What is the progress of research on rice enzymatic proteins?
Rice is mainly composed of starch and protein, of which, starch accounts for about 80% of the total weight of rice, and protein accounts for only about 8% of the total weight.
Rice protein can be divided into four categories according to different solubility: 1. water-soluble protein, clear protein 2. salt-soluble protein, globulin 3. alcohol-soluble protein 4. alkali-soluble protein, gluten; gluten and alcohol protein, also known as storage proteins, are the main components of rice protein.
Rice protein extraction process
1, enzyme preparation: enzyme extraction of an idea is to use protease degradation and modification of rice protein, making it into a soluble peptide and be extracted. This method of reaction conditions are mild, protein peptide chains can be hydrolyzed to short peptide chains, improve the solubility of protein.
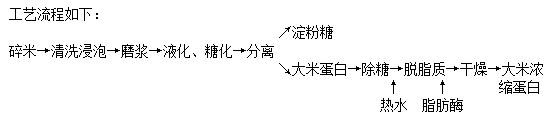
Enzymatic digestion increases the hydrophobicity of proteins, which can effectively improve their solubility, emulsification and foaming, the disadvantage of which is that the production cost is higher, and the extraction rate varies greatly depending on the enzyme used. According to the different conditions of protease action, can be divided into acid protease, neutral protease and alkaline protease and so on.
2, alkaline soluble acid precipitation method: lye can make rice in the tight starch structure becomes loose, while lye on the protein molecules of the secondary bond, especially the hydrogen bond has a destructive effect, and can make some of the polar groups dissociate, so that the surface of the protein molecules have the same charge. Thus, it has a solubilizing effect on protein molecules and promotes the separation of starch and protein.

Enzymatic digestion of rice protein by proteases
Based on the poor water solubility of rice protein and the non-protein components are mainly carbohydrates, the extracted protein should be further purified (Purification). It can also be treated with cellulase, pectinase and isoamylase to promote the solubilization of more carbohydrates.1, alkaline protease-modified rice protein process
Crushed rice → soaking → wet milling → rice slurry liquid → mixing slurry
Rice flour: alkali (0.06mol / L) = 1:8 → room temperature stirring extraction 2h → 3500r/min centrifugation 20min → take the supernatant → adjust the pH to 4.8 isoelectric point acid precipitation → 3500r/min centrifugation 10min → precipitation → freeze-drying → alkaline extraction of rice protein
Alkaline extraction of rice protein powder → 5% (w/v) rice protein suspension → hydration and dissolution at room temperature for 1h → 55 ℃ super-constant temperature water bath → according to the different amount of enzyme, substrate concentration, pH enzyme (pH-Stat [76] method to stabilize the pH of the system, the measurement of the degree of hydrolysis) → 3500r/min centrifugation for 20min → the supernatant → 85 ℃ /10min inactivation of enzymes → vacuum concentration → freeze-drying → rice protein powder → 3500r/min centrifugation for 20min → the supernatant → 85 ℃ /10min inactivation → vacuum concentration Freeze-drying → rice proteolysis alkaline protease Alcalase modification of rice proteolysis compared to alkaline extraction and acid precipitation of rice protein, solubility increased 13.92 times, emulsification increased 3.07 times, emulsification stability increased 2.26 times, foaming increased 1.07 times, foam stability increased 1.21 times, the functional properties of the rice protein proteolysis have different degrees of improvement. The functional properties of rice protein digests were improved to different degrees.
Compared with the hydrolysis of rice protein with Protease N by Ji Wei et al, the improvement of solubility of Alcalase enzyme digestion product was more significant; it was close to the improvement of protein solubility by acid deamidation of modified protein by Jiang Tianyan; and it was in agreement with the conclusions of the study of enzyme digestion on the improvement of solubility of rice protein by Xuan Guodong, Guo Rongrong, and Peng Qinghui that the solubility of the protein had reached more than 90%.
2, pepsin modified rice protein process: rice protein → pepsin hydrolysis → inactivation of the enzyme → measurement of protein concentration of the supernatant → pH value of 7.0 → dialysis → freeze-drying → determination of the functional properties of proteins.
Pepsin has a certain effect on the solubility of rice protein, and the influencing factors are pH value > enzyme addition > hydrolysis time > temperature. The optimal parameters were enzyme addition of 7.0 U/g, pH 1.5, hydrolysis time of 5 h, and temperature of 3 0 ℃. The functional properties of hydrolyzed rice protein were higher than those of untreated rice protein.
Among them, the emulsion stability and emulsification were 3 3 . 2 8mi n , and 0.456, which were even higher than soy protein and egg white protein. Foaming stability and foaming stability were 25.0% and 82.4%, and water holding and oil holding properties were 2.80 and 3.30 g/g, which were 2.09 and 2.92 times higher than those of untreated rice protein, respectively. Summary
In summary, rice protein has a reasonable amino acid composition, high biological potency, hypoallergenic, and high nutritional value. By means of enzymatic digestion, the solubility of rice protein is increased, emulsification, emulsion stability, water holding and oil holding are improved, and the quality of rice protein is improved so that it can be more easily absorbed and utilized by animals.
China is a large rice-producing country, with abundant rice resources, which provides a basis for the development and utilization of rice protein, rice protein as a very valuable plant protein resources, to solve the problem of insufficient feed protein resources in China provides a feasible way.
