What are the applications of xanthan gum and modified starch in baked salad dressings?
Salad Dressing
Salad dressing is a semi-solid, acidic, high-fat emulsion made from vegetable oil, eggs, salt, sugar, spices, vinegar, etc. Salad dressing originated in the Mediterranean Sea, and is a common condiment used in Western cuisine, which is popular with the market and consumers for its delicate organization, distinctive flavor, nutritious nature, and ease of consumption. This western-style condiment is not only used for fruit salad, but also often used as a sandwich or surface decoration in baked goods.
Baked goods need to be baked at high temperatures, and at this stage, salad dressings are mostly suitable for cold processing, which is easy to collapse at high temperatures. However, with the rapid development of bakery food work, the baking resistance of salad dressings is more demanding, and the market demand for baking-type salad dressings is also increasing.
Salad dressings are generally made by emulsification shear process, and baking-type salad dressings are required to have better stiffness, viscosity and high temperature baking performance, so it is necessary to use shear-resistant, acid-resistant, high viscosity, good stability of modified starch. Hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate is the original starch by phosphate cross-linking and hydroxypropyl etherification co-modified products, with good shear resistance, acid resistance, stability, high temperature resistance, as well as good freeze-thaw stability, applied to acidic foods, with good thickening and stabilization performance.
Xanthan gum is a food thickener with the function of emulsifier, in addition, in many food products, modified starch and xanthan gum have a synergistic effect when compounding, the two are used in combination, can improve the stability and texture of the product. Sodium octenyl succinate starch has an emulsifying effect, it is a highly efficient surfactant, it has both lipophilic and hydrophilic groups, it is very suitable for oil-in-water emulsions, to improve the emulsification stability of salad dressings and baking stability, to extend the storage time.
Effects of xanthan gum and modified starch in baked salad dressings
2.1 Results of one-way test 2.1.1 Effects of xanthan gum on the viscosity, baking performance, low temperature stability and sensory of salad dressing
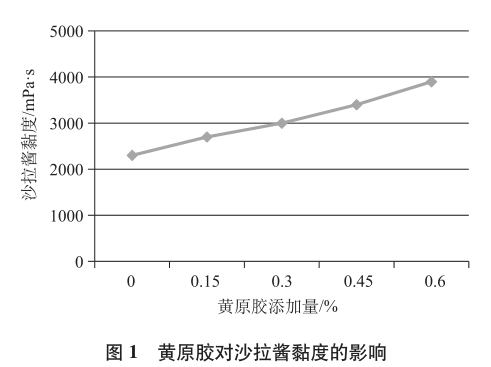
As can be seen from Fig. 1, although the addition amount of xanthan gum was not large, the viscosity of the salad dressing increased significantly with the increase of the addition amount, the reason is that xanthan gum has a high viscosity at a low concentration, which can effectively improve the viscosity of the dressing, so as to make the body of the salad dressing better. From Table 3, it can be seen that in the range of the addition amount of 0.15% to 0.45%, the stiffness, baking performance, low temperature stability, and sensory score of the salad dressing gradually improved, which can reflect that the addition of xanthan gum in a certain range can effectively improve the stability of the salad dressing, the sensory improvement, and the status of the more upright.
The reason is that xanthan gum has a thickening effect and emulsification effect, which can enhance the consistency and emulsification stability of the salad dressing. However, it is not better to add more, when the addition amount reaches 0.6%, although the state is more upright after baking at high temperature, the sauce is not smooth, and there are more air bubbles, which is due to the sauce consistency is too large, wrapped into the air caused by more. Too much addition also caused a decrease in low-temperature stability, because xanthan gum absorbed too much water caused by the instability of the O/W system. Too large an addition caused the dressing to be too viscous and not lubricated enough, resulting in a lower sensory score.

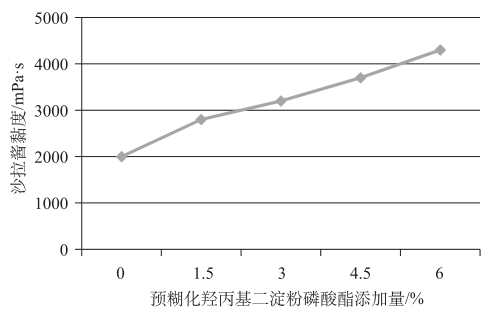
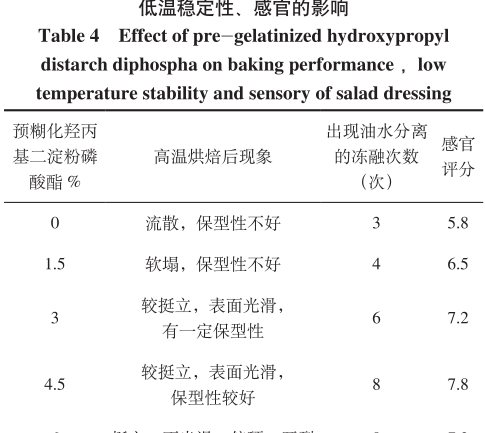
2.1.2 Effect of pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate on the viscosity, baking performance and low temperature stability and sensory of the salad dressing From Figure 2, it can be seen that with the increase in the amount of pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate added, the viscosity of the salad dressing also increased gradually, which indicates that it can effectively improve the viscosity of the sauce body. As seen in Table 4, when the addition amount of pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate is less, the body is thin, easy to flow, and the shape retention is not good, and with the increase of the addition amount, the baking performance and low-temperature stability gradually increase, and the effect is obvious, and it achieves a better shape retention and stability when the addition amount is 4.5% and has the highest organoleptic score.
It can be seen that pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate can improve the quality of salad dressing within a certain range. However, when the addition amount reached 6%, the sauce was too thick, the state was hard, the gloss was poor, the texture was sticky, so that the sensory score decreased, it was easy to crack after high-temperature baking, and the low-temperature stability was not further improved.
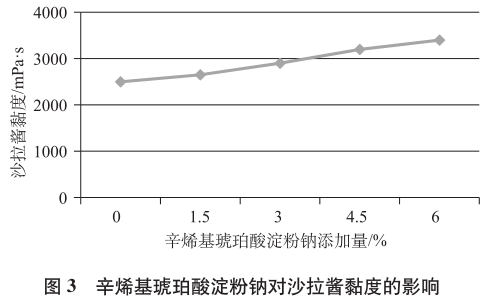
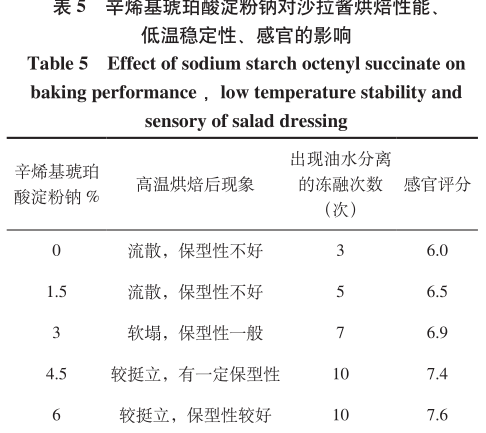
2.1.3 Effect of sodium starch octenylsuccinate on the viscosity, baking performance, and low temperature stability and sensory of salad dressings From Fig. 3, it can be seen that the viscosity of salad dressings tended to increase with the increase in the amount of sodium starch octenylsuccinate, but the thickening effect was not as good as that of pregelatinized hydroxypropylene di-amyl phosphate in comparison.
As can be seen from Table 5, the addition of sodium octenylsuccinate starch can make the baking performance of salad dressings have a certain degree of improvement, but the effect is not as good as the pre-gelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate under the same conditions of addition.
When the addition of sodium octenyl succinate 0%, the low temperature stability is poor, easy to oil-water delamination, with the increase in the amount of additives, the stability of the system can be greatly improved, the effect is better than the pre-gelatinized hydroxypropyl dihydroxypropyl dihydroxypropyl starch phosphate, this is due to the good hydrophilic and lipophilic emulsification properties of sodium octenyl succinate, carboxyl group into the water, the oleophilic long chain of the octenyl group into the oil, the oil-water interface by the long chain of polysaccharides, the oil-water interface by the polysaccharide long chain of the polysaccharide long chain. At the oil-water interface, a tough and unbreakable film is formed by the polysaccharide long chain, which makes it difficult for the dispersed-phase particles to aggregate and separate, and improves the stability of the paste.
However, when the addition amount reaches 6%, there is no further improvement in low temperature stability. The sensory scores increased with the increase of the addition amount, and the gloss and firmness of the salad dressing were improved in this addition range, and the lubricity of the mouthfeel was increased, and the quality was gradually improved.
2.2 Orthogonal test results On the basis of one-factor, selecting the appropriate additive range, designing three-factor three-level orthogonal test, using sensory score as the evaluation index, to study the effect of the combined use of different factors on the quality of baked salad dressings, the results are shown in Table 6.
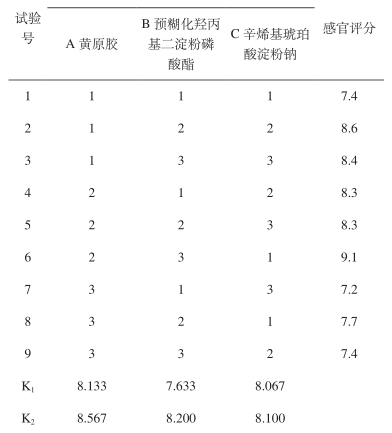
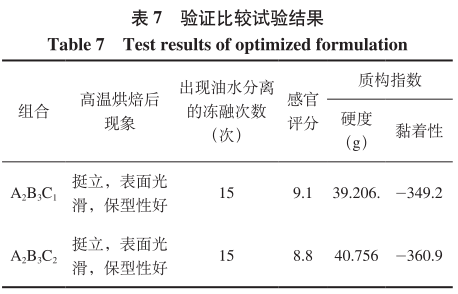
From the polar analysis of Table 6, it can be seen that the main factors affecting the quality of baked salad dressings were A > B > C, i.e. xanthan gum had the greatest influence, followed by pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate, and lastly sodium octenyl succinate starch. By polar analysis, its optimal level combination was A2B3C2 , and the combination with the highest sensory score was A2B3 C1, so the two were then validated and compared, and the results are shown in Table 7.
As can be seen from Table 7, combination A2B3C1 and combination A2B3C2 baking performance are good performance, low temperature stability is the same, in the case of the same effect, you can choose the combination of lower cost, that is, A2B3C1. then analyze the texture index, the combination of A2B3C2 hardness and adhesion is slightly higher, the mouthfeel performance is a little hard and slightly mushy, in the sensory scores, the combination of A2B3C1 is higher. The mouthfeel was lubricated and the condition was fine and smooth. So in a comprehensive comparison, the better program can choose A2B3C1.
Conclusion.
(1) In the one-way test, it was found that xanthan gum, pregelatinized hydroxypropyl dibasic starch phosphate, and sodium starch octenylsuccinate improved the baking performance of salad dressings in a certain range of addition amounts, but the addition of xanthan gum and pregelatinized hydroxypropyl dibasic starch phosphate in too large an amount caused adverse effects, with the former resulting in the non-smoothness of salad dressings and the generation of air bubbles after baking, and the latter resulting in the non-smoothness and Cracking.
(2) The effects of xanthan gum and pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate on viscosity were large and proportional to the amount added. Sodium octenylsuccinate starch can significantly improve the low temperature stability of salad dressings through its hydrophilic and lipophilic emulsification properties.
(3) The ratios optimized by orthogonal test and validation comparison test were: xanthan gum 0.3%, pregelatinized hydroxypropyl diastarch phosphate 4.5%, sodium octenyl succinate starch 3%. The results of the validation test were good, which proved that the baked salad dressing made by this formula had stable performance, high temperature baking resistance, smooth taste, moderate hardness, delicate and glossy state, and was suitable for use in bakery products.
