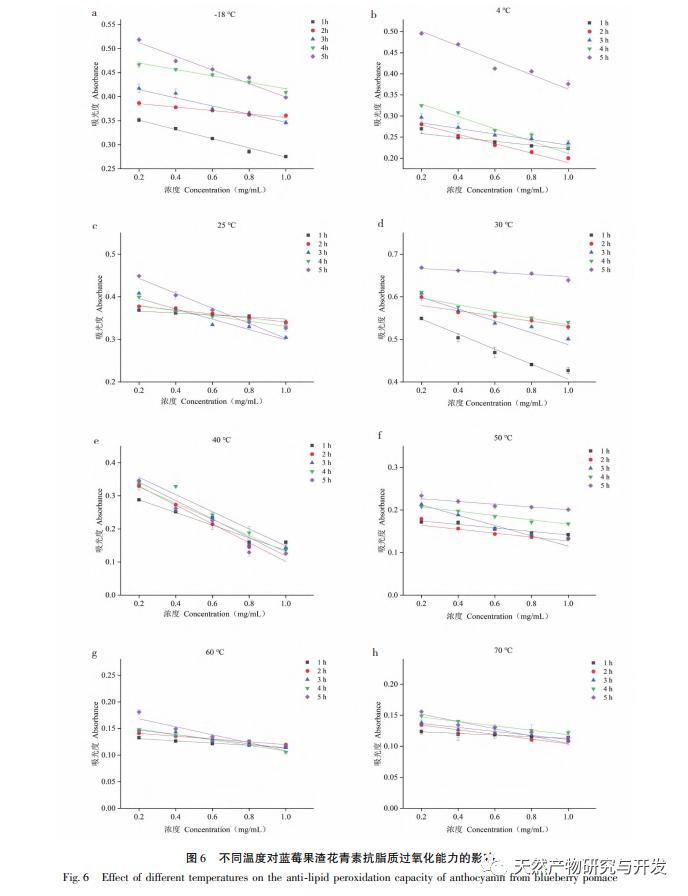
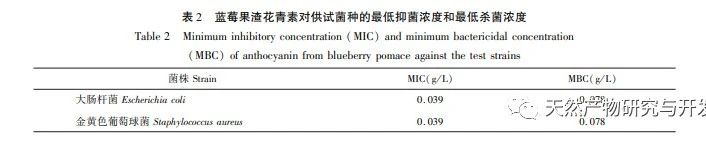
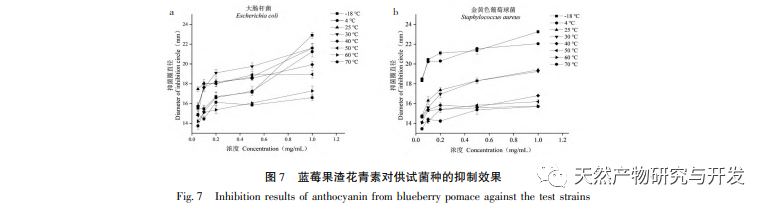
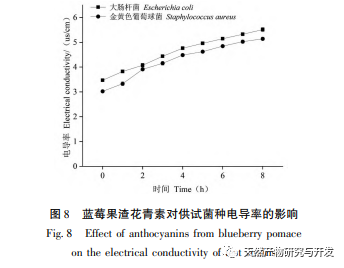
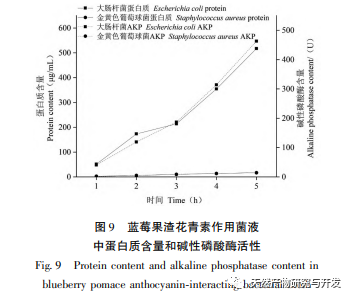 This study used blueberry pomace as the test material to evaluate the effects of different pH and temperature on the color and properties of anthocyanins in blueberry pomace during food processing and storage. The antioxidant and antibacterial activities were evaluated and analyzed, and the antibacterial mechanism was explored. The study showed that within the pH range of 2-8, anthocyanins in blueberry pomace exhibited a significant color change range from deep red to deep purple; Under the treatment temperature conditions of -18 to 70 ℃, the content, antioxidant activity, and antibacterial activity of anthocyanins in blueberry pomace decreased with prolonged treatment time. Blueberry pomace anthocyanins have shown good antibacterial effects on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The mechanism of action is to disrupt cell membrane permeability, leading to an increase in protein content and alkaline phosphatase content in the bacterial solution.
This study used blueberry pomace as the test material to evaluate the effects of different pH and temperature on the color and properties of anthocyanins in blueberry pomace during food processing and storage. The antioxidant and antibacterial activities were evaluated and analyzed, and the antibacterial mechanism was explored. The study showed that within the pH range of 2-8, anthocyanins in blueberry pomace exhibited a significant color change range from deep red to deep purple; Under the treatment temperature conditions of -18 to 70 ℃, the content, antioxidant activity, and antibacterial activity of anthocyanins in blueberry pomace decreased with prolonged treatment time. Blueberry pomace anthocyanins have shown good antibacterial effects on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The mechanism of action is to disrupt cell membrane permeability, leading to an increase in protein content and alkaline phosphatase content in the bacterial solution.
At present, research and utilization of anthocyanins from blueberry pomace mainly focus on extraction, purification, and stability, but there are few reports on their inhibitory effects and mechanisms against foodborne pathogens, which have not generated more utilization value. In terms of antibacterial activity, this study only conducted a preliminary comprehensive comparative analysis of the antibacterial properties and mechanisms of blueberry pomace anthocyanins against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus at different temperatures. Further exploration is needed to determine their safety and food processing applications. Subsequently, the preparation and performance evaluation of edible films with different substrates will be carried out, and the application and preservation mechanism of meat products will be studied. Therefore, based on the results of this study, in the development and utilization of anthocyanins from blueberry pomace, extraction, purification, processing, and storage processes can be selected according to appropriate pH and temperature. By utilizing the changes in color and properties, a new type of color film with antioxidant and antibacterial activity can be developed for the refrigeration preservation of fresh meat and other foods, further improving the utilization value of blueberry pomace, promoting the development of the natural understory resource industry chain, and ultimately driving the development of forestry economy.
